Fermentation and Cellular Respiration
... organic compounds as their source of energy. Organic compounds carry potential energy in the covalent bonds holding their atoms together. When these bonds are broken, the energy released can be used to make ATP through phosphorylation reactions. Chemoheterotrophs can use either substrate level or ox ...
... organic compounds as their source of energy. Organic compounds carry potential energy in the covalent bonds holding their atoms together. When these bonds are broken, the energy released can be used to make ATP through phosphorylation reactions. Chemoheterotrophs can use either substrate level or ox ...
PHOTOSYNTHESIS
... So, plants make the food energy (glucose) in the chloroplasts. When they need to break down their own glucose to make ATP, they use another organelle, the Mitochondria. ...
... So, plants make the food energy (glucose) in the chloroplasts. When they need to break down their own glucose to make ATP, they use another organelle, the Mitochondria. ...
A little less conjugation, a little more accuracy
... Proteins can fold into an incredibly diverse range of structures despite being made from only a limited number of building blocks — the twenty-or-so proteinogenic amino acids. The modular nature of proteins has enabled their evolution into separate species that perform a variety of biological roles; ...
... Proteins can fold into an incredibly diverse range of structures despite being made from only a limited number of building blocks — the twenty-or-so proteinogenic amino acids. The modular nature of proteins has enabled their evolution into separate species that perform a variety of biological roles; ...
THE NORMAL METABOLISM OF PHENYLALANINE (pathways a
... A strictly controlled phenylalanine low diet must be followed for life. No protein rich foods (e.g. meat, eggs, pulses). No aspartame sweetner. As phenylalanine is itself an essential amino acid small doses must be supplied. Other nutrients may need supplementing. Frequency 1 in 10 000 in Caucasians ...
... A strictly controlled phenylalanine low diet must be followed for life. No protein rich foods (e.g. meat, eggs, pulses). No aspartame sweetner. As phenylalanine is itself an essential amino acid small doses must be supplied. Other nutrients may need supplementing. Frequency 1 in 10 000 in Caucasians ...
Week 5 - UW Canvas
... b. transfers electrons directly to oxygen. c. is an electron carrier. d. is produced during the Krebs cycle. 5. The oxidation of glucose to CO2 and H2O… a. is exergonic. b. takes place entirely in the mitochondria. c. requires the electron transport chain. d. generates a pH gradient across the inner ...
... b. transfers electrons directly to oxygen. c. is an electron carrier. d. is produced during the Krebs cycle. 5. The oxidation of glucose to CO2 and H2O… a. is exergonic. b. takes place entirely in the mitochondria. c. requires the electron transport chain. d. generates a pH gradient across the inner ...
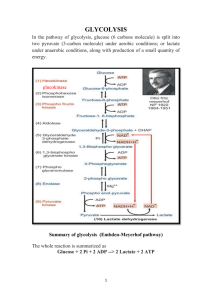
Summary of glycolysis (Embden
... possible, Therefore, the cell has to couple some other reaction in which NAD+ is regenerated in the cytoplasm itself hence, pyruvate is reduced to lactate; the NAD+ thus generated is reutilized for uninterrupted operation of the pathway. But when oxygen is in plenty, the two NADH molecules, generate ...
... possible, Therefore, the cell has to couple some other reaction in which NAD+ is regenerated in the cytoplasm itself hence, pyruvate is reduced to lactate; the NAD+ thus generated is reutilized for uninterrupted operation of the pathway. But when oxygen is in plenty, the two NADH molecules, generate ...
AEROBIC CELLULAR RESPIRATION
... State the products in glycolysis. 1. Does glycolysis require oxygen? 2. Where does glycolysis occur in the cell? Glycolysis animation Activity 12: Look at this animation and answer the following questions: 1. What is the net gain of ATP per glucose? KREB CYCLE (also called the Citric Acid Cycle, the ...
... State the products in glycolysis. 1. Does glycolysis require oxygen? 2. Where does glycolysis occur in the cell? Glycolysis animation Activity 12: Look at this animation and answer the following questions: 1. What is the net gain of ATP per glucose? KREB CYCLE (also called the Citric Acid Cycle, the ...
Chapter 17 Section 2 Earth’s Early History
... different from conditions today -Explain what Miller and Urey’s experiments showed -State the hypotheses that have been proposed for how life first arose on Earth -Identify some of the main evolutionary steps in the early evolution of life ...
