ppt10 - Plant Agriculture
... Different C-C combinations can join together to help form the backbone of amino acids (along with N, S, etc.) and all the other molecules of the cell. How can energy be derived from the 3C molecules? 3C is broken down to 2C, which enters the mitochondrion. There, the C-C bonds are broken to create 2 ...
... Different C-C combinations can join together to help form the backbone of amino acids (along with N, S, etc.) and all the other molecules of the cell. How can energy be derived from the 3C molecules? 3C is broken down to 2C, which enters the mitochondrion. There, the C-C bonds are broken to create 2 ...
Enzymes - Westgate Mennonite Collegiate
... - high temps may denature (unfold) the enzyme. 2. pH (most like 6 - 8 pH near neutral) 3. Ionic concentration (salt ions) ...
... - high temps may denature (unfold) the enzyme. 2. pH (most like 6 - 8 pH near neutral) 3. Ionic concentration (salt ions) ...
Anabolism
... The high-energy electrons still contain most of the chemical energy of the original glucose molecule. Special carrier molecules bring the high-energy electrons to a series of enzymes that convert much of the remaining energy to more ATP molecules. The other products are heat and water. The function ...
... The high-energy electrons still contain most of the chemical energy of the original glucose molecule. Special carrier molecules bring the high-energy electrons to a series of enzymes that convert much of the remaining energy to more ATP molecules. The other products are heat and water. The function ...
fermentation & evolution
... • Muscle cells switch from aerobic respiration to lactic acid fermentation to generate ATP when O2 is scarce. • The waste product, lactate, may cause muscle fatigue, but ultimately it is converted back to pyruvate in the liver. Fig. 9.17b Copyright © 2002 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benja ...
... • Muscle cells switch from aerobic respiration to lactic acid fermentation to generate ATP when O2 is scarce. • The waste product, lactate, may cause muscle fatigue, but ultimately it is converted back to pyruvate in the liver. Fig. 9.17b Copyright © 2002 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benja ...
Enzymes - Westgate Mennonite Collegiate
... - high temps may denature (unfold) the enzyme. 2. pH (most like 6 - 8 pH near neutral) 3. Ionic concentration (salt ions) ...
... - high temps may denature (unfold) the enzyme. 2. pH (most like 6 - 8 pH near neutral) 3. Ionic concentration (salt ions) ...
Human Services Lifetime Nutrition and Wellness Multiple Choice Science Assessment Questions
... nutritive value of various foods (B) assess the effects of nutritional intake on health, appearance, effective job performance and personal life (C) analyze and apply various dietary guidelines throughout the life cycle, including pregnancy, infancy, childhood and late adulthood (D) compare personal ...
... nutritive value of various foods (B) assess the effects of nutritional intake on health, appearance, effective job performance and personal life (C) analyze and apply various dietary guidelines throughout the life cycle, including pregnancy, infancy, childhood and late adulthood (D) compare personal ...
Patient Handout
... Injections can be administered up to twice a week. B12 is purported by its users and practitioners to help speed up the overall metabolic processes and create a greater feeling of overall energy. Because lipotropics directly aid fat breakdown and are closely related to B vitamins, when used together ...
... Injections can be administered up to twice a week. B12 is purported by its users and practitioners to help speed up the overall metabolic processes and create a greater feeling of overall energy. Because lipotropics directly aid fat breakdown and are closely related to B vitamins, when used together ...
CSM 101 Fall 2010 Timeline
... the enzyme’s shape and activity. Once activated, the enzyme can trigger the next step leading to a cellular response. Binding of signaling molecules is reversible. The activating changes in the GPCR, as well as the changes in the G protein and enzyme, are only temporary; these molecules soon become ...
... the enzyme’s shape and activity. Once activated, the enzyme can trigger the next step leading to a cellular response. Binding of signaling molecules is reversible. The activating changes in the GPCR, as well as the changes in the G protein and enzyme, are only temporary; these molecules soon become ...
Unit 2.1.3a
... o What is a catalyst? (We will look at how some work later) A catalyst is a substance that speeds up the rate of a reaction (by lowering the activation energy) but it remains unchanged at the end of the reaction. Without catalysts, 37˚C would be too slow to sustain life. We will look at how differen ...
... o What is a catalyst? (We will look at how some work later) A catalyst is a substance that speeds up the rate of a reaction (by lowering the activation energy) but it remains unchanged at the end of the reaction. Without catalysts, 37˚C would be too slow to sustain life. We will look at how differen ...
