University of Groningen Fructosyltransferases of Lactobacillus
... number of monomeric residues making up a carbohydrate polymer molecule. Depending on their composition and mechanism of biosynthesis, bacterial EPSs can be divided into two classes: heteropolysaccharides and homopolysaccharides. Bacterial heteropolysaccharides Heteropolysaccharides are composed of a ...
... number of monomeric residues making up a carbohydrate polymer molecule. Depending on their composition and mechanism of biosynthesis, bacterial EPSs can be divided into two classes: heteropolysaccharides and homopolysaccharides. Bacterial heteropolysaccharides Heteropolysaccharides are composed of a ...
Cloning and Functional Characterization of a Phospholipid
... are more distantly positioned in the two Arabidopsis sequences (Fig. 2). While the second oxyanion hole residue is a Leu residue in HsLCAT as well as in most other animal LCATs, it is replaced by a Met in the aligned sequences from the two Arabidopsis proteins, ScPDAT (Fig. 2) and in the chicken LCA ...
... are more distantly positioned in the two Arabidopsis sequences (Fig. 2). While the second oxyanion hole residue is a Leu residue in HsLCAT as well as in most other animal LCATs, it is replaced by a Met in the aligned sequences from the two Arabidopsis proteins, ScPDAT (Fig. 2) and in the chicken LCA ...
fhms coshh 2010
... growth of campylobacter jejuni in minimal media with iron sources growth of campylobacter jejuni in minimal media with carbon sources staphylococcus aureus (growth and manipulation in the laboratory listeria monocytogenes (growth and manipulation in the laboratory) vibrio parahaemolyticus (growth an ...
... growth of campylobacter jejuni in minimal media with iron sources growth of campylobacter jejuni in minimal media with carbon sources staphylococcus aureus (growth and manipulation in the laboratory listeria monocytogenes (growth and manipulation in the laboratory) vibrio parahaemolyticus (growth an ...
bme-biochem-5-1-atp-adp-cycle-kh-6
... Glycogenesis: The process by which glycogen is synthesized from glucose; in which glucose molecules are added to chains of glycogen for storage. Glycogenolysis: (also known as "Glycogenlysis") is the break down of glycogen to glucose-1-phosphate and glucose for ATP production. Gluconeogenesis (abbre ...
... Glycogenesis: The process by which glycogen is synthesized from glucose; in which glucose molecules are added to chains of glycogen for storage. Glycogenolysis: (also known as "Glycogenlysis") is the break down of glycogen to glucose-1-phosphate and glucose for ATP production. Gluconeogenesis (abbre ...
Annex 1
... alphabet, it shall also be indicated in characters of the Latin alphabet either as a mere transliteration or through translation into English. The data elements, except those under numeric identifiers <110>, <120> and <160>, shall be repeated for each sequence included in the sequence listing. Only ...
... alphabet, it shall also be indicated in characters of the Latin alphabet either as a mere transliteration or through translation into English. The data elements, except those under numeric identifiers <110>, <120> and <160>, shall be repeated for each sequence included in the sequence listing. Only ...
4-Coumarate:Coenzyme A Ligase Has the Catalytic Capacity to
... both p4A and diadenosine 5⬘,5,-P1,P4-tetraphosphate synthesis. These results indicate that the cinnamoyl-adenylate intermediate synthesized by At4CL2 not only functions as an intermediate in coenzyme A ester formation but can also act as a cocatalytic AMP-donor in (di)adenosine polyphosphate synthe ...
... both p4A and diadenosine 5⬘,5,-P1,P4-tetraphosphate synthesis. These results indicate that the cinnamoyl-adenylate intermediate synthesized by At4CL2 not only functions as an intermediate in coenzyme A ester formation but can also act as a cocatalytic AMP-donor in (di)adenosine polyphosphate synthe ...
Presentation Slides - Society of Barley Engineers
... Protein: a chain made up of 20 different amino acids from a few to as many as 34,350 residues ...
... Protein: a chain made up of 20 different amino acids from a few to as many as 34,350 residues ...
glycolysis4bio
... that make a little bit of ATP from the partial breakdown of sugar into energy. • Organisms usually choose one of two paths after glycolysis: Fermentation or Aerobic Respiration. ...
