Catalase - Alpha Diagnostic International
... decomposition of hydrogen peroxide to water and oxygen. Catalase has one of the highest turnover numbers of all enzymes; one molecule of catalase can convert 40 million molecules of hydrogen peroxide to water and oxygen each second. Catalase is a tetramer of four polypeptide chains, each over 500 am ...
... decomposition of hydrogen peroxide to water and oxygen. Catalase has one of the highest turnover numbers of all enzymes; one molecule of catalase can convert 40 million molecules of hydrogen peroxide to water and oxygen each second. Catalase is a tetramer of four polypeptide chains, each over 500 am ...
Microbial Metabolism PowerPoint
... 3) harnesses the energy in ea) e- donor loses an e- (oxidation) which is taken up by an e- acceptor (reduction) i) e- is usually part of H atom b) energy is released every time the e- (H) is transferred c) often incorporates an intermediate eacceptor i) results in 2 transfers (more E) ...
... 3) harnesses the energy in ea) e- donor loses an e- (oxidation) which is taken up by an e- acceptor (reduction) i) e- is usually part of H atom b) energy is released every time the e- (H) is transferred c) often incorporates an intermediate eacceptor i) results in 2 transfers (more E) ...
Poster
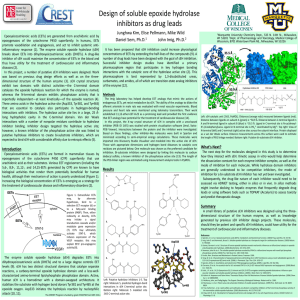
... diseases (2). In this project, a number of putative sEH inhibitors were designed. Work was based on previous drug design efforts as well as on the threedimensional structure of the human enzyme (3). sEH crystal structures exhibit two domains with distinct activities—the C-terminal domain catalyzes t ...
... diseases (2). In this project, a number of putative sEH inhibitors were designed. Work was based on previous drug design efforts as well as on the threedimensional structure of the human enzyme (3). sEH crystal structures exhibit two domains with distinct activities—the C-terminal domain catalyzes t ...
The Euglena gracilis chloroplast rpoB gene
... were identified. INTRODUCTION Chloroplast genes are transcribed, and the resulting mRNAs are translated via plastid-specific RNA polymerase(s) and ribosomes, respectively. The genes for tRNAs, rRNAs and several messenger RNAs are chloroplast encoded (I, 2, 3, 4). In the chloroplast of the unicellula ...
... were identified. INTRODUCTION Chloroplast genes are transcribed, and the resulting mRNAs are translated via plastid-specific RNA polymerase(s) and ribosomes, respectively. The genes for tRNAs, rRNAs and several messenger RNAs are chloroplast encoded (I, 2, 3, 4). In the chloroplast of the unicellula ...
cell metabolism
... There is a considerable amount of energy still trapped in the released hydrogen atoms (electrons at high energy levels). Electron Transport occurs on the membrane lining the mitochondrial cristae (“folds, crests”). 1. Electrons extracted from NADH & FADH2 are transferred to electron carrier molecule ...
... There is a considerable amount of energy still trapped in the released hydrogen atoms (electrons at high energy levels). Electron Transport occurs on the membrane lining the mitochondrial cristae (“folds, crests”). 1. Electrons extracted from NADH & FADH2 are transferred to electron carrier molecule ...
Protein digestion in poultry – the value of an
... • Protein digestion in poultry (and other animals) is a complex process of hydrolysis of incoming proteins, absorption, further processing and the concurrent secretion and recovery of endogenous protein • Endogenous proteins are often less well recovered that exogenous proteins and ProAct may assist ...
... • Protein digestion in poultry (and other animals) is a complex process of hydrolysis of incoming proteins, absorption, further processing and the concurrent secretion and recovery of endogenous protein • Endogenous proteins are often less well recovered that exogenous proteins and ProAct may assist ...
T M 24,
... Paints and coatings are generally known for serving two key functions: decoration and protection. We rely on these coatings to add color and character to our homes, to the cars we drive, and to a wide variety of other surfaces in the world around us. These coatings are also serving to protect the su ...
... Paints and coatings are generally known for serving two key functions: decoration and protection. We rely on these coatings to add color and character to our homes, to the cars we drive, and to a wide variety of other surfaces in the world around us. These coatings are also serving to protect the su ...
Enzymes - Food Science & Human Nutrition
... their ability to bind to their substrates with very high specificity and significantly lower the activation energy (Ea) of the reaction converting a substrate to a product Speed up reactions by 103-1011 compared to other catalysts; 108-1020 compared to uncatalyzed reactions ...
... their ability to bind to their substrates with very high specificity and significantly lower the activation energy (Ea) of the reaction converting a substrate to a product Speed up reactions by 103-1011 compared to other catalysts; 108-1020 compared to uncatalyzed reactions ...
Pathway Architect
... curated pathways, graphically projecting data onto pathway nodes or edges for interactive user analysis. Researchers can specify search criteria for particular organisms and browse a table of pathway results before projecting data onto a particular pathway. ...
