Raven/Johnson Biology 8e
... 3. Predict whether gene expression (from initiation of transcription to final protein product) would be faster in a prokaryotic or eukaryotic cell. Explain your answer. Answer—The process of gene expression would occur more quickly in the prokaryotic cell for a number of reasons. The process of tran ...
... 3. Predict whether gene expression (from initiation of transcription to final protein product) would be faster in a prokaryotic or eukaryotic cell. Explain your answer. Answer—The process of gene expression would occur more quickly in the prokaryotic cell for a number of reasons. The process of tran ...
Production of functional protein hydrolysates from Egyptian
... Braun 1994). The hydrolysis process generates smaller peptides with improved nutritional characteristics compared to the original protein. Enzymatic hydrolysis of protein in vitro mimics parts of the enzymatic hydrolysis of the in vivo ingested protein. In fact, in vitro proteolysis can also be cons ...
... Braun 1994). The hydrolysis process generates smaller peptides with improved nutritional characteristics compared to the original protein. Enzymatic hydrolysis of protein in vitro mimics parts of the enzymatic hydrolysis of the in vivo ingested protein. In fact, in vitro proteolysis can also be cons ...
Raven/Johnson Biology 8e Chapter 15 Answers 1. The
... 3. Predict whether gene expression (from initiation of transcription to final protein product) would be faster in a prokaryotic or eukaryotic cell. Explain your answer. Answer—The process of gene expression would occur more quickly in the prokaryotic cell for a number of reasons. The process of tran ...
... 3. Predict whether gene expression (from initiation of transcription to final protein product) would be faster in a prokaryotic or eukaryotic cell. Explain your answer. Answer—The process of gene expression would occur more quickly in the prokaryotic cell for a number of reasons. The process of tran ...
General Chemistry 110 Quiz 1
... BOTH sugars enter into glycolysis). Mention the first few reactions for the entry of each hexose into glycolysis. Which hexose is energetically more costly to metabolize? d. The steps where NADH and FADH2 are produced by the citric acid cycle. List both enzymes and reactants and products involved in ...
... BOTH sugars enter into glycolysis). Mention the first few reactions for the entry of each hexose into glycolysis. Which hexose is energetically more costly to metabolize? d. The steps where NADH and FADH2 are produced by the citric acid cycle. List both enzymes and reactants and products involved in ...
Inhibition of Serine Amidohydrolases by Complexes of Vanadate
... will probably require crystallographic studies. A new class of inhibitors of serine amidohydrolases has thus been described. It is not clear at present whether the original rationale for their mode of action (Scheme 2) is correct, but studies of the structure of these inhibitors at representative ac ...
... will probably require crystallographic studies. A new class of inhibitors of serine amidohydrolases has thus been described. It is not clear at present whether the original rationale for their mode of action (Scheme 2) is correct, but studies of the structure of these inhibitors at representative ac ...
Cellular Respiration
... carbon dioxide is removed from each three-carbon pyruvic acid molecule to form acetic acid. This little step is the source of some of the carbon dioxide we produce. ...
... carbon dioxide is removed from each three-carbon pyruvic acid molecule to form acetic acid. This little step is the source of some of the carbon dioxide we produce. ...
Manuscript title - Journal of Tropical Resources and Sustainable
... There were three kinds of organic acids present in the extracts of Eleiodoxa conferta which are oxalic, malic and ascorbic. The main organic acid was oxalic acid. In this study, we found that young stage of Eleiodoxa conferta extracts which has the highest concentration of organic acid contents also ...
... There were three kinds of organic acids present in the extracts of Eleiodoxa conferta which are oxalic, malic and ascorbic. The main organic acid was oxalic acid. In this study, we found that young stage of Eleiodoxa conferta extracts which has the highest concentration of organic acid contents also ...
Positively selected sites on the surface glycoprotein (G) of infectious
... at positions 230 and 231. We saw no amino acid changes at these positions in any of our sequences. Because we did not sequence the whole molecule, we could not observe the state of positions 78 and 81. It has been suggested that passage in cell culture may select for anomalous changes in virus prote ...
... at positions 230 and 231. We saw no amino acid changes at these positions in any of our sequences. Because we did not sequence the whole molecule, we could not observe the state of positions 78 and 81. It has been suggested that passage in cell culture may select for anomalous changes in virus prote ...
Ch 8 Chapter Summary
... regenerated by the addition of a phosphate group to ADP. The free energy to phosphorylate ADP comes from exergonic (catabolic) reactions in the cell. The ATP cycle, the shuttling of inorganic phosphate and energy, couples the cell’s energyyielding (exergonic) processes to the energy-consuming (ender ...
... regenerated by the addition of a phosphate group to ADP. The free energy to phosphorylate ADP comes from exergonic (catabolic) reactions in the cell. The ATP cycle, the shuttling of inorganic phosphate and energy, couples the cell’s energyyielding (exergonic) processes to the energy-consuming (ender ...
Defelipe, L.A, Dolghih E, Roitberg A.E., Nouzova M., Mayoral
... nicely to form hydrogen bonds with the Trp-120 indole nitrogen and the amide nitrogen of Gln-14, while their carbon chains reside in a hydrophobic pocket formed by Ile-151, Ile-154, Tyr 155, Leu158, Val-221 and Val-224 (Fig. 4A). Docking results indicated a clear difference in the interaction of (10 ...
... nicely to form hydrogen bonds with the Trp-120 indole nitrogen and the amide nitrogen of Gln-14, while their carbon chains reside in a hydrophobic pocket formed by Ile-151, Ile-154, Tyr 155, Leu158, Val-221 and Val-224 (Fig. 4A). Docking results indicated a clear difference in the interaction of (10 ...
