Aims of lecture
... Prevalence of overweight and obesity by age, women, latest available year, England, Scotland and Wales ...
... Prevalence of overweight and obesity by age, women, latest available year, England, Scotland and Wales ...
Carbohydrate Metabolism
... • In aerobic condition, cell pyruvate is oxidized to acetyl-CoA and CO2 by multienzyme complex pyruvate dehydrogenase, instead of being reduced to lactate. • In erythrocytes, the first site for generation of ATP in glycolysis may be bypassed leading to the formation of 2,3 bisphosphoglycerate. • Cit ...
... • In aerobic condition, cell pyruvate is oxidized to acetyl-CoA and CO2 by multienzyme complex pyruvate dehydrogenase, instead of being reduced to lactate. • In erythrocytes, the first site for generation of ATP in glycolysis may be bypassed leading to the formation of 2,3 bisphosphoglycerate. • Cit ...
Ch 17 HW - WordPress.com
... 2. The attachment of a free amino acid to a specific RNA molecule is the key step in charging of tRNA . 3. In translation , the nucleotide sequence of a piece of RNA is converted into a sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide. 4. The final RNA template for protein synthesis in eukaryotes is differ ...
... 2. The attachment of a free amino acid to a specific RNA molecule is the key step in charging of tRNA . 3. In translation , the nucleotide sequence of a piece of RNA is converted into a sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide. 4. The final RNA template for protein synthesis in eukaryotes is differ ...
UNIT 7 Metabolism and generation of ATP
... space, and a matrix, located within the inner membrane. The outer membrane is porous, whereas the inner membrane is much tighter, serving as a barrier to many biological metabolites. 4.2 The inner membrane is highly folded into cristae, which project into, and often nearly through the interior of th ...
... space, and a matrix, located within the inner membrane. The outer membrane is porous, whereas the inner membrane is much tighter, serving as a barrier to many biological metabolites. 4.2 The inner membrane is highly folded into cristae, which project into, and often nearly through the interior of th ...
Chapter 25: Metabolism
... • Breaks down glucose (6C) in cytosol – Into 2 pyruvic acid (3C) molecules used by the mitochondria ...
... • Breaks down glucose (6C) in cytosol – Into 2 pyruvic acid (3C) molecules used by the mitochondria ...
PHOTOSYNTHESIS
... must be able to make biomass like sugars that can be turned into cellulose for their cell walls or other important chemicals. In order to do this they need a carbon source and a source of hydrogens to attach to the carbons . ...
... must be able to make biomass like sugars that can be turned into cellulose for their cell walls or other important chemicals. In order to do this they need a carbon source and a source of hydrogens to attach to the carbons . ...
glycocholic acid
... • About 1g of cholesterol is synthesized per day in adults, liver: 50%; intestine 15%; other tissues: 35%. • All C-atoms of cholesterol come from acetyl CoA; reducing equivalents come from NADPH • Energy to drive synthesis comes from ATP hydrolysis • Key enzyme (rate limiting enzyme) in cholesterol ...
... • About 1g of cholesterol is synthesized per day in adults, liver: 50%; intestine 15%; other tissues: 35%. • All C-atoms of cholesterol come from acetyl CoA; reducing equivalents come from NADPH • Energy to drive synthesis comes from ATP hydrolysis • Key enzyme (rate limiting enzyme) in cholesterol ...
Multiple Choice Questions
... 1. The site in the cell at which cellular respiration occurs is the ___________. a. endoplasmic reticulum b. Golgi complex c. ribosome d. nucleus e. mitochondria 2. One molecule of water is capable of forming ___________ hydrogen bonds. a. two b. three c. four d. five e. six 3. The pKa of glutamic a ...
... 1. The site in the cell at which cellular respiration occurs is the ___________. a. endoplasmic reticulum b. Golgi complex c. ribosome d. nucleus e. mitochondria 2. One molecule of water is capable of forming ___________ hydrogen bonds. a. two b. three c. four d. five e. six 3. The pKa of glutamic a ...
Citric Acid Cycle
... citric acid cycle, generating three NADH, one FADH2, and one ATP (by substrate-level phophorylation). • Intermediates of citric acid cycle are also used as biosynthetic precursors for many other biomolecules, including fatty acids, steroids, amino acids, heme, pyrimidines, and glucose. ...
... citric acid cycle, generating three NADH, one FADH2, and one ATP (by substrate-level phophorylation). • Intermediates of citric acid cycle are also used as biosynthetic precursors for many other biomolecules, including fatty acids, steroids, amino acids, heme, pyrimidines, and glucose. ...
LABORATORY Exercise Protein Structure
... The sequence of Amino Acid Sidechains that you determined when placing them on the minitoober is called the Primary Structure of your protein. As a general rule the final shape of a protein is determined by its primary structure (the sequence of its Amino Acids). 5) Now you can begin to fold your 15 ...