... that make a little bit of ATP from the partial breakdown of sugar into energy. • Organisms usually choose one of two paths after glycolysis: Fermentation or Aerobic Respiration. ...
Relationship Between Biogenic Amines and Free Amino Acid
... as aroma compounds[1] or which have physiological significance, such as ethyl carbamate,[2–5] or which can even be related to wine authenticity.[6–8] Besides this, free amino acids are precursors of biogenic amines, other trace compounds important to human health existing in wines. These, which alth ...
... as aroma compounds[1] or which have physiological significance, such as ethyl carbamate,[2–5] or which can even be related to wine authenticity.[6–8] Besides this, free amino acids are precursors of biogenic amines, other trace compounds important to human health existing in wines. These, which alth ...
File
... activity, by PKA (itself activated through receptormediated mechanisms). PKA also phosphorylates PPI-1 leading to an inhibition of phosphate removal allowing the activated enzymes to remain so longer. Calcium ions can activate phosphorylase kinase even in the absence of the enzyme being phosphorylat ...
... activity, by PKA (itself activated through receptormediated mechanisms). PKA also phosphorylates PPI-1 leading to an inhibition of phosphate removal allowing the activated enzymes to remain so longer. Calcium ions can activate phosphorylase kinase even in the absence of the enzyme being phosphorylat ...
The Two Major Membrane Skeletal Proteins (Articulins) of Euglena
... solution of 10 mM sodium phosphate at pH 7.8 with 0.15 M NaC1 (PBS) and homogenized. An equal volume of Freund's adjuvant was added to the homogenate, and the mixture was emulsified. Female white New Zealand rabbits were injected subcutaneously at multiple sites along the back, followed by booster i ...
... solution of 10 mM sodium phosphate at pH 7.8 with 0.15 M NaC1 (PBS) and homogenized. An equal volume of Freund's adjuvant was added to the homogenate, and the mixture was emulsified. Female white New Zealand rabbits were injected subcutaneously at multiple sites along the back, followed by booster i ...
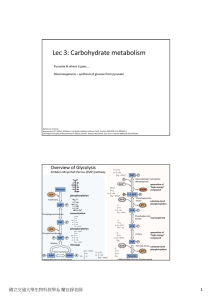
Lec 3: Carbohydrate metabolism
... formation of lactate, this reaction is reversible as cells can utilize lactate (through oxidation back into pyruvate) ...
... formation of lactate, this reaction is reversible as cells can utilize lactate (through oxidation back into pyruvate) ...
Science 11th grade LEARNING OBJECT Why are carboxylic acids
... Acetylsalicylic acid has been one of the most commonly used analgesics for thousands of years, even before Christ. Hippocrates was one of the first people to use it for soothing pain and fever. He observed that a bitter powder with analgesic properties could be obtained from the bark of the willow t ...
... Acetylsalicylic acid has been one of the most commonly used analgesics for thousands of years, even before Christ. Hippocrates was one of the first people to use it for soothing pain and fever. He observed that a bitter powder with analgesic properties could be obtained from the bark of the willow t ...
1 The hydrolysis pattern of procasomorphin by gut proteases from
... Protection of plants is a very important task and some approaches have been proposed to defend plant against insect damage such as the introduction in the plant of (a) genes encoding for proteinase inhibitors in order to affect the insect digestion process (1-3) or (b) genes encoding for neuropeptid ...
... Protection of plants is a very important task and some approaches have been proposed to defend plant against insect damage such as the introduction in the plant of (a) genes encoding for proteinase inhibitors in order to affect the insect digestion process (1-3) or (b) genes encoding for neuropeptid ...
Identification of catalytically essential amino acid residues and immobilization Rumex
... Broadening of the pH curve, shifts of pH-optimum and enhanced tolerance to unfavorable conditions are well known properties of many immobilized enzymes [7 ,2 7 ]. The fixed position of immobilized enzyme on the surface of the carrier is thought to prevent extensive distortion of the native conformat ...