Lipid Biosynthesis - Chemistry Courses: About: Department
... Are those which are required for cell survival. Are required for synthesis of cholesterol. Must be acquired by diet because they contain an odd number of carbon atoms. Cannot be synthesized by humans because we lack enzymes necessary to make them. ...
... Are those which are required for cell survival. Are required for synthesis of cholesterol. Must be acquired by diet because they contain an odd number of carbon atoms. Cannot be synthesized by humans because we lack enzymes necessary to make them. ...
Chapter 12 Powerpoint
... The 3 billion base pairs in each human cell provide the blueprint for producing a human being. The specific sequence of base pairing is important in conveying the mechanism of how genetic information is expressed. The expression is seen through proteins. Through directing the synthesis of proteins, ...
... The 3 billion base pairs in each human cell provide the blueprint for producing a human being. The specific sequence of base pairing is important in conveying the mechanism of how genetic information is expressed. The expression is seen through proteins. Through directing the synthesis of proteins, ...
More Exam Practice - Iowa State University
... their stomata to take in CO2 during the day, they would also lose too much water. This way, they can keep their stomata partially closed during the day and use CO2 that is concentrated in bundle-sheath cells to generate sugar. 3. How is energy conserved in an ecosystem? Discuss the role of photosynt ...
... their stomata to take in CO2 during the day, they would also lose too much water. This way, they can keep their stomata partially closed during the day and use CO2 that is concentrated in bundle-sheath cells to generate sugar. 3. How is energy conserved in an ecosystem? Discuss the role of photosynt ...
ADP, ATP and Cellular Respiration Powerpoint
... Animals, some fungi pyruvate lactic acid 3C NADH ...
... Animals, some fungi pyruvate lactic acid 3C NADH ...
Pathology Ketone bodies are created at moderate
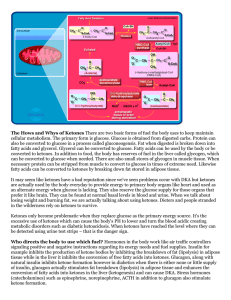
... The Hows and Whys of Ketones There are two basic forms of fuel the body uses to keep maintain cellular metabolism. The primary form is glucose. Glucose is obtained from digested carbs. Protein can also be converted to glucose in a process called gluconeogensis. Fat when digested is broken down into ...
... The Hows and Whys of Ketones There are two basic forms of fuel the body uses to keep maintain cellular metabolism. The primary form is glucose. Glucose is obtained from digested carbs. Protein can also be converted to glucose in a process called gluconeogensis. Fat when digested is broken down into ...
b-oxidation - mustafaaltinisik.org.uk
... • Acyl-CoAs are converted to acyl-carnitines by carnitine acyltransferase. • A translocator then imports Acyl carnitine into the matrix while simultaneously exporting free carnitine to the cytosol • Acyl-carnitine is then converted back to acylCoA in the matrix ...
... • Acyl-CoAs are converted to acyl-carnitines by carnitine acyltransferase. • A translocator then imports Acyl carnitine into the matrix while simultaneously exporting free carnitine to the cytosol • Acyl-carnitine is then converted back to acylCoA in the matrix ...
Introduction to Biotechnology
... Processes −E.g Fermentation Whereas, fermentation, uses an endogenous (from within the cells) electron acceptor usually ...
... Processes −E.g Fermentation Whereas, fermentation, uses an endogenous (from within the cells) electron acceptor usually ...
Organic Molecules Organic molecules are the molecules which exist
... 3. All of the organic molecules are based on which element? 4. Many times, the molecules join to form long chains with what kind of backbone? 5. How are the building blocks of organic molecules like bricks? 6. What is the building block of each of the four classes of organic molecules? 7. What is a ...
... 3. All of the organic molecules are based on which element? 4. Many times, the molecules join to form long chains with what kind of backbone? 5. How are the building blocks of organic molecules like bricks? 6. What is the building block of each of the four classes of organic molecules? 7. What is a ...
Cellular Respiration Packet
... I. Breathing versus Cellular Respiration • _____________________________: physical process that allows animals and humans to come into contact with gases in the air. • _____________________________: chemical process that releases energy from organic compounds (food), gradually converting it into ene ...
