Mastering the Chemistry Core 40
... Introduction to the Student Welcome to Mastering the Chemistry Core 40 This workbook is designed to strengthen your knowledge of the Indiana Chemistry I Academic Standards and provide additional chapter content review of your Glencoe textbook, Chemistry: Matter and Change. For each chapter in the G ...
... Introduction to the Student Welcome to Mastering the Chemistry Core 40 This workbook is designed to strengthen your knowledge of the Indiana Chemistry I Academic Standards and provide additional chapter content review of your Glencoe textbook, Chemistry: Matter and Change. For each chapter in the G ...
NUCL 1 Early life of Albert Ghiorso: Preparation for future role as
... Although young Albert was a good student in classical subjects, he early on showed his mechanical ability. His family lived close to the Oakland Airport and Albert set his sights on becoming an aeronautical engineer. When he graduated from high school in 1932 in the depth of the Great Depression he ...
... Although young Albert was a good student in classical subjects, he early on showed his mechanical ability. His family lived close to the Oakland Airport and Albert set his sights on becoming an aeronautical engineer. When he graduated from high school in 1932 in the depth of the Great Depression he ...
UNIVERSITI MALAYSIA SABAH
... solution shaking the solution after each addition. Note the colour of the resulting solution. ...
... solution shaking the solution after each addition. Note the colour of the resulting solution. ...
SENSORS
... form the core of research in basic and applied nuclear physics. It may not be an exaggeration to state that what is 'discoverable' at frontier fields of science is often limited by the then available detector technologies. Experimental high energy physics (HEP) programmes of our country depend heavi ...
... form the core of research in basic and applied nuclear physics. It may not be an exaggeration to state that what is 'discoverable' at frontier fields of science is often limited by the then available detector technologies. Experimental high energy physics (HEP) programmes of our country depend heavi ...
Chap4 Review - armstrongchemistry
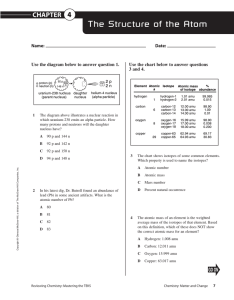
... gamma rays are affected by two electrically charged plates. Based on the paths the rays follow, what are the respective charges of alpha, beta, and gamma rays? A ...
... gamma rays are affected by two electrically charged plates. Based on the paths the rays follow, what are the respective charges of alpha, beta, and gamma rays? A ...
Qualitative Analysis of Anions
... Waste Disposal Your teacher will provide a waste container for the solutions used in this experiment. ...
... Waste Disposal Your teacher will provide a waste container for the solutions used in this experiment. ...
02_Lecture SK
... • 2.4 Radioactivity and Radioisotopes – Some atomic isotopes emit radiation (a form of energy) spontaneously from their nucleus in a process called radioactive decay. – Isotopes that undergo radioactive decay are called radioisotopes, and the high-energy particles given off in this process are refer ...
... • 2.4 Radioactivity and Radioisotopes – Some atomic isotopes emit radiation (a form of energy) spontaneously from their nucleus in a process called radioactive decay. – Isotopes that undergo radioactive decay are called radioisotopes, and the high-energy particles given off in this process are refer ...
Reviewing Chemistry: Mastering the TEKS - Student
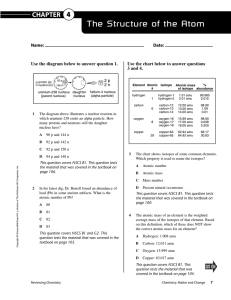
... The atomic mass of an element is the weighted average mass of the isotopes of that element. Based on this definition, which of these does NOT show the correct atomic mass for an element? A ...
... The atomic mass of an element is the weighted average mass of the isotopes of that element. Based on this definition, which of these does NOT show the correct atomic mass for an element? A ...
Scheme of work
... unstable. The nucleus gives out ionising radiation as it changes to become more stable. This is a random process called radioactive decay. ...
