DOC
... Cellular respiration is the oxidative, chemical attack on energy-rich molecules to provide useful energy for the cell. Enzymes catalyze the oxidation reactions. These reactions are known as catabolic reactions because they break molecules down to release energy. Anaerobic respiration The first part ...
... Cellular respiration is the oxidative, chemical attack on energy-rich molecules to provide useful energy for the cell. Enzymes catalyze the oxidation reactions. These reactions are known as catabolic reactions because they break molecules down to release energy. Anaerobic respiration The first part ...
Associated with Interstitial Lung Disease Asparaginyl
... least common, occurring in , 2%(5, 13, 14). Isoleucyl-tRNA synthetase is the only one of these synthetase autoantigens that is a component of the multienzyme synthetase complex, and some antiOJ sera also react with other components of the synthetase complex, but such additional reactivity does not c ...
... least common, occurring in , 2%(5, 13, 14). Isoleucyl-tRNA synthetase is the only one of these synthetase autoantigens that is a component of the multienzyme synthetase complex, and some antiOJ sera also react with other components of the synthetase complex, but such additional reactivity does not c ...
Quantitative analysis of acetyl-CoA production in hypoxic cancer cells reveals substantial contribution from acetate
... Background: Cell growth requires fatty acids for membrane synthesis. Fatty acids are assembled from 2-carbon units in the form of acetyl-CoA (AcCoA). In nutrient and oxygen replete conditions, acetyl-CoA is predominantly derived from glucose. In hypoxia, however, flux from glucose to acetyl-CoA decr ...
... Background: Cell growth requires fatty acids for membrane synthesis. Fatty acids are assembled from 2-carbon units in the form of acetyl-CoA (AcCoA). In nutrient and oxygen replete conditions, acetyl-CoA is predominantly derived from glucose. In hypoxia, however, flux from glucose to acetyl-CoA decr ...
Is structural flexibility of antigen-binding loops
... indicate identity with the consensus sequence deduced from VH and VL sequences of individual mAb. The sequence of 59 end (8 bases) of the 59 primer for PCR is not shown. Amino acid sequences of CDR are boxed according to the definition of Kabat et al. (26). ...
... indicate identity with the consensus sequence deduced from VH and VL sequences of individual mAb. The sequence of 59 end (8 bases) of the 59 primer for PCR is not shown. Amino acid sequences of CDR are boxed according to the definition of Kabat et al. (26). ...
PPt Chapter 5 - columbusisd.org
... • Lipids are the one class of large biological molecules that do not form polymers • The unifying feature of lipids is having little or no affinity for water • Lipids are hydrophobic because they consist mostly of hydrocarbons, which form nonpolar covalent bonds • The most biologically important lip ...
... • Lipids are the one class of large biological molecules that do not form polymers • The unifying feature of lipids is having little or no affinity for water • Lipids are hydrophobic because they consist mostly of hydrocarbons, which form nonpolar covalent bonds • The most biologically important lip ...
LABORATORY MANUAL ON BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY
... photoelectrocolorimeter with a red light filter. Then draw a plot (calibration curve) according to obtained results. Experiment 2. Protein precipitation with sulfosalicylic acid. Principle. Proteins dissolve in water with formation of homogenous solutions. There are two main factors of the stabiliza ...
... photoelectrocolorimeter with a red light filter. Then draw a plot (calibration curve) according to obtained results. Experiment 2. Protein precipitation with sulfosalicylic acid. Principle. Proteins dissolve in water with formation of homogenous solutions. There are two main factors of the stabiliza ...
Enzymes - Ústav lékařské biochemie a laboratorní diagnostiky
... and perform a test for starch using Lugol solution (pre-diluted with water: 4 drops/10 ml of water). Evaluation: Indicate to the table in your lab report where the cleavage of the substrate occurred using symbols + (substrate cleaved) or − (substrate not cleaved). ...
... and perform a test for starch using Lugol solution (pre-diluted with water: 4 drops/10 ml of water). Evaluation: Indicate to the table in your lab report where the cleavage of the substrate occurred using symbols + (substrate cleaved) or − (substrate not cleaved). ...
