SENSORY STRUCTURES/FEATURES
... Body Cavity (coelom) present or absent • Have a coelom • Nutrients are transported in the fluid in the pseudocoelom • The fluid under high pressure ...
... Body Cavity (coelom) present or absent • Have a coelom • Nutrients are transported in the fluid in the pseudocoelom • The fluid under high pressure ...
Chapter 9
... longitudinal axis produces mirrored halves n Usually sessile, freely floating, or weakly swimming animals n No anterior or posterior end n Can interact with environment in all directions ...
... longitudinal axis produces mirrored halves n Usually sessile, freely floating, or weakly swimming animals n No anterior or posterior end n Can interact with environment in all directions ...
BIOL 2015 – Evolution and Diversity
... openings are the diverticula of the gastrovascular cavity. Pharynx region: This cross section shows the pharynx, which is retracted into the pharyngeal cavity (the empty white space surrounding the pharynx). The pharynx itself is a thick, muscular tube; when Planaria eats, it everts the pharynx ...
... openings are the diverticula of the gastrovascular cavity. Pharynx region: This cross section shows the pharynx, which is retracted into the pharyngeal cavity (the empty white space surrounding the pharynx). The pharynx itself is a thick, muscular tube; when Planaria eats, it everts the pharynx ...
Exam 3 study guide Lecture 1 Animal Structure and Function Most
... Two types: open and closed Used to transport oxygen to cells and waste carbon dioxide away. Also transport of other substances such as hormones, glucose, nitrogenous wastes Open circulatory system Found in invertebrates such as clams and insects Heart pumps fluid to through vessels out to body into ...
... Two types: open and closed Used to transport oxygen to cells and waste carbon dioxide away. Also transport of other substances such as hormones, glucose, nitrogenous wastes Open circulatory system Found in invertebrates such as clams and insects Heart pumps fluid to through vessels out to body into ...
Anim Overview key
... •Diffusion of gases between the environment & animals requires a thin moist membrane •Small animals that live in wtaer or in moist soil may respire through their skin •Large animals - respiration through skin not efficient enough - respiratory systems have taken many different forms in adapting to d ...
... •Diffusion of gases between the environment & animals requires a thin moist membrane •Small animals that live in wtaer or in moist soil may respire through their skin •Large animals - respiration through skin not efficient enough - respiratory systems have taken many different forms in adapting to d ...
INVERTEBRATES
... -The head has two antennae. -The thorax has six legs (three pairs). -Many species presents four wings: they are the only invertebrates that can fly. -They breathe through tracheae. -Some of them can be carnivorous, but many others are herbivorous. ...
... -The head has two antennae. -The thorax has six legs (three pairs). -Many species presents four wings: they are the only invertebrates that can fly. -They breathe through tracheae. -Some of them can be carnivorous, but many others are herbivorous. ...
Unit 12 Invertebrate Diagrams and Videos
... Oysters, Clams, Octopuses and Squids Most have hard shell made of calcium carbonate Gills Muscular foot Radula to scrape up food Nerve cords Visceral mass Open circulatory system Mantle Dorsal heart Circulatory fluid (hemolymph) Arteries Excretory organs (nephridia) Most separate sexes, with gonads ...
... Oysters, Clams, Octopuses and Squids Most have hard shell made of calcium carbonate Gills Muscular foot Radula to scrape up food Nerve cords Visceral mass Open circulatory system Mantle Dorsal heart Circulatory fluid (hemolymph) Arteries Excretory organs (nephridia) Most separate sexes, with gonads ...
Sponges, Cnidarian, Ctenophora, Worms Review - Cy
... 5. Define dioecious and monecious 6. Simple animals with no true organs must rely on which process in order to respirate (get oxygen to their cells)? 7. What characteristic sets cnidarians and ctenophores apart? Which features do each possess? 8. Define coelom. Which type of worms have a true coelom ...
... 5. Define dioecious and monecious 6. Simple animals with no true organs must rely on which process in order to respirate (get oxygen to their cells)? 7. What characteristic sets cnidarians and ctenophores apart? Which features do each possess? 8. Define coelom. Which type of worms have a true coelom ...
CHAPTER 15 CHORDATA STUDY GUIDE
... 4. Food particles separated from the mucus are passed into a hepatic cecum where they are phagocytized. 5. Filtered water leaves the body by an atriopore. 6. The closed circulatory system is complex but lacks a heart. 7. Blood is pumped by peristaltic contractions in the ventral aorta, passes upward ...