... unstable. The nucleus gives out ionising radiation as it changes to become more stable. This is a random process called radioactive decay. ...
Atomic Number
... – Unstable isotopes emit radiation more rapidly. – The rate of decay is measured as half-life, the time it takes for one-half (50%) of the atoms in a sample to decay. – Decay is measured on a Geiger counter. ...
... – Unstable isotopes emit radiation more rapidly. – The rate of decay is measured as half-life, the time it takes for one-half (50%) of the atoms in a sample to decay. – Decay is measured on a Geiger counter. ...
Modern Physics
... • Above element 83, the protons are farther and farther away from each other in the nucleus, therefore requiring a greater nuclear force to overcome the electrostatic repulsive forces. The nuclear force is not strong enough to hold together the protons when more than 83 of them are packed into a nuc ...
... • Above element 83, the protons are farther and farther away from each other in the nucleus, therefore requiring a greater nuclear force to overcome the electrostatic repulsive forces. The nuclear force is not strong enough to hold together the protons when more than 83 of them are packed into a nuc ...
FOUNTAIN UNIVERSITY, OSOGBO
... officially sanctioned, scheduled University extracurricular activity will be given the opportunity to make up class assignments or other graded assignments missed as a result of their participation. It is the responsibility of the student to make arrangements with the instructor prior to any missed ...
... officially sanctioned, scheduled University extracurricular activity will be given the opportunity to make up class assignments or other graded assignments missed as a result of their participation. It is the responsibility of the student to make arrangements with the instructor prior to any missed ...
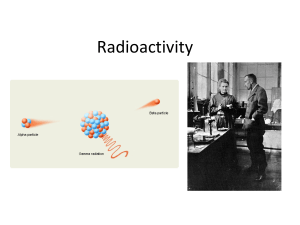
Radioactivity
... absorbed by the film the darker the colour it will go when it is developed. This is useful for people working with radiation, they wear radiation badges to show them how much radiation they are being exposed to. 4. Dating materials – The older a radioactive substance is the less radiation it will re ...
... absorbed by the film the darker the colour it will go when it is developed. This is useful for people working with radiation, they wear radiation badges to show them how much radiation they are being exposed to. 4. Dating materials – The older a radioactive substance is the less radiation it will re ...
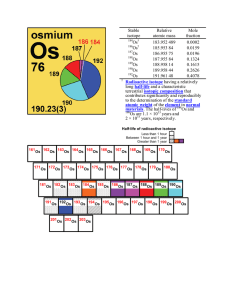
Stable isotope Relative atomic mass Mole fraction Os 183.952 489
... radiation, neutrons or protons to reach a final stable energy state. radioisotope (radioactive isotope) – an atom for which radioactive decay has been experimentally measured (also see half-life). [return] radiogenic – produced by the decay of a radioactive isotope, but which itself may or may not b ...
... radiation, neutrons or protons to reach a final stable energy state. radioisotope (radioactive isotope) – an atom for which radioactive decay has been experimentally measured (also see half-life). [return] radiogenic – produced by the decay of a radioactive isotope, but which itself may or may not b ...
P2 Knowledge Powerpoint – WIP Part 2
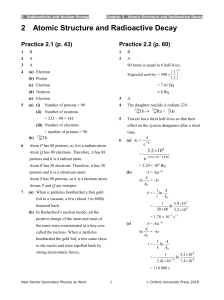
... • 1Bq is one nuclear decay each second • Radioactive decay is a random process (cannot predict it) • Half life = the time taken for half the unstable nuclei in a sample of a radioactive isotope to decay. • Half life does not change as the sample gets smaller • After decaying = more stable nucle ...
... • 1Bq is one nuclear decay each second • Radioactive decay is a random process (cannot predict it) • Half life = the time taken for half the unstable nuclei in a sample of a radioactive isotope to decay. • Half life does not change as the sample gets smaller • After decaying = more stable nucle ...
- Los Banos Unified School District
... foil. He established that the nucleus was: very dense, very small and positively charged. 1938 Enrico Fermi Conducted the first controlled chain reaction releasing energy from the atoms nucleus. Received the Nobel prize in physics for producing new radioactive elements via neutron irradiation, and w ...