Chapter Sixteen - Wright State University
... -COOH, and an R group, all bonded to the central carbon atom. The R group may be a hydrocarbon or it may contain a functional group. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. ...
... -COOH, and an R group, all bonded to the central carbon atom. The R group may be a hydrocarbon or it may contain a functional group. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. ...
GLYCOLYSIS
... This chart outlines the steps in the biochemical pathway called glycolysis. Glycolysis takes place in the cytoplasm of both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells GLUCOSE ...
... This chart outlines the steps in the biochemical pathway called glycolysis. Glycolysis takes place in the cytoplasm of both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells GLUCOSE ...
Received June 19, 1964.
... has apparently not been reported. Anabolism of uracil may occur either by addition of ribose from ribose-1-phosphate to produce uridine (11) or by -conversion directly to UMP upon reaction with PRPP (11, 13). Uridine was converted to UMP in the presence of ATP and a uridine kinase (11). The enzymes ...
... has apparently not been reported. Anabolism of uracil may occur either by addition of ribose from ribose-1-phosphate to produce uridine (11) or by -conversion directly to UMP upon reaction with PRPP (11, 13). Uridine was converted to UMP in the presence of ATP and a uridine kinase (11). The enzymes ...
Sequence Architecture Downstream of the
... translational efficiency, an increase in activity of the proteins due to altered N-terminal conformation, decrease in their rate of intracellular degradation, or a combination of one or more of these aspects. The different GUS constructs were examined in detail to resolve these possibilities. Substr ...
... translational efficiency, an increase in activity of the proteins due to altered N-terminal conformation, decrease in their rate of intracellular degradation, or a combination of one or more of these aspects. The different GUS constructs were examined in detail to resolve these possibilities. Substr ...
Belarus, National Final, 2008 (PDF 405K).
... e) Which solvent, water or benzene, would favor dimerization of acetic acid in solution? Give your reasoning. f) Ionization constants of most carboxylic acids in aqueous solutions are similar. Which of the two solvents, pyridine or propionic acid, would you use for titrating a mixture of HCOOH and C ...
... e) Which solvent, water or benzene, would favor dimerization of acetic acid in solution? Give your reasoning. f) Ionization constants of most carboxylic acids in aqueous solutions are similar. Which of the two solvents, pyridine or propionic acid, would you use for titrating a mixture of HCOOH and C ...
Qualifying Liquid Co-Products
... is highly palatable to livestock. Amino acid fermentation by-products result from processes designed to produce lysine and glutamic acid (or monosodium glutamate) for both animal and human food products. In these processes a high sugar substrate is inoculated with specialized microbial cultures whic ...
... is highly palatable to livestock. Amino acid fermentation by-products result from processes designed to produce lysine and glutamic acid (or monosodium glutamate) for both animal and human food products. In these processes a high sugar substrate is inoculated with specialized microbial cultures whic ...
2005 MCB 3020 Study Objectives, Part 2
... • Understand the DETAILS of DNA structure. (See study guide on slide 482.) Be able to contrast this with RNA structure. Note that the “origin” is the part of the DNA where replication starts (slide 456). You do NOT need to recognize the chemical structures. • Explain how DNA replicated (copied) in p ...
... • Understand the DETAILS of DNA structure. (See study guide on slide 482.) Be able to contrast this with RNA structure. Note that the “origin” is the part of the DNA where replication starts (slide 456). You do NOT need to recognize the chemical structures. • Explain how DNA replicated (copied) in p ...
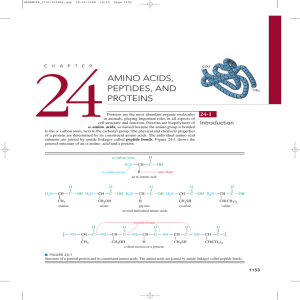
Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins
... The side chains of aspartic acid and glutamic acid contain acidic carboxyl groups. These amino acids have acidic isoelectric points around pH 3. An acidic solution is needed to prevent deprotonation of the second carboxylic acid group and to keep the amino acid in its neutral isoelectric state. Basi ...