... I. Breathing versus Cellular Respiration • _____________________________: physical process that allows animals and humans to come into contact with gases in the air. • _____________________________: chemical process that releases energy from organic compounds (food), gradually converting it into ene ...
TRANSLATION NOTES - Randolph High School
... Definition of Translation The decoding of mRNA’s message into a protein Happens in the ribosome Also known as Protein Synthesis, which is when proteins are made by stringing amino acids together to form long chains (20+ types of amino acids in humans) ...
... Definition of Translation The decoding of mRNA’s message into a protein Happens in the ribosome Also known as Protein Synthesis, which is when proteins are made by stringing amino acids together to form long chains (20+ types of amino acids in humans) ...
how cells release chemical energy
... produce (number) molecules of ATP. [p.llS] 14. The total net harvest of ATP, involving all stages of aerobic respiration, is _ _ _ _ __ =--:-::___ (number) molecules of ATP. [p.llS] 15. Be able to summarize the biochemistry of alcoholic fermentation and lactate fermentation and tell what types of or ...
... produce (number) molecules of ATP. [p.llS] 14. The total net harvest of ATP, involving all stages of aerobic respiration, is _ _ _ _ __ =--:-::___ (number) molecules of ATP. [p.llS] 15. Be able to summarize the biochemistry of alcoholic fermentation and lactate fermentation and tell what types of or ...
Review Sheet Exam 1 C483 Spring 2014
... hierarchy of protein structure (primary-secondary-tertiary-quaternary). Understand basic motifs of protein structure and the forces that govern them. Be familiar with supersecondary structures. Be conversant with the various methods of depicting protein structures. Understand domains and the assembl ...
... hierarchy of protein structure (primary-secondary-tertiary-quaternary). Understand basic motifs of protein structure and the forces that govern them. Be familiar with supersecondary structures. Be conversant with the various methods of depicting protein structures. Understand domains and the assembl ...
Cellular Respiration
... Occurs in mitochondria; uses the high energy electrons captured in the Krebs Cycle (in NADH and FADH2) to form ATP and water. ...
... Occurs in mitochondria; uses the high energy electrons captured in the Krebs Cycle (in NADH and FADH2) to form ATP and water. ...
Gluconeogenesis - Assignment Point
... cycle can also be used for gluconeogenesis. Amino acids, after their amino group has been removed, feed into parts of the citric acid cycle, and can thus can generate glucose in this pathway. • Fatty acids cannot be turned into glucose, as they are broken down into the two carbon acetyl CoA. (Howeve ...
... cycle can also be used for gluconeogenesis. Amino acids, after their amino group has been removed, feed into parts of the citric acid cycle, and can thus can generate glucose in this pathway. • Fatty acids cannot be turned into glucose, as they are broken down into the two carbon acetyl CoA. (Howeve ...
Metabolism

Metabolism (from Greek: μεταβολή metabolē, ""change"") is the set of life-sustaining chemical transformations within the cells of living organisms. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. The word metabolism can also refer to all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transport of substances into and between different cells, in which case the set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary metabolism or intermediate metabolism.Metabolism is usually divided into two categories: catabolism, the breaking down of organic matter by way of cellular respiration, and anabolism, the building up of components of cells such as proteins and nucleic acids. Usually, breaking down releases energy and building up consumes energy.The chemical reactions of metabolism are organized into metabolic pathways, in which one chemical is transformed through a series of steps into another chemical, by a sequence of enzymes. Enzymes are crucial to metabolism because they allow organisms to drive desirable reactions that require energy that will not occur by themselves, by coupling them to spontaneous reactions that release energy. Enzymes act as catalysts that allow the reactions to proceed more rapidly. Enzymes also allow the regulation of metabolic pathways in response to changes in the cell's environment or to signals from other cells.The metabolic system of a particular organism determines which substances it will find nutritious and which poisonous. For example, some prokaryotes use hydrogen sulfide as a nutrient, yet this gas is poisonous to animals. The speed of metabolism, the metabolic rate, influences how much food an organism will require, and also affects how it is able to obtain that food.A striking feature of metabolism is the similarity of the basic metabolic pathways and components between even vastly different species. For example, the set of carboxylic acids that are best known as the intermediates in the citric acid cycle are present in all known organisms, being found in species as diverse as the unicellular bacterium Escherichia coli and huge multicellular organisms like elephants. These striking similarities in metabolic pathways are likely due to their early appearance in evolutionary history, and their retention because of their efficacy.