... curated pathways, graphically projecting data onto pathway nodes or edges for interactive user analysis. Researchers can specify search criteria for particular organisms and browse a table of pathway results before projecting data onto a particular pathway. ...
The sequence of the tms transcript 2 locus of the A. tumefaciens
... Kd protein in E. coli minicells, a protein that is consistent with the open reading frame we have detected (see below). The promoter for transcription was apparently within Hind III fragment 22e. Schroder,et. al.(34) have also shown that coupled j ^ vitro transcription/translation systems prepared f ...
... Kd protein in E. coli minicells, a protein that is consistent with the open reading frame we have detected (see below). The promoter for transcription was apparently within Hind III fragment 22e. Schroder,et. al.(34) have also shown that coupled j ^ vitro transcription/translation systems prepared f ...
CHAPTER 19 LIPID METABOLISM Introduction: Fats are much more
... Fatty acid biosynthesis is chemically very similar to the reverse of beta oxidation. However, beta oxidation and fatty acid biosynthesis utilize different enzymes and different cellular compartments; biosynthesis occurs in the cytoplasm. In eukaryotes the multiple enzyme functions associated with fa ...
... Fatty acid biosynthesis is chemically very similar to the reverse of beta oxidation. However, beta oxidation and fatty acid biosynthesis utilize different enzymes and different cellular compartments; biosynthesis occurs in the cytoplasm. In eukaryotes the multiple enzyme functions associated with fa ...
Essential Cell Biology (3rd ed.)
... protein can be unfolded, or denatured, by treatment with solvents that disrupt the noncovalent interactions holding the folded chain together. This treatment converts the protein into a flexible polypeptide chain that has lost its natural shape. When the denaturing solvent is removed, the protein of ...
... protein can be unfolded, or denatured, by treatment with solvents that disrupt the noncovalent interactions holding the folded chain together. This treatment converts the protein into a flexible polypeptide chain that has lost its natural shape. When the denaturing solvent is removed, the protein of ...
TbMP42 is a structure-sensitive ribonuclease that likely follows a
... transcripts. The process is catalyzed by a multienzyme complex, the editosome, which consists of approximately 20 proteins. While for some of the polypeptides a contribution to the editing reaction can be deduced from their domain structure, the involvement of other proteins remains elusive. TbMP42, ...
... transcripts. The process is catalyzed by a multienzyme complex, the editosome, which consists of approximately 20 proteins. While for some of the polypeptides a contribution to the editing reaction can be deduced from their domain structure, the involvement of other proteins remains elusive. TbMP42, ...
21. Which of the electron carriers in the electron transport
... of conformational change caused by a single proton binding in the F0 portion of the F type ATP synthase? a) 45 degrees b) *30 degrees c) 120 degrees d) 360 degrees e) none of the above 23. What type of redox center within the respiratory chain does not contain any non-amino acid components? a) cytoc ...
... of conformational change caused by a single proton binding in the F0 portion of the F type ATP synthase? a) 45 degrees b) *30 degrees c) 120 degrees d) 360 degrees e) none of the above 23. What type of redox center within the respiratory chain does not contain any non-amino acid components? a) cytoc ...
Chapter 4 Acids and bases
... behave as though they are solutions of H3O+ regardless HI is intrinsincally stronger than HBr. Water is therefore said to have a leveling effect that brings all strong acids down to the acidity of H3O+. To distinguish the acidity strengths of HBr and HI, one has to use a less basic solvent. Similar ...
... behave as though they are solutions of H3O+ regardless HI is intrinsincally stronger than HBr. Water is therefore said to have a leveling effect that brings all strong acids down to the acidity of H3O+. To distinguish the acidity strengths of HBr and HI, one has to use a less basic solvent. Similar ...
Enzymes | Principles of Biology from Nature Education
... Enzymes lower activation energy of biochemical reactions, but the substrates still need to have enough kinetic energy to reach their transition state, allowing the reaction to occur. The temperature at which the enzyme works best is called the enzyme's optimum temperature. Lowering the temperature d ...
... Enzymes lower activation energy of biochemical reactions, but the substrates still need to have enough kinetic energy to reach their transition state, allowing the reaction to occur. The temperature at which the enzyme works best is called the enzyme's optimum temperature. Lowering the temperature d ...
The Living World - Chapter 9 - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... 7. Phosphorylation or other chemical modifications can alter the activity of a protein after it is translated. ...
... 7. Phosphorylation or other chemical modifications can alter the activity of a protein after it is translated. ...
Metabolism
... – Glucose to Carbon dioxide + Water +Energy – C6H12O6 + O2 è 6CO2 + 6H2O + 38 ATP – Glucose is highly reduced; contains energy – Oxygen receives the electrons to form energy ...
... – Glucose to Carbon dioxide + Water +Energy – C6H12O6 + O2 è 6CO2 + 6H2O + 38 ATP – Glucose is highly reduced; contains energy – Oxygen receives the electrons to form energy ...
Biosynthesis

Biosynthesis (also called biogenesis or anabolism) is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined together to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides.The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bonds, and DNA molecules, which are composed of nucleotides joined via phosphodiester bonds.