Cheng BY 123 Raut – Mock Exam Unit I 09/21/14 1. Which of the
... 52. Microfilaments are well known for their role in which of the following? A) ameboid movement B) formation of cleavage furrows C) contracting of muscle cells D) A and B only E) A, B, and C 53. The cell walls of bacteria, fungi, and plant cells and the extracellular matrix of animal cells are all e ...
... 52. Microfilaments are well known for their role in which of the following? A) ameboid movement B) formation of cleavage furrows C) contracting of muscle cells D) A and B only E) A, B, and C 53. The cell walls of bacteria, fungi, and plant cells and the extracellular matrix of animal cells are all e ...
Bacterial Growth and Nutrition
... – Enzymes for metabolizing it might not be present – Chemical may be used, but more expensive – These differences are used for identification ...
... – Enzymes for metabolizing it might not be present – Chemical may be used, but more expensive – These differences are used for identification ...
ch_12 - WordPress.com
... amination, in which it reacts with α-ketoglutaric acid to from glutamic acid (amino acid). Then by transfer of amino group form one amino acid (glutamic acid) to the keto group of a keto acid, other amino acids are produced and this process is called as transamination catalysed by an enzyme transa ...
... amination, in which it reacts with α-ketoglutaric acid to from glutamic acid (amino acid). Then by transfer of amino group form one amino acid (glutamic acid) to the keto group of a keto acid, other amino acids are produced and this process is called as transamination catalysed by an enzyme transa ...
BIOL 3010
... Recinto Universitario de Mayagüez Colegio de Artes y Ciencias Departamento de Biología Programa de Biología, Pre-médica, Microbiología Industrial ...
... Recinto Universitario de Mayagüez Colegio de Artes y Ciencias Departamento de Biología Programa de Biología, Pre-médica, Microbiología Industrial ...
Homework #4: VERSION 2.1
... Don’t forget 2 – the hard copy you hand in during class should only have the last four digits of your PID # as an identifier. ...
... Don’t forget 2 – the hard copy you hand in during class should only have the last four digits of your PID # as an identifier. ...
Biochemistry I, Spring Term 2001 - Third Exam:
... C2. (15 pts) Answer ONE of the following three questions. i) In biosynthetic and degradative pathways, several steps are similar, often catalyzed by the same enzyme. Other steps are different, catalyzed by one or more different enzymes. As an example of the latter, pick one such step in either glyco ...
... C2. (15 pts) Answer ONE of the following three questions. i) In biosynthetic and degradative pathways, several steps are similar, often catalyzed by the same enzyme. Other steps are different, catalyzed by one or more different enzymes. As an example of the latter, pick one such step in either glyco ...
Lab Biochemistry File
... Introduction: As biologists, we depend on chemists for our understanding of how many chemicals play an important role in the life processes. Carbohydrates, proteins and fats are organic compounds made up of carbon, hydrogen and other elements. They are large molecules which are used by the cell for ...
... Introduction: As biologists, we depend on chemists for our understanding of how many chemicals play an important role in the life processes. Carbohydrates, proteins and fats are organic compounds made up of carbon, hydrogen and other elements. They are large molecules which are used by the cell for ...
2.4 Enzymes PPT 2.4 Enzymes
... Main energy transport molecule & source for metabolism All digested carbohydrates broken down to this for absorption in the small intestine. Only fuel used by the brain/nervous tissue ...
... Main energy transport molecule & source for metabolism All digested carbohydrates broken down to this for absorption in the small intestine. Only fuel used by the brain/nervous tissue ...
Monterey Bay Vocabulary
... Otolith-earstone found in the ear canal of fish and used for body orientation (also used for aging fish) Photosynthesis-the chemical process by which plants (algae and some bacteria) make their own food; the process uses carbon dioxide, water, nutrients, and sunlight ...
... Otolith-earstone found in the ear canal of fish and used for body orientation (also used for aging fish) Photosynthesis-the chemical process by which plants (algae and some bacteria) make their own food; the process uses carbon dioxide, water, nutrients, and sunlight ...