... 4. Food particles separated from the mucus are passed into a hepatic cecum where they are phagocytized. 5. Filtered water leaves the body by an atriopore. 6. The closed circulatory system is complex but lacks a heart. 7. Blood is pumped by peristaltic contractions in the ventral aorta, passes upward ...
Phylum Platyhelminthes
... Highly adapted to constant internal environments Lacks sensory organs, coordination for mobility and a digestive system (more room for reproductive structures!) Have a modified epidermis “tegument” which protects against the digestive enzymes and the immune systems of the host Can reach 7m in length ...
... Highly adapted to constant internal environments Lacks sensory organs, coordination for mobility and a digestive system (more room for reproductive structures!) Have a modified epidermis “tegument” which protects against the digestive enzymes and the immune systems of the host Can reach 7m in length ...
Lecture 5
... digestive tract running from anterior mouth to posterior anus; gut supported by longitudinal mesenteries and septa, ventral nerve cord with segmental ganglia and anterior brain, circulatory system of high pressure blood in vessels, excretion by metameric nephidrida. Each compartment has its own pair ...
... digestive tract running from anterior mouth to posterior anus; gut supported by longitudinal mesenteries and septa, ventral nerve cord with segmental ganglia and anterior brain, circulatory system of high pressure blood in vessels, excretion by metameric nephidrida. Each compartment has its own pair ...
Breeding and Non-breeding Survival of Lesser Prairie
... ► Each collecting event must be labeled Location (both written and GPS coordinates), date, collecting method, brief habitat description, and collector should all be included on label ARGENTINA: Jujuy,P.N. Calilegua, Arroyo 3 Cruces, 1110m, 23°41.629’S64°52.070'W 14.i.2008 TACatanach Hg vapor light ...
... ► Each collecting event must be labeled Location (both written and GPS coordinates), date, collecting method, brief habitat description, and collector should all be included on label ARGENTINA: Jujuy,P.N. Calilegua, Arroyo 3 Cruces, 1110m, 23°41.629’S64°52.070'W 14.i.2008 TACatanach Hg vapor light ...
Study Guide Evolution of Animals Chapters 32-35
... incomplete digestive system with only mouth, space between internal organs and body wall filled = Acoelomate, bisexual = monoecious animals. 68. Planaria – a member of free-living flat worms, head has 2 eye-spots, 2 auricles – lateral extensions of head, mouth in the middle, branching gut (digestive ...
... incomplete digestive system with only mouth, space between internal organs and body wall filled = Acoelomate, bisexual = monoecious animals. 68. Planaria – a member of free-living flat worms, head has 2 eye-spots, 2 auricles – lateral extensions of head, mouth in the middle, branching gut (digestive ...
1 - BrainMass
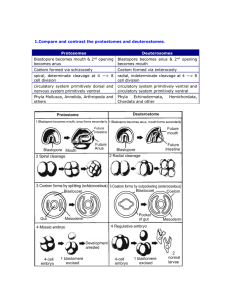
... 2. Describe the enterocoel hypothesis of coelom origin and discuss the implications. Enterocoelous development is the stage of embryological development of deuterostomes in which the coelom forms. The stage starts with the gastrula; as the archenteron forms, pockets of migrating cells also form, cr ...
... 2. Describe the enterocoel hypothesis of coelom origin and discuss the implications. Enterocoelous development is the stage of embryological development of deuterostomes in which the coelom forms. The stage starts with the gastrula; as the archenteron forms, pockets of migrating cells also form, cr ...
Cnidarian
... • The medusae of hydroids are smaller than those of jellyfishes (C. Scyphozoa) • Also, the margin of the bell projects inward forming a shelf-like velum ...
... • The medusae of hydroids are smaller than those of jellyfishes (C. Scyphozoa) • Also, the margin of the bell projects inward forming a shelf-like velum ...
Rat LAB
... individual air sacs called ALVEOLI (sing.ALVEOLUS) to increase surface area for greater gas exchange. The DIAPHRAGM (a sheet of muscle below the ribcage contracts to pull air into the lungs. A voice box is located in the trachea and makes sound as air passes through. ENDOCRINE: The endocrine system ...
... individual air sacs called ALVEOLI (sing.ALVEOLUS) to increase surface area for greater gas exchange. The DIAPHRAGM (a sheet of muscle below the ribcage contracts to pull air into the lungs. A voice box is located in the trachea and makes sound as air passes through. ENDOCRINE: The endocrine system ...
Cnidarians - carverbiology11
... microscopic food particles from the water Digestion is intracellular (takes place inside cells) Choanocytes trap and engulf food from water passing through the sponge, then archaeocytes complete the digestive process ...
