* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 9
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
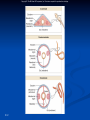
CHAPTER 9 Architectural Pattern of an Animal 9-1 Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Animal Body Plans n 9-2 Animal Symmetry n Symmetry n Correspondence of size and shape of parts on opposite sides of a median plane n Spherical symmetry n Any plane passing through center divides body into mirrored halves n Best suited for floating and rolling n Found chiefly among some unicellular forms n Rare in animals Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Animal Body Plans n Radial n Body symmetry divided into similar halves by more than 2 planes passing through longitudinal axis n Biradial symmetry n Variant form radial symmetry n Have part that is single or paired rather than radial n Only 2 planes passing through longitudinal axis produces mirrored halves n Usually sessile, freely floating, or weakly swimming animals n No anterior or posterior end n Can interact with environment in all directions 9-3 Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Animal Body Plans n Bilateral Symmetry n Organism can be divided along a sagittal plane into two mirror portions n Right and left halves n Much better fitted for directional (forward) movement n Associated with cephalization n Differentiation of a head region with concentration of nervous tissue and sense organs n Advantageous to an animal moving through its environment head first 9-4 Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Animal Body Plans n Regions of bilaterally symmetrical animals n n n n n n 9-5 Anterior n Head end Posterior n Tail end Dorsal n Back side Ventral n Front or belly side Medial n Midline of body Lateral n Sides Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Animal Body Plans n Distal n Parts n Proximal n Parts n farther from the middle of body are nearer the middle of body Frontal plane (coronal plane) n Divides halves n Sagittal plane n Divides n bilateral body into dorsal and ventral body into right and left halves Transverse plane (cross section) n Divides body into anterior and posterior portions 9-6 Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 9-7 Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Body Cavities and Germ Layers n Body cavity n Sponges n Acoelomate: n In no body cavity sponges n After blastula formation, cells reorganize to form adult body n Blastula has no external opening n No gut forms 9-8 Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Body Cavities and Germ Layers n 9-9 Other animal phyla n Development proceeds from blastula to gastrula n Invagination of surface cells form the primitive gut n Opening to the primitive gut is the blastocoel n Becomes the mouth or the anus n Gut is lined by endoderm n Outer layer of cells is ectoderm n Embryo now has 2 cavities n Gut and blastocoel n Blastocoel persists in some animals n In others, becomes filled with a 3rd germ layer, mesoderm n Cells forming mesoderm n Derived from endoderm Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Body Cavities and Germ Layers n 9-10 Three body plans are possible n Acoelomate plan n Mesodermal cells completely fill the blastocoel n Gut is only body cavity n Pseudocoelomate plan n Mesodermal cells line the outer edge of the blastocoel n 2 body cavities formed n Persistent blastocoel (pseudocoelom) and a gut cavity n Pseudocoelom is a false body cavity (only partially lined with mesoderm) Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Body Cavities and Germ Layers n Schizocoelous (Eucoelomate) plan n Mesodermal cells fill blastocoel n Mesoderm splits n The space is called a coelom n True body cavity (completely lined by mesoderm) n 2 body cavities formed n Gut and coelom 9-11 Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 9-12 Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. A Complete Gut Design and Segmentation n n 9-13 Few diploblasts and triploblasts form blind gut n Same opening for entrance of food and exit of wastes Most form a complete gut n Allows for one-way flow of food from mouth to anus n Tube-within-a-tube design Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. A Complete Gut Design and Segmentation n 9-14 Metamerism (Segmentation) n Serial repetition of similar body segments along longitudinal axis of body n Each segment is a metamere or somite n Permits greater body mobility and complexity of structure and function n Annelids, Arthropods, Chordates Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 9-15