... different from conditions today -Explain what Miller and Urey’s experiments showed -State the hypotheses that have been proposed for how life first arose on Earth -Identify some of the main evolutionary steps in the early evolution of life ...
Name: Cell Energy Exam Study Guide Study the following
... 9. Identify 3 factors that can affect the rate of photosynthesis, and explain how the rate of photosynthesis changes as each of these factors is increased. CO2 concentration: as it is increased, rate of photosynthesis increases until it eventually levels off. Light intensity: as it is increased, rat ...
... 9. Identify 3 factors that can affect the rate of photosynthesis, and explain how the rate of photosynthesis changes as each of these factors is increased. CO2 concentration: as it is increased, rate of photosynthesis increases until it eventually levels off. Light intensity: as it is increased, rat ...
glucose, faKy acids, amino acids
... removal or addiDon of a phosphate group (kinases are enzymes that add phosphate groups ...
... removal or addiDon of a phosphate group (kinases are enzymes that add phosphate groups ...
Microbial Metabolism- Energy and Enzymes
... Key issue: how can cells achieve essential reactions with a positive G´? Examples: Nutrient uptake DNA replication Amino acid biosynthesis CO2 fixation Flagellar motion ATP synthesis ...
... Key issue: how can cells achieve essential reactions with a positive G´? Examples: Nutrient uptake DNA replication Amino acid biosynthesis CO2 fixation Flagellar motion ATP synthesis ...
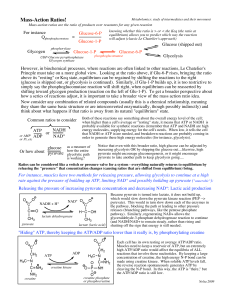
Mass-Action Ratios!
... above its "resting" or Keq state, equilibrium can be regained by shifting the reactions to the right (glucose is shipped out, or glycolysis is continued). Similarly, if Glu-1-P builds up, it is too restrictive to simply say the phosphoglucomutase reaction will shift right, when equilibrium can be re ...
... above its "resting" or Keq state, equilibrium can be regained by shifting the reactions to the right (glucose is shipped out, or glycolysis is continued). Similarly, if Glu-1-P builds up, it is too restrictive to simply say the phosphoglucomutase reaction will shift right, when equilibrium can be re ...
Amino Acid/Protein Structure
... Honors Anatomy and Physiology Amino Acids and Proteins THE AMINO ACID http://www.vivo.colostate.edu/hbooks/genetics/biotech/basics/prostruct.html ...
... Honors Anatomy and Physiology Amino Acids and Proteins THE AMINO ACID http://www.vivo.colostate.edu/hbooks/genetics/biotech/basics/prostruct.html ...
Uncommon amino acids, amino acids forming proteins
... An example of where a small change can have a huge effect is in the protein of the blood, hemoglobin. A change in one amino acid can cause the disease sickle ...
... An example of where a small change can have a huge effect is in the protein of the blood, hemoglobin. A change in one amino acid can cause the disease sickle ...
Life, 6th Edition
... Macromolecules are formed by covalent bonds between monomers and include polysaccharides, proteins, and nucleic acids. Lipids are crucial biomolecules, but are not considered ‘macromolecules’ ...
... Macromolecules are formed by covalent bonds between monomers and include polysaccharides, proteins, and nucleic acids. Lipids are crucial biomolecules, but are not considered ‘macromolecules’ ...
Chapter 7 Cellular Respiration
... – Organic compounds are converted into carbon molecules of pyruvic acid, which makes a small amount of ATP and NADH (electron carrier) – Anaerobic process = does not require oxygen – Occurs outside of the mitochondria ...
... – Organic compounds are converted into carbon molecules of pyruvic acid, which makes a small amount of ATP and NADH (electron carrier) – Anaerobic process = does not require oxygen – Occurs outside of the mitochondria ...
UNIT 1 - OCCC.edu
... A functional protein consists of one or more polypeptides precisely twisted, folded, and coiled into a unique shape The sequence of amino acids determines a protein’s ______________________ structure A protein’s ______________________ determines its ________________________ ...
... A functional protein consists of one or more polypeptides precisely twisted, folded, and coiled into a unique shape The sequence of amino acids determines a protein’s ______________________ structure A protein’s ______________________ determines its ________________________ ...
Proteins Hwk KEY
... Structural component of connective tissue and bone Reversibly binds oxygen so it can be delivered to the tissues from the lungs; found inside red blood cells Also known as antibodies, these proteins bind to and inactivate antigens (molecules on germs) Hormone secreted by the pancreas that promotes t ...
