Chapter 9
... was important because it clarified how DNA could serve as genetic material Scientists **Watson & Crick** pieced together a model of the structure of DNA ...
... was important because it clarified how DNA could serve as genetic material Scientists **Watson & Crick** pieced together a model of the structure of DNA ...
IOSR Journal of Pharmacy and Biological Sciences (IOSR-JPBS) e-ISSN: 2278-3008, p-ISSN:2319-7676.
... Amino acids are the hydrolysed units of proteins (also known as polypeptides). Amino acid units in protein are arranged in a linear chain usually folded into a globular form joined together by the peptide bonds between the carboxyl and amino groups of adjacent amino acid residues. Proteins are also ...
... Amino acids are the hydrolysed units of proteins (also known as polypeptides). Amino acid units in protein are arranged in a linear chain usually folded into a globular form joined together by the peptide bonds between the carboxyl and amino groups of adjacent amino acid residues. Proteins are also ...
doc
... B. Cells. Life could only exist in a form compartmentalized by a lipid bilayer. C. Self-sustained metabolic system that does not require input from any other living system. D. An interacting web with intricate feedback loops to ensure homeostasis. E. Anything that can reproduce itself perfectly with ...
... B. Cells. Life could only exist in a form compartmentalized by a lipid bilayer. C. Self-sustained metabolic system that does not require input from any other living system. D. An interacting web with intricate feedback loops to ensure homeostasis. E. Anything that can reproduce itself perfectly with ...
design of energy metabolism
... - Stored lipids (triacylglycerol) mobilized by hormonally controlled triacylglycerol lipases; yields 3 long-chain fatty acids + glycerol. Glycerol is catabolized via glycolysis. Fatty acids broken down 2-C per cycle in -oxidation pathway and then enter Krebs Cycle via acetyl-CoA. (See Figs 6.11 and ...
... - Stored lipids (triacylglycerol) mobilized by hormonally controlled triacylglycerol lipases; yields 3 long-chain fatty acids + glycerol. Glycerol is catabolized via glycolysis. Fatty acids broken down 2-C per cycle in -oxidation pathway and then enter Krebs Cycle via acetyl-CoA. (See Figs 6.11 and ...
Early days of tRNA research: Discovery, function, purification and
... (pH 5 enzyme) which activated amino acids in the presence of ATP to yield aminoacyl-adenylates (Hoagland et al 1956; Zamecnik 2005). The formation of aminoacyl-adenylates was demonstrated using amino acid-dependent ATP-PPi exchange and by their reaction with neutral hydroxylamine to form amino acid ...
... (pH 5 enzyme) which activated amino acids in the presence of ATP to yield aminoacyl-adenylates (Hoagland et al 1956; Zamecnik 2005). The formation of aminoacyl-adenylates was demonstrated using amino acid-dependent ATP-PPi exchange and by their reaction with neutral hydroxylamine to form amino acid ...
Allosteric Regulation of an Enzyme
... More about enzymes and kinetics • More about M-M kinetics hyperbolic curves, and approximations • LB plots, straight lines, and exact predictions • Why is it valuable to know km, Vm, V1/2, etc with respect to cell culture or drug metabolism by cells? • Drugs as non-competitive and competitive inhib ...
... More about enzymes and kinetics • More about M-M kinetics hyperbolic curves, and approximations • LB plots, straight lines, and exact predictions • Why is it valuable to know km, Vm, V1/2, etc with respect to cell culture or drug metabolism by cells? • Drugs as non-competitive and competitive inhib ...
LB Fat metabolism A
... liver: via the enzyme Lipoprotein Lipase (LPL) Thus, unlike carbohydrates and protein, most lipids do not use the enterohepatic circulatory system. This allows lipids to be cleared by the whole body and avoids overwhelming the liver with lipid. ...
... liver: via the enzyme Lipoprotein Lipase (LPL) Thus, unlike carbohydrates and protein, most lipids do not use the enterohepatic circulatory system. This allows lipids to be cleared by the whole body and avoids overwhelming the liver with lipid. ...
SAMIE: STATISTICAL ALGORITHM FOR MODELING
... the 426 of those examples, that both the DNA and the protein was xed in all positions (see example, below). Thus, we ended up with 675 single nger vectors, which constituted our training set. In this set 115 di erent \proteins" (with respect to the four \critical" amino acids) had \selected" a tot ...
... the 426 of those examples, that both the DNA and the protein was xed in all positions (see example, below). Thus, we ended up with 675 single nger vectors, which constituted our training set. In this set 115 di erent \proteins" (with respect to the four \critical" amino acids) had \selected" a tot ...
2.3 Carbon-Based Molecules TEKS 9A
... • Proteins are polymers of amino acid monomers. – Twenty different amino acids are used to build proteins in organisms. – Amino acids differ in side groups, or R groups. – Amino acids are linked by peptide bonds. ...
... • Proteins are polymers of amino acid monomers. – Twenty different amino acids are used to build proteins in organisms. – Amino acids differ in side groups, or R groups. – Amino acids are linked by peptide bonds. ...
BIO-5002A - BIOCHEMISTRY
... achieved through the use of membrane proteins by either facilitated diffusion or active transport. Describe, using one appropriate example of each mechanism, how the selective membrane transport of sodium and potassium is achieved. ...
... achieved through the use of membrane proteins by either facilitated diffusion or active transport. Describe, using one appropriate example of each mechanism, how the selective membrane transport of sodium and potassium is achieved. ...
ch3b_SP13x
... • Collection of biochemical rxns within a cell • Metabolic pathways – Sequence of rxns – Each step catalyzed by a different enzyme • Enzymes of a pathway often physically interact to form large complexes – Limits amount of diffusion needed at each step of the pathway – The product of the preceding s ...