... The side chains of aspartic acid and glutamic acid contain acidic carboxyl groups. These amino acids have acidic isoelectric points around pH 3. An acidic solution is needed to prevent deprotonation of the second carboxylic acid group and to keep the amino acid in its neutral isoelectric state. Basi ...
I. Cellular Energy • ATP: a) When the terminal phosphate is removed
... a) Aerobic Respiration: occurs in the presence of O2 & is capable of producing large quantities of ATP. Practiced by some unicellular & ALL multicellular organisms. b) Anaerobic Respiration: does not utilize oxygen, but rather some other electronegative atom or molecule to drive ATP synthesis. Is no ...
... a) Aerobic Respiration: occurs in the presence of O2 & is capable of producing large quantities of ATP. Practiced by some unicellular & ALL multicellular organisms. b) Anaerobic Respiration: does not utilize oxygen, but rather some other electronegative atom or molecule to drive ATP synthesis. Is no ...
Cloning and expression of maize-leaf pyruvate, Pi dikinase
... We then proceeded to clone the corresponding cDNA for the ZmGI TC220929 gene (GenBank Accession No. AY106855) by screening a maize leaf cDNA library with a cloned 491 bp PCR fragment complementary to sequences internal to the respective AY106855 ORF. Screening of the library with this 491 bp 32P-lab ...
... We then proceeded to clone the corresponding cDNA for the ZmGI TC220929 gene (GenBank Accession No. AY106855) by screening a maize leaf cDNA library with a cloned 491 bp PCR fragment complementary to sequences internal to the respective AY106855 ORF. Screening of the library with this 491 bp 32P-lab ...
Two conformations of a crystalline human tRNA synthetasetRNA
... complex with Trp-AMP) (Yang et al, 2003) and in the NMR structure of the isolated WHEP-TRS domain of human GluProRS (Jeong et al, 2000). Although the WHEP-TRS domain of human Glu-ProRS was reported to weakly bind tRNA (Jeong et al, 2000), the homologous N-terminal domain in human TrpRS is completely ...
... complex with Trp-AMP) (Yang et al, 2003) and in the NMR structure of the isolated WHEP-TRS domain of human GluProRS (Jeong et al, 2000). Although the WHEP-TRS domain of human Glu-ProRS was reported to weakly bind tRNA (Jeong et al, 2000), the homologous N-terminal domain in human TrpRS is completely ...
Cortrosyn® Professional Prescribing Information
... CORTROSYNTM (cosyntropin) for Injection may be administered intramuscularly or as a direct intravenous injection when used as a rapid screening test of adrenal function. It may also be given as an intravenous infusion over a 4 to 8 hour period to provide a greater stimulus to the adrenal glands. Dos ...
... CORTROSYNTM (cosyntropin) for Injection may be administered intramuscularly or as a direct intravenous injection when used as a rapid screening test of adrenal function. It may also be given as an intravenous infusion over a 4 to 8 hour period to provide a greater stimulus to the adrenal glands. Dos ...
study material class X (science)
... carbon dioxide .it is a double displacement reaction CaCO3+2HCl CaCl2 + H2O +CO2 (b) Zinc granules react with dilute hydrochloric acid to give hydrogen gas. it is a displacement reaction Zn(s)+2HCl ZnCl2(aq)+H2(g) 3. The gases hydrogen & chlorine do not react with each other even if kept togethe ...
... carbon dioxide .it is a double displacement reaction CaCO3+2HCl CaCl2 + H2O +CO2 (b) Zinc granules react with dilute hydrochloric acid to give hydrogen gas. it is a displacement reaction Zn(s)+2HCl ZnCl2(aq)+H2(g) 3. The gases hydrogen & chlorine do not react with each other even if kept togethe ...
Biosynthesis

Biosynthesis (also called biogenesis or anabolism) is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined together to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides.The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bonds, and DNA molecules, which are composed of nucleotides joined via phosphodiester bonds.