... Structural component of connective tissue and bone Reversibly binds oxygen so it can be delivered to the tissues from the lungs; found inside red blood cells Also known as antibodies, these proteins bind to and inactivate antigens (molecules on germs) Hormone secreted by the pancreas that promotes t ...
Class Starter
... Enzymes • Each enzyme has an active site, the region where the reaction takes place. • The shape of the active site determines which reactants, or substrates, will bind to it. Each different enzyme acts only on specific substrates. • Binding of the substrates causes the enzyme’s shape to change. Thi ...
... Enzymes • Each enzyme has an active site, the region where the reaction takes place. • The shape of the active site determines which reactants, or substrates, will bind to it. Each different enzyme acts only on specific substrates. • Binding of the substrates causes the enzyme’s shape to change. Thi ...
chapter 5 the structure and function of macromolecules
... 2. An immense variety of polymers can be built from a small set of monomers • Each cell has thousands of different macromolecules. – These molecules vary among cells of the same individual, even more among unrelated individuals of a species, and are even greater between species. • This diversity co ...
... 2. An immense variety of polymers can be built from a small set of monomers • Each cell has thousands of different macromolecules. – These molecules vary among cells of the same individual, even more among unrelated individuals of a species, and are even greater between species. • This diversity co ...
PhotosynthesisCalving CycleON
... Environmental factors affects the rate of photosynthesis. 1. Light intensity- At first an increase in the light intensity results in a corresponding increase in the rate of photosynthesis as the photosystems are activated. As the photosystems become saturated, an increase in light intensity will no ...
... Environmental factors affects the rate of photosynthesis. 1. Light intensity- At first an increase in the light intensity results in a corresponding increase in the rate of photosynthesis as the photosystems are activated. As the photosystems become saturated, an increase in light intensity will no ...
Anaerobic Respiration
... 2. Ethyl Alcohol + CO2 Alcoholic Fermentation (Bacteria, Yeasts) 3. Acetic Acid (vinegar) + CO2 (Bacteria) ...
... 2. Ethyl Alcohol + CO2 Alcoholic Fermentation (Bacteria, Yeasts) 3. Acetic Acid (vinegar) + CO2 (Bacteria) ...
Name
... Write the letter that best answers the question or completes the statement on the line provided. _____ 1. Which of the following is NOT a true statement about ATP? a. ATP consists of ribose, adenine, and three phosphate groups. b. ADP is produced when ATP releases energy. c. ATP provides energy for ...
... Write the letter that best answers the question or completes the statement on the line provided. _____ 1. Which of the following is NOT a true statement about ATP? a. ATP consists of ribose, adenine, and three phosphate groups. b. ADP is produced when ATP releases energy. c. ATP provides energy for ...
Metabolism

Metabolism (from Greek: μεταβολή metabolē, ""change"") is the set of life-sustaining chemical transformations within the cells of living organisms. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. The word metabolism can also refer to all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transport of substances into and between different cells, in which case the set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary metabolism or intermediate metabolism.Metabolism is usually divided into two categories: catabolism, the breaking down of organic matter by way of cellular respiration, and anabolism, the building up of components of cells such as proteins and nucleic acids. Usually, breaking down releases energy and building up consumes energy.The chemical reactions of metabolism are organized into metabolic pathways, in which one chemical is transformed through a series of steps into another chemical, by a sequence of enzymes. Enzymes are crucial to metabolism because they allow organisms to drive desirable reactions that require energy that will not occur by themselves, by coupling them to spontaneous reactions that release energy. Enzymes act as catalysts that allow the reactions to proceed more rapidly. Enzymes also allow the regulation of metabolic pathways in response to changes in the cell's environment or to signals from other cells.The metabolic system of a particular organism determines which substances it will find nutritious and which poisonous. For example, some prokaryotes use hydrogen sulfide as a nutrient, yet this gas is poisonous to animals. The speed of metabolism, the metabolic rate, influences how much food an organism will require, and also affects how it is able to obtain that food.A striking feature of metabolism is the similarity of the basic metabolic pathways and components between even vastly different species. For example, the set of carboxylic acids that are best known as the intermediates in the citric acid cycle are present in all known organisms, being found in species as diverse as the unicellular bacterium Escherichia coli and huge multicellular organisms like elephants. These striking similarities in metabolic pathways are likely due to their early appearance in evolutionary history, and their retention because of their efficacy.