... • Collection of biochemical rxns within a cell • Metabolic pathways – Sequence of rxns – Each step catalyzed by a different enzyme • Enzymes of a pathway often physically interact to form large complexes – Limits amount of diffusion needed at each step of the pathway – The product of the preceding s ...
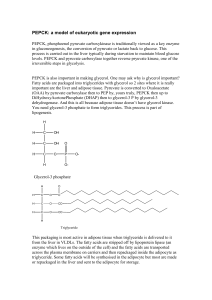
PEPCK: a model of eukaryotic gene expression
... PEPCK: a model of eukaryotic gene expression PEPCK, phosphoenol pyruvate carboxykinase is traditionally viewed as a key enzyme in gluconeogenesis, the conversion of pyruvate or lactate back to glucose. This process is carried out in the liver typically during starvation to maintain blood glucose lev ...
... PEPCK: a model of eukaryotic gene expression PEPCK, phosphoenol pyruvate carboxykinase is traditionally viewed as a key enzyme in gluconeogenesis, the conversion of pyruvate or lactate back to glucose. This process is carried out in the liver typically during starvation to maintain blood glucose lev ...
Biology 7th hour Chapter 6 Krebs Cycle and Fermentation Quiz
... d) Electrons are transferred to the electron transport chain _____ 9) If muscles do not get enough oxygen during heavy exercise, glycolysis is followed by: a) Lactic acid fermentation c) Alcoholic fermentation b) Photosynthesis d) Calvin Cycle _____ 10) All the energy-releasing pathways within the c ...
... d) Electrons are transferred to the electron transport chain _____ 9) If muscles do not get enough oxygen during heavy exercise, glycolysis is followed by: a) Lactic acid fermentation c) Alcoholic fermentation b) Photosynthesis d) Calvin Cycle _____ 10) All the energy-releasing pathways within the c ...
Uncommon pathways of metabolism among lactic acid bacteria
... Synthesis of malate permease and mafic enzyme were repressed by the addition of glucose at concentrations greater than 5 mM. However, the addition of 10 mM glucose to resting cells had no effect on the transport of the dicarboxylic acid suggesting that neither components of the glucose PTS nor inter ...
... Synthesis of malate permease and mafic enzyme were repressed by the addition of glucose at concentrations greater than 5 mM. However, the addition of 10 mM glucose to resting cells had no effect on the transport of the dicarboxylic acid suggesting that neither components of the glucose PTS nor inter ...
Table S1. - BioMed Central
... Key enzyme of the glycolysis; HK 2 is involved in increased utilization of glucose by cancer cells; target of new antineoplastic pharmacologic agents [35, 36]. Key enzyme of the glycolysis; PFK-1 is inhibited by ATP and citrate (from the citric acid cycle) [127]. Executes the final step of aerobic g ...
... Key enzyme of the glycolysis; HK 2 is involved in increased utilization of glucose by cancer cells; target of new antineoplastic pharmacologic agents [35, 36]. Key enzyme of the glycolysis; PFK-1 is inhibited by ATP and citrate (from the citric acid cycle) [127]. Executes the final step of aerobic g ...
Metabolism, Glycolysis, & Fermentation
... explain how fermentation reactions are used in the identification of bacteria. ...
... explain how fermentation reactions are used in the identification of bacteria. ...
Slide 1
... have come a long way towards constructing antibodies that can neutralize cancer cells. ...
... have come a long way towards constructing antibodies that can neutralize cancer cells. ...
Lecture 14: BSCI437 - University of Maryland, College Park
... – After DNA replication, the two DNA strands are hopelessly intertwined (catenated). Can resolve this by creating double stranded breaks, allowing one DNA molecule to pass through the other. Done by DNA ...
... – After DNA replication, the two DNA strands are hopelessly intertwined (catenated). Can resolve this by creating double stranded breaks, allowing one DNA molecule to pass through the other. Done by DNA ...
Biology I Review_2016
... a long, nonpolar hydrocarbon chain (12-28 C’s) with a polar carboxyl (COOH) head. The ratio of C-H is significantly higher than O bonds (in its single carboxyl group), and therefore, lipids have more energy stored in their bonds than carbohydrates do in theirs. As you know, fats & waxes do not mix w ...
... a long, nonpolar hydrocarbon chain (12-28 C’s) with a polar carboxyl (COOH) head. The ratio of C-H is significantly higher than O bonds (in its single carboxyl group), and therefore, lipids have more energy stored in their bonds than carbohydrates do in theirs. As you know, fats & waxes do not mix w ...
Slide 1
... that grasp the zinc. This zinc finger is from a frog protein of unknown function. (A) Schematic drawing of the amino acid sequence of the zinc finger. (B) The three-dimensional structure of the zinc finger is constructed from an antiparallel b-sheet (amino acids 1 to 10) followed by an a-helix (amin ...
... that grasp the zinc. This zinc finger is from a frog protein of unknown function. (A) Schematic drawing of the amino acid sequence of the zinc finger. (B) The three-dimensional structure of the zinc finger is constructed from an antiparallel b-sheet (amino acids 1 to 10) followed by an a-helix (amin ...
Biosynthesis

Biosynthesis (also called biogenesis or anabolism) is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined together to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides.The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bonds, and DNA molecules, which are composed of nucleotides joined via phosphodiester bonds.