CHAPTER 6
... • Step 6: FGAM cyclase (AIR synthetase) – Produce aminoimidazole nucleotide (AIR) – Similar in some ways to step 5. ATP activates the formyl group by phosphorylation, facilitating attack by N. – In avian liver, the enzymes for step 3, 4, and 6 (GAR synthetase, GAR transformylase, and AIR synthetase) ...
... • Step 6: FGAM cyclase (AIR synthetase) – Produce aminoimidazole nucleotide (AIR) – Similar in some ways to step 5. ATP activates the formyl group by phosphorylation, facilitating attack by N. – In avian liver, the enzymes for step 3, 4, and 6 (GAR synthetase, GAR transformylase, and AIR synthetase) ...
f212 biological molecules
... • There are more branches containing a smaller number of glucose molecules than amylopectin ...
... • There are more branches containing a smaller number of glucose molecules than amylopectin ...
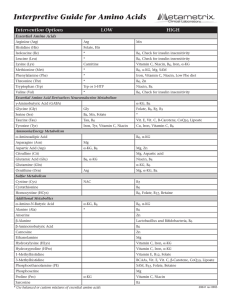
Interpretive Guide for Amino Acids
... of essential amino acids (glutamine is derived fiom histidine). Check overall amino acid level of diet. High - marker of vitamin B6 deficiency. Ammonia accumulation suspected, if low or low normal glutamic acid. Extra α-KG needed to combine with ammonia and to make up for energy deficit caused by overu ...
... of essential amino acids (glutamine is derived fiom histidine). Check overall amino acid level of diet. High - marker of vitamin B6 deficiency. Ammonia accumulation suspected, if low or low normal glutamic acid. Extra α-KG needed to combine with ammonia and to make up for energy deficit caused by overu ...
Citric Acid Cycle Overview
... in [lactate] so that the [lactate]/[pyruvate] ratio is many times larger than normal. Explain. ...
... in [lactate] so that the [lactate]/[pyruvate] ratio is many times larger than normal. Explain. ...
Anaerobic Respiration
... electron acceptor is reduced and used as the source of nutrient for cell growth. Dissimilative metabolism: A large amount of the electron acceptor is reduced for energy and the reduced product is excreted into the environment. ...
... electron acceptor is reduced and used as the source of nutrient for cell growth. Dissimilative metabolism: A large amount of the electron acceptor is reduced for energy and the reduced product is excreted into the environment. ...
Pro-Cycle PMS Formula 120s
... glucose, sucrose, fructose, lactose, starch, calcium sulfate, calcium phosphate, calcium stearate, aluminum salts, aluminum hydroxide (lakes), yeast bases, fish oil, corn, dairy products and artificial colors, flavors or preservatives. Amino acids used in the chelation of minerals and traces element ...
... glucose, sucrose, fructose, lactose, starch, calcium sulfate, calcium phosphate, calcium stearate, aluminum salts, aluminum hydroxide (lakes), yeast bases, fish oil, corn, dairy products and artificial colors, flavors or preservatives. Amino acids used in the chelation of minerals and traces element ...
Enzymes
... 1. Enzymes speed up chemical reactions that take place in cells. 2. Enzymes are very specific, generally catalyzing only one chemical reaction. 3. For this reason, part of an enzyme’s name is usually derived from the reaction it catalyzes. Enzymes usually end in the suffix “–ase”. Ex. Alcohol dehydr ...
... 1. Enzymes speed up chemical reactions that take place in cells. 2. Enzymes are very specific, generally catalyzing only one chemical reaction. 3. For this reason, part of an enzyme’s name is usually derived from the reaction it catalyzes. Enzymes usually end in the suffix “–ase”. Ex. Alcohol dehydr ...
Chapter 17 (Oct 23, 27, 28)
... (a) An mRNA molecule is generally translated simultaneously by several ribosomes in clusters called polyribosomes. ...
... (a) An mRNA molecule is generally translated simultaneously by several ribosomes in clusters called polyribosomes. ...