File - Ms. Poole`s Biology
... 12. A new window will pop up that provides you with the alignment and a link to the file of your results. Take a moment and look at the screen in front of you. Each line is the amino acid sequence of the same protein (hemoglobin beta) in different species. It is interesting to scan along the amino a ...
... 12. A new window will pop up that provides you with the alignment and a link to the file of your results. Take a moment and look at the screen in front of you. Each line is the amino acid sequence of the same protein (hemoglobin beta) in different species. It is interesting to scan along the amino a ...
Metabolismus xenobiotik - Univerzita Karlova v Praze
... Examples from metabolism of xenobiotics electrophilic xenobiotic (e.g. epoxide) + GSH + acetyl CoA mercapturic acid (= conjugate of the xenobiotic) generally: S-substituted N-acetyl cysteine ...
... Examples from metabolism of xenobiotics electrophilic xenobiotic (e.g. epoxide) + GSH + acetyl CoA mercapturic acid (= conjugate of the xenobiotic) generally: S-substituted N-acetyl cysteine ...
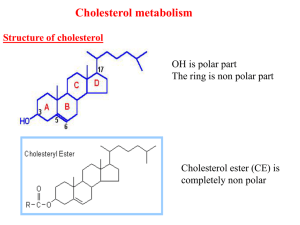
Lec4 Cholesterol met..
... decreased mobilization of cholesterol from blood to tissues. 2- Diabetes: due to increased absorption of dietary cholesterol 3- Diet rich in carbohydrates, and fats: increase the synthesis of cholesterol in liver due to: a - Increased the activity of the key enzyme (HMG-CoA reductase). b - Formation ...
... decreased mobilization of cholesterol from blood to tissues. 2- Diabetes: due to increased absorption of dietary cholesterol 3- Diet rich in carbohydrates, and fats: increase the synthesis of cholesterol in liver due to: a - Increased the activity of the key enzyme (HMG-CoA reductase). b - Formation ...
CWI Learning List for ANAT 111
... 4. State the first law and second law of thermodynamics. 5. Explain why energy conversion is always less than 100%. ...
... 4. State the first law and second law of thermodynamics. 5. Explain why energy conversion is always less than 100%. ...
Biol 1406 Ch 5
... x) Know about commonalities in amino acid structure. Where will each amino acid differ? ...
... x) Know about commonalities in amino acid structure. Where will each amino acid differ? ...
computer simulation of a living cell: part i
... given to the computer as input data. If the program represents a living cell, the program generates cell behavior as output. In order to analyse interactions among DNA, RNA, protein and the activities of self-reproduction and metabolism in a living cell, a simulation of the simple unicellular bacter ...
... given to the computer as input data. If the program represents a living cell, the program generates cell behavior as output. In order to analyse interactions among DNA, RNA, protein and the activities of self-reproduction and metabolism in a living cell, a simulation of the simple unicellular bacter ...
Riveting Respiration
... oxygen is present – pyruvate moves into the mitochondria Pyruvate is converted to Acetyl CoA in a series of 3 reactions (all with enzymes) CO2 is released ...
... oxygen is present – pyruvate moves into the mitochondria Pyruvate is converted to Acetyl CoA in a series of 3 reactions (all with enzymes) CO2 is released ...
7.012 Quiz 1 Answers
... ii) protein primary structure iii) protein secondary structure iv) complementary base pairing in RNA c) Your friend tried to remove some writing on a plastic box. He used a napkin dampened with water, which did not work. Then as you advised, he used ethanol (instead of water), and successfully remov ...
... ii) protein primary structure iii) protein secondary structure iv) complementary base pairing in RNA c) Your friend tried to remove some writing on a plastic box. He used a napkin dampened with water, which did not work. Then as you advised, he used ethanol (instead of water), and successfully remov ...
GMS BI 555/755 Lecture 3: Techniques for
... acids in a peptide hydrolysate can be separated by ionexchange chromatography on a sulfonated polystyrene resin (such as Dowex-50). Buffers (in this case, sodium citrate) of increasing pH are used to elute the amino acids from the column. The amount of each amino acid present is determined from the ...
... acids in a peptide hydrolysate can be separated by ionexchange chromatography on a sulfonated polystyrene resin (such as Dowex-50). Buffers (in this case, sodium citrate) of increasing pH are used to elute the amino acids from the column. The amount of each amino acid present is determined from the ...
video slide - Wayne State University
... Now, life is written by a similar code. DNA is made of a chain of 4 links or “colors” (nucleotides) AGCT. Protein is made of a chain of 20 different links—amino acids. You can specify any amino acid you want, by using triplets like ...
... Now, life is written by a similar code. DNA is made of a chain of 4 links or “colors” (nucleotides) AGCT. Protein is made of a chain of 20 different links—amino acids. You can specify any amino acid you want, by using triplets like ...
Compiling DNA strand displacement reactions using a functional
... Despite their apparent simplicity, strand displacement reactions like those outlined in Figure 1b are capable of rich behavior. Since the output strand produced by one strand displacement reaction may serve as the input to another reaction, strand displacement systems may be scaled up to produce mor ...
... Despite their apparent simplicity, strand displacement reactions like those outlined in Figure 1b are capable of rich behavior. Since the output strand produced by one strand displacement reaction may serve as the input to another reaction, strand displacement systems may be scaled up to produce mor ...
Biosynthesis

Biosynthesis (also called biogenesis or anabolism) is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined together to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides.The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bonds, and DNA molecules, which are composed of nucleotides joined via phosphodiester bonds.