Cellular Respiration (CR
... eukaryotic cells (location and names of processes involved)? How many ATP’s are produced from each cell type? --------------------------------------------Define: The process of releasing energy (ATP) from food (glucose). Both consumers AND producers need to go through cellular respiration to turn th ...
... eukaryotic cells (location and names of processes involved)? How many ATP’s are produced from each cell type? --------------------------------------------Define: The process of releasing energy (ATP) from food (glucose). Both consumers AND producers need to go through cellular respiration to turn th ...
Chapter 7
... hydrogen ions from the matrix to the intermembrane space. This creates an electrochemical gradient across the inner mitochondrial membrane; with the intermembrane space having a higher concentration of hydrogen ions. Oxygen accepts the electron from the final cytochrome in the chain, and it is reduc ...
... hydrogen ions from the matrix to the intermembrane space. This creates an electrochemical gradient across the inner mitochondrial membrane; with the intermembrane space having a higher concentration of hydrogen ions. Oxygen accepts the electron from the final cytochrome in the chain, and it is reduc ...
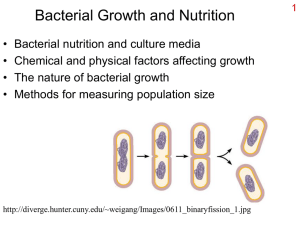
lecture notes ch27 prokaryotes
... light energy and depend on finding energy-rich organic molecules in their environment. 12) Autotrophs have the ability to acquire and use carbon from carbon dioxide (CO 2). Heterotrophs must acquire carbon from non-gaseous sources, usually organic molecules (e.g. sugars, fats and proteins). 13) Most ...
... light energy and depend on finding energy-rich organic molecules in their environment. 12) Autotrophs have the ability to acquire and use carbon from carbon dioxide (CO 2). Heterotrophs must acquire carbon from non-gaseous sources, usually organic molecules (e.g. sugars, fats and proteins). 13) Most ...
Chapter 4 - Open Yale Courses
... • There are 20 different amino acids; each with its unique chemical properties conferred by the side chain. The amino acids can be placed into broad categories: polar, nonpolar, acidic, and basic. • There are four levels of structure for proteins. The amino acid sequence is the primary structure, th ...
... • There are 20 different amino acids; each with its unique chemical properties conferred by the side chain. The amino acids can be placed into broad categories: polar, nonpolar, acidic, and basic. • There are four levels of structure for proteins. The amino acid sequence is the primary structure, th ...
History of Fermentation Processes and Their Fundamental
... The function of metabolism is to ensure the life of the organism ...
... The function of metabolism is to ensure the life of the organism ...
Complete Protein - Kelloggs Nutrition
... Proteins, along with carbohydrates and fats, make up the bulk of our diet. We tend to think of proteins as body builders, and they are;; they form the structure of things like muscle, hair and connective tissue. They also make up hormones that regulate our system, enzymes that trigger chemical react ...
... Proteins, along with carbohydrates and fats, make up the bulk of our diet. We tend to think of proteins as body builders, and they are;; they form the structure of things like muscle, hair and connective tissue. They also make up hormones that regulate our system, enzymes that trigger chemical react ...
Study Guide for Chapter 3
... * take notes and make drawings in your notebook 3. Meet the following objectives: *Write them all out in your spiral bound science notebook Describe and draw the structure of a water molecule Explain how water’s polarity affects it’s ability to dissolve substances List 2 of water’s properties ...
... * take notes and make drawings in your notebook 3. Meet the following objectives: *Write them all out in your spiral bound science notebook Describe and draw the structure of a water molecule Explain how water’s polarity affects it’s ability to dissolve substances List 2 of water’s properties ...
Cellular Respiration
... What happens with respiration of lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids? Starch: broken down into glucose, which enters glycolysis Fats: broken down into fatty acids and glycerol; fatty acids are cut into 2-carbon compounds, converted to Acetyl-CoA, and enter the Krebs Cycle Proteins: broken down into ...