Lecture
... #3 Nucleic Acids RNA -single polypeptide chains DNA - double helix Two backbones run in opposite 5→ 3 direction antiparallel ...
... #3 Nucleic Acids RNA -single polypeptide chains DNA - double helix Two backbones run in opposite 5→ 3 direction antiparallel ...
Supplementary Methods
... uridine (U), according to standard solid phase oligonucleotide synthesis protocols1. For antagomirs. i.e., cholesterol conjugated RNAs, the synthesis started from a controlledpore glass solid support carrying a cholesterol- hydroxyprolinol linker2. Antagomirs with phosphorothioate backbone at a give ...
... uridine (U), according to standard solid phase oligonucleotide synthesis protocols1. For antagomirs. i.e., cholesterol conjugated RNAs, the synthesis started from a controlledpore glass solid support carrying a cholesterol- hydroxyprolinol linker2. Antagomirs with phosphorothioate backbone at a give ...
BIOCHEMISTRY WEBQUEST
... “triglycerides”? (hint: what does “tri-“ mean? What do they have three of?) 1 pt ...
... “triglycerides”? (hint: what does “tri-“ mean? What do they have three of?) 1 pt ...
Chemistry of Life
... STRUCTURE In a hydroxyl group (—OH), a hydrogen atom is bonded to an oxygen atom, which in turn is bonded to the carbon skeleton of the organic molecule. (Do not confuse this functional group with the ...
... STRUCTURE In a hydroxyl group (—OH), a hydrogen atom is bonded to an oxygen atom, which in turn is bonded to the carbon skeleton of the organic molecule. (Do not confuse this functional group with the ...
Comprehenexam- - HCC Learning Web
... carbohydrates as a polymer called _________________ 31) How will you distinguish between hydrolysis and dehydration reactions? Give an example each. _______________________________________________________________ 32) The molecular formula for glucose is C6H12O6. What would be the molecular formula f ...
... carbohydrates as a polymer called _________________ 31) How will you distinguish between hydrolysis and dehydration reactions? Give an example each. _______________________________________________________________ 32) The molecular formula for glucose is C6H12O6. What would be the molecular formula f ...
Definitions
... Symbol (P). It is an element which is needed to make bones, ATP and DNA is a chain of many peptides is a long chain of amino acids folded up to form 3-D shapes. Each protein has a different job. this is a food molecule where large numbers of sugar molecules have been joined together these are elemen ...
... Symbol (P). It is an element which is needed to make bones, ATP and DNA is a chain of many peptides is a long chain of amino acids folded up to form 3-D shapes. Each protein has a different job. this is a food molecule where large numbers of sugar molecules have been joined together these are elemen ...
Proteins and Their Synthesis
... genes. However, suppressor mutations also occur in protein-coding genes. Using the tertiary structure of the β subunit of hemoglobin shown in Figure 93(c), explain in structural terms how a mutation could cause the loss of globin protein function. Now explain how a mutation at a second site in the s ...
... genes. However, suppressor mutations also occur in protein-coding genes. Using the tertiary structure of the β subunit of hemoglobin shown in Figure 93(c), explain in structural terms how a mutation could cause the loss of globin protein function. Now explain how a mutation at a second site in the s ...
Evidence for the absence of amino acid isomerization in microwave
... isomerization was measured after hydrolysis of the samples. This process is known also to induce some isomerization to varying extent depending on the nature of the amino acid (Liardon et al., 1981). Therefore, untreated samples were analyzed in the same way, and the contribution of microwave treatm ...
... isomerization was measured after hydrolysis of the samples. This process is known also to induce some isomerization to varying extent depending on the nature of the amino acid (Liardon et al., 1981). Therefore, untreated samples were analyzed in the same way, and the contribution of microwave treatm ...
Biosynthesis

Biosynthesis (also called biogenesis or anabolism) is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined together to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides.The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bonds, and DNA molecules, which are composed of nucleotides joined via phosphodiester bonds.