... Broadening of the pH curve, shifts of pH-optimum and enhanced tolerance to unfavorable conditions are well known properties of many immobilized enzymes [7 ,2 7 ]. The fixed position of immobilized enzyme on the surface of the carrier is thought to prevent extensive distortion of the native conformat ...
Hexokinase
... – Then oxidized to DHAP by the action of glycerol phosphate dehydrogenase – NAD+ as the required coenzyme ...
... – Then oxidized to DHAP by the action of glycerol phosphate dehydrogenase – NAD+ as the required coenzyme ...
Central carbon metabolism of Saccharomyces
... cleavage pathway (GCV) which interconverts glycine into a C1 unit and CO2 [46]. Biosynthesis of proteinogenic amino acids in S. cerevisiae In order to recruit proteinogenic amino acids as probes to study central carbon metabolism [1,4], their biosynthetic pathways must be available. When applying th ...
... cleavage pathway (GCV) which interconverts glycine into a C1 unit and CO2 [46]. Biosynthesis of proteinogenic amino acids in S. cerevisiae In order to recruit proteinogenic amino acids as probes to study central carbon metabolism [1,4], their biosynthetic pathways must be available. When applying th ...
Characterization of the Plasmid-Encoded Arsenic Salts Resistance
... Both the N-terminal and C-terminal contained the glycinerich clusters, G15KGGVGKTS23 and G335KRCVGKT343, suggesting that the ArsA protein is the catalytic subunit of an arsenate-translocating ATPase [4]. The predicted ArsA protein also contained two independent domains with 32% homology, possibly du ...
... Both the N-terminal and C-terminal contained the glycinerich clusters, G15KGGVGKTS23 and G335KRCVGKT343, suggesting that the ArsA protein is the catalytic subunit of an arsenate-translocating ATPase [4]. The predicted ArsA protein also contained two independent domains with 32% homology, possibly du ...
Osmoadaptative Strategy and Its Molecular
... polyols, and lack a strong signature of halophilicity in the amino acid composition of cytoplasmic proteins. Studies to date have examined halophilic prokaryotes, yeasts, or algae, thus virtually nothing is known about the molecular adaptations of the other eukaryotic microbes, that is, heterotrophi ...
... polyols, and lack a strong signature of halophilicity in the amino acid composition of cytoplasmic proteins. Studies to date have examined halophilic prokaryotes, yeasts, or algae, thus virtually nothing is known about the molecular adaptations of the other eukaryotic microbes, that is, heterotrophi ...
Enzymes
... and new bonds will be formed. ●If reactants do not have enough energy, no reaction will take place. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall ...
... and new bonds will be formed. ●If reactants do not have enough energy, no reaction will take place. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall ...
Arginine metabolism in human infants
... 1. Protein synthesis 2. Amidino group for creatine synthesis 3. Polyamine synthesis via ornithine and agmatine 4. Synthesis of nitric oxide 5. Urea Synthesis 6. Activates N-acetyl glutamate synthase 7. Post-transational modification of proteins through methylation and citrullination ...
... 1. Protein synthesis 2. Amidino group for creatine synthesis 3. Polyamine synthesis via ornithine and agmatine 4. Synthesis of nitric oxide 5. Urea Synthesis 6. Activates N-acetyl glutamate synthase 7. Post-transational modification of proteins through methylation and citrullination ...
PDF - Biochemical Society Transactions
... Walsh, 1977). Transamination of the holoenzyme by an a-amino acid produces the corresponding imine of the a-amino acid (I). Concurrently, the aza-allylic bonds are activated to cleavage by the facility with which the protonated pyridyl ring of the pyridoxal moiety can delocalize a negative charge. T ...
... Walsh, 1977). Transamination of the holoenzyme by an a-amino acid produces the corresponding imine of the a-amino acid (I). Concurrently, the aza-allylic bonds are activated to cleavage by the facility with which the protonated pyridyl ring of the pyridoxal moiety can delocalize a negative charge. T ...
Biosynthesis

Biosynthesis (also called biogenesis or anabolism) is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined together to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides.The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bonds, and DNA molecules, which are composed of nucleotides joined via phosphodiester bonds.