Worked solutions: Chapter 2 Human biochemistry
... The rate of reaction reaches a peak around 400C because this is just a little higher than the usual temperature of the body. The rate falls off rapidly above 420C because the high temperature denatures the enzyme and it is no longer able to function. The rate also falls off rapidly at temperatures b ...
... The rate of reaction reaches a peak around 400C because this is just a little higher than the usual temperature of the body. The rate falls off rapidly above 420C because the high temperature denatures the enzyme and it is no longer able to function. The rate also falls off rapidly at temperatures b ...
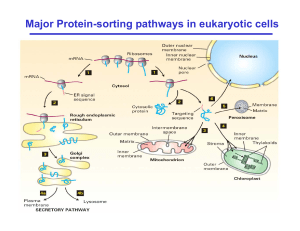
Major Protein-sorting pathways in eukaryotic cells
... Major topological classes of integral membrane proteins synthesized on the rough ER ...
... Major topological classes of integral membrane proteins synthesized on the rough ER ...
Name - wvhs.wlwv.k12.or.us
... 7) What is the energy content of ATP relative to that of glucose? 8) What produces the “high energy” nature of ATP? 9) What happens when a molecule becomes phosphorylated? 10) What are the three stages of cellular respiration? ...
... 7) What is the energy content of ATP relative to that of glucose? 8) What produces the “high energy” nature of ATP? 9) What happens when a molecule becomes phosphorylated? 10) What are the three stages of cellular respiration? ...
MMG 301, Lecture 19 Fermentation
... and simple chemical tests (e.g., VogesProskauer assay, pH indicators). ...
... and simple chemical tests (e.g., VogesProskauer assay, pH indicators). ...
Electron Transport Chain
... (including plant and animal cells) have mitochondria _______________ for cellular respiration Prokaryotes All __________________ (bacteria) have their electron transport enzymes attached to their Cell membranes _____________________ ...
... (including plant and animal cells) have mitochondria _______________ for cellular respiration Prokaryotes All __________________ (bacteria) have their electron transport enzymes attached to their Cell membranes _____________________ ...
MULTIPLE CHOICE
... what are they, where do they occur, what are their reactants and products 5. Main products of the LDR? (i,e. Photosystems II, photosystem I, electron transport system Where are they, what happens in each (i.e. reactants and products) Role of photons, electrons and water, what does pumping H+ across ...
... what are they, where do they occur, what are their reactants and products 5. Main products of the LDR? (i,e. Photosystems II, photosystem I, electron transport system Where are they, what happens in each (i.e. reactants and products) Role of photons, electrons and water, what does pumping H+ across ...
A1982NC82400001
... Tissue cell cultures grew in free gas ex- HeLa cell line, revealed that the essential change with the atmosphere when the bicar- amino acids could be incorporated in media bonate buffer was replaced by the free base at much higher concentrations and that he amino acids, especially L-arginine. Glycol ...
... Tissue cell cultures grew in free gas ex- HeLa cell line, revealed that the essential change with the atmosphere when the bicar- amino acids could be incorporated in media bonate buffer was replaced by the free base at much higher concentrations and that he amino acids, especially L-arginine. Glycol ...
CARBOHYDRATES B.SC Ist SEMESTER INTRODUCTION TO
... •CONVERSION TO FAT : Excess of calories fed in diet in the form of carbohydrate is stored as fat in adipose tissue. When the body is in need of energy it can be realized from the adipose tissue. •PROMOTES GROWTH OF DESIRABLE BACTERIA : Lactose has several functions in the gastrointestinal tract. It ...
... •CONVERSION TO FAT : Excess of calories fed in diet in the form of carbohydrate is stored as fat in adipose tissue. When the body is in need of energy it can be realized from the adipose tissue. •PROMOTES GROWTH OF DESIRABLE BACTERIA : Lactose has several functions in the gastrointestinal tract. It ...
ascendant cerebral 5-hydroxytryptamine
... slice preparations. The metabolic effects in vivo, like those of barbiturates, can be attributed to the general damping down ofelectrical activity, thus diminishing ionic fluxes induced by action potentials and by the release of excitatory transmitters. However, a direct effect of the inhibitory ami ...