... The sequence of Amino Acid Sidechains that you determined when placing them on the minitoober is called the Primary Structure of your protein. As a general rule the final shape of a protein is determined by its primary structure (the sequence of its Amino Acids). 5) Now you can begin to fold your 15 ...
Energy Metabolism and Mitochondria
... The process of glycolysis and citric acid cycle generates high-energy electrons that are carried by the NADH and FADH2 molecules. The NADH (and FADH2) molecules transfer their electrons via multiple electron carriers that are components of the electron transport chain. These are located in the mitoc ...
... The process of glycolysis and citric acid cycle generates high-energy electrons that are carried by the NADH and FADH2 molecules. The NADH (and FADH2) molecules transfer their electrons via multiple electron carriers that are components of the electron transport chain. These are located in the mitoc ...
PDF - Bentham Open
... NrfD/PsrC protein family. It is involved in the quinolquinone redox system [10]. It is assumed that only DsrP proteins from proteobacterial sulfur-oxidizing bacteria bind heme. The heme b that was found in DsrP could be involved in electron transfer from DsrP to DsrM. The putative quinone binding si ...
... NrfD/PsrC protein family. It is involved in the quinolquinone redox system [10]. It is assumed that only DsrP proteins from proteobacterial sulfur-oxidizing bacteria bind heme. The heme b that was found in DsrP could be involved in electron transfer from DsrP to DsrM. The putative quinone binding si ...
Slide 1
... pathways that produce acetyl-CoA for different metabolic functions How glucose and glutamine derived C2 units are maintained as functionally distinct pools and transported from their respective organelles to different sites of acetylation remains to be investigated The metabolic labeling data su ...
... pathways that produce acetyl-CoA for different metabolic functions How glucose and glutamine derived C2 units are maintained as functionally distinct pools and transported from their respective organelles to different sites of acetylation remains to be investigated The metabolic labeling data su ...
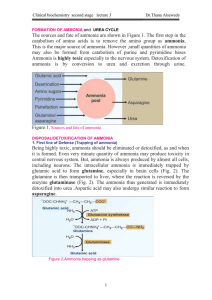
FORMATION OF AMMONIA
... cells, ammonia is purposely generated from glutamine with the helpof glutaminase. This is for buffering the acids, and maintaining acid-base balance (see Fig. 4). ...
... cells, ammonia is purposely generated from glutamine with the helpof glutaminase. This is for buffering the acids, and maintaining acid-base balance (see Fig. 4). ...
Cell Respiration Basics
... During the Krebs cycle Acetyl CoA molecules formed from pyruvic acid molecules, are broken down. CO2 is given off, and ATP is produced. (1 ATP per each pyruvic acid or each turn of the cycle.) ...
... During the Krebs cycle Acetyl CoA molecules formed from pyruvic acid molecules, are broken down. CO2 is given off, and ATP is produced. (1 ATP per each pyruvic acid or each turn of the cycle.) ...
L. LEWIS ACID CATALYSIS
... Carol Fierke’s group investigated this effect further and examined the role of amino acid substitutions in the coordination environment surrounding Zn2+in CA (Figure L.12).4,5 The choice of direct ligands to the zinc ion has a clear effect on pKa (Table L.2). Of the three histidine residues that bi ...
... Carol Fierke’s group investigated this effect further and examined the role of amino acid substitutions in the coordination environment surrounding Zn2+in CA (Figure L.12).4,5 The choice of direct ligands to the zinc ion has a clear effect on pKa (Table L.2). Of the three histidine residues that bi ...
Location and characterization of the three carbohydrate prosthetic
... two N-glycosidic linkages, differ from those previously reported for the oq-microglobulin, which indicated the presence of three identical N-glycosidic linked carbohydrate chains without specifying their location in the polypeptide chain [19]. The main reason for this discrepancy may reside in the f ...
... two N-glycosidic linkages, differ from those previously reported for the oq-microglobulin, which indicated the presence of three identical N-glycosidic linked carbohydrate chains without specifying their location in the polypeptide chain [19]. The main reason for this discrepancy may reside in the f ...
AP review
... • Extra –OH group at 2’ pentose sugar, sugar is ribose, not deoxyribose • RNA usually does not form double helix, makes loops within one strand, often contains modified bases • RNA has an additional 2’-OH group which can form HB, stabilizing tertiary structure ...
... • Extra –OH group at 2’ pentose sugar, sugar is ribose, not deoxyribose • RNA usually does not form double helix, makes loops within one strand, often contains modified bases • RNA has an additional 2’-OH group which can form HB, stabilizing tertiary structure ...
Biosynthesis

Biosynthesis (also called biogenesis or anabolism) is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined together to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides.The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bonds, and DNA molecules, which are composed of nucleotides joined via phosphodiester bonds.