Describe and discuss the process of chemiosmosis in eukaryotic
... C. The absence of O2 is problematic to the process of cellular respiration. Describe how a muscle cell may attempt to compensate during strenuous exercise. (3 pt maximum) __glycolysis may continue ...
... C. The absence of O2 is problematic to the process of cellular respiration. Describe how a muscle cell may attempt to compensate during strenuous exercise. (3 pt maximum) __glycolysis may continue ...
The Molecules of Life Biochem! - Belle Vernon Area School District
... R group (thus the amino acids) are classified according to several criteria (two very important) Polar or nonpolar nature of the side chain Presence of an acidic or basic group in the side chain ...
... R group (thus the amino acids) are classified according to several criteria (two very important) Polar or nonpolar nature of the side chain Presence of an acidic or basic group in the side chain ...
What minerals in trident gum make your mouth clean?
... Artificial flavorings so you do not know which one is actually in the product (Some can be VERY bad for you) ...
... Artificial flavorings so you do not know which one is actually in the product (Some can be VERY bad for you) ...
Practice Exam #2.1 - Montana State University Billings
... 78. Which of the following is an example of diffusion? A. Movement of a protein into a cell against its concentration gradient B. Movement of oxygen from the tissue fluid into a respiring cell C. Movement of carbon dioxide from a respiring cell into the tissue fluid D. A and B E. B and C 79. Water e ...
... 78. Which of the following is an example of diffusion? A. Movement of a protein into a cell against its concentration gradient B. Movement of oxygen from the tissue fluid into a respiring cell C. Movement of carbon dioxide from a respiring cell into the tissue fluid D. A and B E. B and C 79. Water e ...
Introductory Chemistry: Concepts & Connections 4th Edition
... • There are 30 elements which are essential for life. • The study of the chemistry of living things is biochemistry. • Biological compounds are often large and complex with molar masses greater than 1,000,000 g/mol. • These large molecules are polymers of smaller molecules. Chapter 20 ...
... • There are 30 elements which are essential for life. • The study of the chemistry of living things is biochemistry. • Biological compounds are often large and complex with molar masses greater than 1,000,000 g/mol. • These large molecules are polymers of smaller molecules. Chapter 20 ...
Document
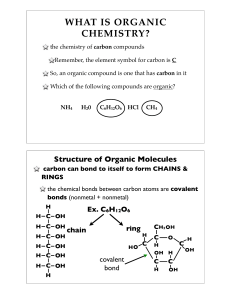
... WHAT IS BIOCHEMISTRY? the chemistry of LIFE Remember, the elements found in all living things include Carbon, Hydrogen, Nitrogen, Oxygen, Phosphorus, and Sulfur (CHNOPS) Thus, biochemistry involves carbon compounds. ...
... WHAT IS BIOCHEMISTRY? the chemistry of LIFE Remember, the elements found in all living things include Carbon, Hydrogen, Nitrogen, Oxygen, Phosphorus, and Sulfur (CHNOPS) Thus, biochemistry involves carbon compounds. ...
Whoops! Wrong Calvin…
... Remember what it means to be a plant… Need to produce all organic molecules necessary for growth carbohydrates, lipids proteins, nucleic acids ...
... Remember what it means to be a plant… Need to produce all organic molecules necessary for growth carbohydrates, lipids proteins, nucleic acids ...
CHAPTER 4: CELLULAR METABOLISM
... Introduction: 1. CR is how animal cells use oxygen to release chemical energy from food to generate cellular energy (ATP). 2. The chemical reactions in CR must occur in a particular sequence, with each reaction being catalyzed by a different (specific) enzyme. There are three major series of reactio ...
... Introduction: 1. CR is how animal cells use oxygen to release chemical energy from food to generate cellular energy (ATP). 2. The chemical reactions in CR must occur in a particular sequence, with each reaction being catalyzed by a different (specific) enzyme. There are three major series of reactio ...
Amino Acids Worksheet and Problem Set
... What does the R group determine for an amino acid and why is it important? Which are the aliphatic amino acids? (Group 1) Which are the Group 2 amino acids and why? Which are the Group 3 amino acids and why? Which are the Group 4 amino acids and why? Chapter 3.3: Draw the normal structure of a gener ...
... What does the R group determine for an amino acid and why is it important? Which are the aliphatic amino acids? (Group 1) Which are the Group 2 amino acids and why? Which are the Group 3 amino acids and why? Which are the Group 4 amino acids and why? Chapter 3.3: Draw the normal structure of a gener ...
22. Think of two different proteins: both are enzymes. a) What
... b) In what conditions, and why, do cells do fermentation? For anaerobic organisms, which do not use molecular oxygen and can grow and divide without it, glycolysis is the principal source of the cell's ATP. So, fermentations allow ATP to be produced in the absence of oxygen. Fermentation is done to ...
... b) In what conditions, and why, do cells do fermentation? For anaerobic organisms, which do not use molecular oxygen and can grow and divide without it, glycolysis is the principal source of the cell's ATP. So, fermentations allow ATP to be produced in the absence of oxygen. Fermentation is done to ...