... foil. He established that the nucleus was: very dense, very small and positively charged. 1938 Enrico Fermi Conducted the first controlled chain reaction releasing energy from the atoms nucleus. Received the Nobel prize in physics for producing new radioactive elements via neutron irradiation, and w ...
V Ch 2
... (b) Radon in the body decays to emit radiation which has strong ionizing power. (1A) Also, the decay product polonium is a radioactive solid which will stay inside the body and undergo further radioactive decay. ...
... (b) Radon in the body decays to emit radiation which has strong ionizing power. (1A) Also, the decay product polonium is a radioactive solid which will stay inside the body and undergo further radioactive decay. ...
Radioactive Decay Laws
... Now whenever mass disappears energy is created, according to Einstein's formula E = mc2, and... the mass was just equivalent to 200 MeV; it all fitted! Meitner was convinced that the product actually was Barium rather than a homologue. The nightmare of contradictory evidence all fit the explanation ...
... Now whenever mass disappears energy is created, according to Einstein's formula E = mc2, and... the mass was just equivalent to 200 MeV; it all fitted! Meitner was convinced that the product actually was Barium rather than a homologue. The nightmare of contradictory evidence all fit the explanation ...
DEMONSTRATE UNDERSTANDING OF ATOMS AND
... How long does material remain radioactive? Some atomic nuclei are very unstable, existing for a few minutes or seconds. Others are very stable and take millions of years to decay to form another atom. The half-life of a radioisotope is the average time it takes for half of the remaining radioactive ...
... How long does material remain radioactive? Some atomic nuclei are very unstable, existing for a few minutes or seconds. Others are very stable and take millions of years to decay to form another atom. The half-life of a radioisotope is the average time it takes for half of the remaining radioactive ...
Atomic Structure
... These are fuel rods in a nuclear reactor and they contain radioactive uranium-235. However, natural uranium contains more than 99% non-radioactive 238U and only 0.71% radioactive 235U. Uranium-235 is needed for the fission reactions that generate energy in nuclear power plants. In order to increase ...
... These are fuel rods in a nuclear reactor and they contain radioactive uranium-235. However, natural uranium contains more than 99% non-radioactive 238U and only 0.71% radioactive 235U. Uranium-235 is needed for the fission reactions that generate energy in nuclear power plants. In order to increase ...
Chapter 7
... Radiation dosage is measured in sieverts, or millisieverts, where 1 Sv is the amount of any radiation that has the same biological effects as those produced when 1 kg of body tissue absorbs 1 joule of x-rays or gamma rays. A similar unit is called a rem, or millirem. This unit is somewhat outmoded, ...
... Radiation dosage is measured in sieverts, or millisieverts, where 1 Sv is the amount of any radiation that has the same biological effects as those produced when 1 kg of body tissue absorbs 1 joule of x-rays or gamma rays. A similar unit is called a rem, or millirem. This unit is somewhat outmoded, ...
RaLa Experiment

The RaLa Experiment, or RaLa, was a series of tests during and after the Manhattan Project designed to study the behavior of converging shock waves to achieve the spherical implosion necessary for compression of the plutonium pit of the nuclear weapon. The experiment used significant amounts of a short-lived radioisotope lanthanum-140, a potent source of gamma radiation; the RaLa is a contraction of Radioactive Lanthanum. The method was proposed by Robert Serber and developed by a team led by the Italian experimental physicist Bruno Rossi.The tests were performed with 1/8 inch (3.2 mm) spheres of radioactive lanthanum, equal to about 100 curies (3.7 TBq) and later 1,000 Ci (37 TBq), located in the center of a simulated nuclear device. The explosive lenses were designed primarily using this series of tests. Some 254 tests were conducted between September 1944 and March 1962. In his history of the Los Alamos project, David Hawkins wrote: “RaLa became the most important single experiment affecting the final bomb design”.