... What happens with respiration of lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids? Starch: broken down into glucose, which enters glycolysis Fats: broken down into fatty acids and glycerol; fatty acids are cut into 2-carbon compounds, converted to Acetyl-CoA, and enter the Krebs Cycle Proteins: broken down into ...
Balancing Reactions 1
... 5. Write balanced formula unit equations for the following redox reactions: a. Aluminum reacts with sulfuric acid, H2SO4, to produce aluminum sulfate and hydrogen. b. Nitrogen reacts with hydrogen to form ammonia, NH3 c. Zinc sulfide, ZnS, reacts with oxygen to from zinc oxide and sulfur dioxide ...
... 5. Write balanced formula unit equations for the following redox reactions: a. Aluminum reacts with sulfuric acid, H2SO4, to produce aluminum sulfate and hydrogen. b. Nitrogen reacts with hydrogen to form ammonia, NH3 c. Zinc sulfide, ZnS, reacts with oxygen to from zinc oxide and sulfur dioxide ...
Krebs cycle
... 6.12 Chemiosmosis powers ATP production • The electrons from NADH and FADH2 travel down the electron transport chain to oxygen • Energy released by the electrons is used to pump H+ ions into the space between the mitochondrial membranes • In chemiosmosis, the H+ ions diffuse back through the inner m ...
... 6.12 Chemiosmosis powers ATP production • The electrons from NADH and FADH2 travel down the electron transport chain to oxygen • Energy released by the electrons is used to pump H+ ions into the space between the mitochondrial membranes • In chemiosmosis, the H+ ions diffuse back through the inner m ...
terminal end
... Components of the important nucleotide, adenosine triphosphate (ATP) The energy of hydrolysis of a phosphoanhydride bond (shown as squiggles) is greater than that of a phosphate ester and will have significance in Chapter 5 (Section 5.8) [Brock, 10th ed.] ...
... Components of the important nucleotide, adenosine triphosphate (ATP) The energy of hydrolysis of a phosphoanhydride bond (shown as squiggles) is greater than that of a phosphate ester and will have significance in Chapter 5 (Section 5.8) [Brock, 10th ed.] ...
Metabolism

Metabolism (from Greek: μεταβολή metabolē, ""change"") is the set of life-sustaining chemical transformations within the cells of living organisms. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. The word metabolism can also refer to all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transport of substances into and between different cells, in which case the set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary metabolism or intermediate metabolism.Metabolism is usually divided into two categories: catabolism, the breaking down of organic matter by way of cellular respiration, and anabolism, the building up of components of cells such as proteins and nucleic acids. Usually, breaking down releases energy and building up consumes energy.The chemical reactions of metabolism are organized into metabolic pathways, in which one chemical is transformed through a series of steps into another chemical, by a sequence of enzymes. Enzymes are crucial to metabolism because they allow organisms to drive desirable reactions that require energy that will not occur by themselves, by coupling them to spontaneous reactions that release energy. Enzymes act as catalysts that allow the reactions to proceed more rapidly. Enzymes also allow the regulation of metabolic pathways in response to changes in the cell's environment or to signals from other cells.The metabolic system of a particular organism determines which substances it will find nutritious and which poisonous. For example, some prokaryotes use hydrogen sulfide as a nutrient, yet this gas is poisonous to animals. The speed of metabolism, the metabolic rate, influences how much food an organism will require, and also affects how it is able to obtain that food.A striking feature of metabolism is the similarity of the basic metabolic pathways and components between even vastly different species. For example, the set of carboxylic acids that are best known as the intermediates in the citric acid cycle are present in all known organisms, being found in species as diverse as the unicellular bacterium Escherichia coli and huge multicellular organisms like elephants. These striking similarities in metabolic pathways are likely due to their early appearance in evolutionary history, and their retention because of their efficacy.