Biology 20 Lecture Quiz #3 – Take Home Cellular Respiration
... Cellular Respiration – DUE 23 June 2010 at 7:50 AM – I do not want any late quizzes! 1. The main function of cellular respiration is _____. a) breaking down toxic molecules; b) making ATP to power cell activities; c) making food; d) producing cell structures from chemical building blocks; e) breakin ...
... Cellular Respiration – DUE 23 June 2010 at 7:50 AM – I do not want any late quizzes! 1. The main function of cellular respiration is _____. a) breaking down toxic molecules; b) making ATP to power cell activities; c) making food; d) producing cell structures from chemical building blocks; e) breakin ...
Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry 5/e
... 3. Synthesis and transport to another organ (TAGs) (excess sugar in liver fatty acids) Many hibernating animals, such as grizzly bears rely almost exclusively on fats as their source of energy ...
... 3. Synthesis and transport to another organ (TAGs) (excess sugar in liver fatty acids) Many hibernating animals, such as grizzly bears rely almost exclusively on fats as their source of energy ...
Part Two – Lecture I
... stranded DNA occurs, the hydrogen bonds open, the duplex unwinds, and the strand separate No covalent bonds break so that the ...
... stranded DNA occurs, the hydrogen bonds open, the duplex unwinds, and the strand separate No covalent bonds break so that the ...
PHY3072 - MUSCLE AND EXERCISE LECTURE 2: Introduction to
... Example: Glucose phosphorylation to glucose-6-phosphate Muscle and brain: hexokinase Km = 20-120uM. Phosphorylates glucose even when blood glucose is low. Important in brain which relies solely on glucose Liver: glucokinase Km=5mM. Responds when blood glucose elevated (i.e. after meal) to minimise h ...
... Example: Glucose phosphorylation to glucose-6-phosphate Muscle and brain: hexokinase Km = 20-120uM. Phosphorylates glucose even when blood glucose is low. Important in brain which relies solely on glucose Liver: glucokinase Km=5mM. Responds when blood glucose elevated (i.e. after meal) to minimise h ...
Cell Respiration - Glycolysis PPT
... 2.F.1 Glycolysis rearranges the bonds in glucose molecules, releasing free energy to form ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate, and resulting in the production of pyruvate. ...
... 2.F.1 Glycolysis rearranges the bonds in glucose molecules, releasing free energy to form ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate, and resulting in the production of pyruvate. ...
Cellular Respiration
... • Oxygen is required – Aerobic Respiration • A series of chemical rxns… a cycle – Pyruvic Acid is further broken down: • into Acetyl CoA • CO2 is produced and • released into the air from animal cells • Or in plants move to the chloroplasts to be used for photosynthesis ...
... • Oxygen is required – Aerobic Respiration • A series of chemical rxns… a cycle – Pyruvic Acid is further broken down: • into Acetyl CoA • CO2 is produced and • released into the air from animal cells • Or in plants move to the chloroplasts to be used for photosynthesis ...
U4L26 Nitrogen - The University of Sydney
... Defects in Processing • Both in urea cycle and skeleton breakdown – See textbook for full table (18-2) ...
... Defects in Processing • Both in urea cycle and skeleton breakdown – See textbook for full table (18-2) ...
Metabolism

Metabolism (from Greek: μεταβολή metabolē, ""change"") is the set of life-sustaining chemical transformations within the cells of living organisms. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. The word metabolism can also refer to all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transport of substances into and between different cells, in which case the set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary metabolism or intermediate metabolism.Metabolism is usually divided into two categories: catabolism, the breaking down of organic matter by way of cellular respiration, and anabolism, the building up of components of cells such as proteins and nucleic acids. Usually, breaking down releases energy and building up consumes energy.The chemical reactions of metabolism are organized into metabolic pathways, in which one chemical is transformed through a series of steps into another chemical, by a sequence of enzymes. Enzymes are crucial to metabolism because they allow organisms to drive desirable reactions that require energy that will not occur by themselves, by coupling them to spontaneous reactions that release energy. Enzymes act as catalysts that allow the reactions to proceed more rapidly. Enzymes also allow the regulation of metabolic pathways in response to changes in the cell's environment or to signals from other cells.The metabolic system of a particular organism determines which substances it will find nutritious and which poisonous. For example, some prokaryotes use hydrogen sulfide as a nutrient, yet this gas is poisonous to animals. The speed of metabolism, the metabolic rate, influences how much food an organism will require, and also affects how it is able to obtain that food.A striking feature of metabolism is the similarity of the basic metabolic pathways and components between even vastly different species. For example, the set of carboxylic acids that are best known as the intermediates in the citric acid cycle are present in all known organisms, being found in species as diverse as the unicellular bacterium Escherichia coli and huge multicellular organisms like elephants. These striking similarities in metabolic pathways are likely due to their early appearance in evolutionary history, and their retention because of their efficacy.