... microscopic food particles from the water Digestion is intracellular (takes place inside cells) Choanocytes trap and engulf food from water passing through the sponge, then archaeocytes complete the digestive process ...
Post-Lab Information Sheet
... 1. Locate the salivary glands, which on the sides of the neck, between muscles. Carefully remove the skin of the neck and face to reveal these glands. Salivary glands are soft spongy tissue that secrete saliva and amylase (an enzyme that helps break down food). There are three salivary glands - the ...
... 1. Locate the salivary glands, which on the sides of the neck, between muscles. Carefully remove the skin of the neck and face to reveal these glands. Salivary glands are soft spongy tissue that secrete saliva and amylase (an enzyme that helps break down food). There are three salivary glands - the ...
Phylum Cnidaria
... consuming plankton and some of the sea anenomes consuming small fishes They use they tentacles to capture prey and direct it toward the mouth so that it can be digested in the gastrovascular cavity via secretions from gland cells (extracellular digestion); some food is phagocytized by special cell ...
... consuming plankton and some of the sea anenomes consuming small fishes They use they tentacles to capture prey and direct it toward the mouth so that it can be digested in the gastrovascular cavity via secretions from gland cells (extracellular digestion); some food is phagocytized by special cell ...
Biology 11
... •specialized cells in the gastroderm (endoderm) release _____________ that partially digest food •food fragments taken up by gastroderm cells (via ____________________) & further digestion takes place inside cells (________cellular digestion) •nutrients transported throughout body by _______________ ...
... •specialized cells in the gastroderm (endoderm) release _____________ that partially digest food •food fragments taken up by gastroderm cells (via ____________________) & further digestion takes place inside cells (________cellular digestion) •nutrients transported throughout body by _______________ ...
Wetland Invertebrates
... flattened shape and have a specialized lower lip with two teeth used for snaring food. They inch slowly toward their prey or just lie in wait for prey to pass by. Adult dragonflies are beautiful flying insects with four large, fragile wings that look like fine gauze. Their long, slender bodies may b ...
... flattened shape and have a specialized lower lip with two teeth used for snaring food. They inch slowly toward their prey or just lie in wait for prey to pass by. Adult dragonflies are beautiful flying insects with four large, fragile wings that look like fine gauze. Their long, slender bodies may b ...
Mini-beasts and microhabitats
... Identify that most living things live in habitats to which they are suited and describe how different habitats provide for the basic needs of different kinds of animals and plants, and how they depend on each other ...
... Identify that most living things live in habitats to which they are suited and describe how different habitats provide for the basic needs of different kinds of animals and plants, and how they depend on each other ...
Earthworm Dissection
... b. Does the skin have an even smooth texture, or is it bumpy and divided into segments? Find the thick light colored band encircling the body. c. What is the thick light colored band encircling the body called? d. Is the band closer to the anterior or the posterior end of the animal? 2. Slide your f ...
... b. Does the skin have an even smooth texture, or is it bumpy and divided into segments? Find the thick light colored band encircling the body. c. What is the thick light colored band encircling the body called? d. Is the band closer to the anterior or the posterior end of the animal? 2. Slide your f ...
Section 07 Lecture Notes
... 2. Ventral body wall specialized as a muscular foot 3. Dorsal body wall forms the mantle, which encloses the mantle cavity, is modified into gills or a lung, and secretes the shell 4. Surface epithelium usually ciliated and bears mucous glands and sensors 5. Coelom present 6. Complex digestive syste ...
... 2. Ventral body wall specialized as a muscular foot 3. Dorsal body wall forms the mantle, which encloses the mantle cavity, is modified into gills or a lung, and secretes the shell 4. Surface epithelium usually ciliated and bears mucous glands and sensors 5. Coelom present 6. Complex digestive syste ...
Insect physiology
Insect physiology includes the physiology and biochemistry of insect organ systems.Although diverse, insects are quite indifferent in overall design, internally and externally. The insect is made up of three main body regions (tagmata), the head, thorax and abdomen.The head comprises six fused segments with compound eyes, ocelli, antennae and mouthparts, which differ according to the insect’s particular diet, e.g. grinding, sucking, lapping and chewing. The thorax is made up of three segments: the pro, meso and meta thorax, each supporting a pair of legs which may also differ, depending on function, e.g. jumping, digging, swimming and running. Usually the middle and the last segment of the thorax have paired wings. The abdomen generally comprises eleven segments and contains the digestive and reproductive organs.A general overview of the internal structure and physiology of the insect is presented, including digestive, circulatory, respiratory, muscular, endocrine and nervous systems, as well as sensory organs, temperature control, flight and molting.