... slice preparations. The metabolic effects in vivo, like those of barbiturates, can be attributed to the general damping down ofelectrical activity, thus diminishing ionic fluxes induced by action potentials and by the release of excitatory transmitters. However, a direct effect of the inhibitory ami ...
Lecture 33 - Carbohydrate Metabolism 1
... • The most important function of the pentose phosphate pathway is to reduce two molecules of NADP+ to NADPH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate) for each glucose-6-phosphate that is oxidatively decarboxylated to ribulose-5-phosphate. • NADPH is functionally similar to NAD+ however, NADPH is ...
... • The most important function of the pentose phosphate pathway is to reduce two molecules of NADP+ to NADPH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate) for each glucose-6-phosphate that is oxidatively decarboxylated to ribulose-5-phosphate. • NADPH is functionally similar to NAD+ however, NADPH is ...
Respiration - Northwest ISD Moodle
... 1 Which type of energy does food contain? 2 What is this energy converted to by other organisms? Give at least 3 examples. (i) (ii) (iii) 3 What name is given to the process by which organisms release energy? 4 What kind of energy is always released in respiration? ...
... 1 Which type of energy does food contain? 2 What is this energy converted to by other organisms? Give at least 3 examples. (i) (ii) (iii) 3 What name is given to the process by which organisms release energy? 4 What kind of energy is always released in respiration? ...
Table of Contents
... Antitrypanosomal effects of polyamine biosynthesis inhibitors correlate with increases in Trypanosoma brucei brucei S-adenosyl-Lmethionine Modulation of the activity of acetyl-CoA carboxylase and other lipogenic enzymes by growth hormone, insulin and dexamethasone in sheep adipose tissue and relatio ...
... Antitrypanosomal effects of polyamine biosynthesis inhibitors correlate with increases in Trypanosoma brucei brucei S-adenosyl-Lmethionine Modulation of the activity of acetyl-CoA carboxylase and other lipogenic enzymes by growth hormone, insulin and dexamethasone in sheep adipose tissue and relatio ...
Food Processing and Utilization
... pancreas that catalyze the catabolism of carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. Nutrient absorption then occurs in the small intestine, primarily in the jejunum, and the nutrients enter the bloodstream. Indigestible materials and wastes enter the large intestine, where water is reabsorb ...
... pancreas that catalyze the catabolism of carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. Nutrient absorption then occurs in the small intestine, primarily in the jejunum, and the nutrients enter the bloodstream. Indigestible materials and wastes enter the large intestine, where water is reabsorb ...
Instructor`s Copy Lab Worksheet
... Horse and pigeon – both have 12 differences compared to humans 6. Is it possible that the two organisms you listed in question 7 are equally related to humans but not equally related to each other (HINT: are you sure that the amino acid differences in each organism’s cytochrome-c are the same)? EXPL ...
... Horse and pigeon – both have 12 differences compared to humans 6. Is it possible that the two organisms you listed in question 7 are equally related to humans but not equally related to each other (HINT: are you sure that the amino acid differences in each organism’s cytochrome-c are the same)? EXPL ...
CHAPTER 9
... 2. Photosystems I and II are embedded in the internal membranes of chloroplasts (thylakoids) and are connected by the transfer of higher free energy electrons through an electron transport chain (ETC). [See also 4.A.2] 3. When electrons are transferred between molecules in a sequence of reactions as ...
... 2. Photosystems I and II are embedded in the internal membranes of chloroplasts (thylakoids) and are connected by the transfer of higher free energy electrons through an electron transport chain (ETC). [See also 4.A.2] 3. When electrons are transferred between molecules in a sequence of reactions as ...
Exercise 3 key
... amino group transfer from alanine to ketoglutarate to form Glutamate and pyruvate. YOl.ftext on pg 721 shows the mechanism for stage I of this reaction; the transformation of the amino acid to the keto acid (we also did this in lecture). ...
... amino group transfer from alanine to ketoglutarate to form Glutamate and pyruvate. YOl.ftext on pg 721 shows the mechanism for stage I of this reaction; the transformation of the amino acid to the keto acid (we also did this in lecture). ...
Amino Acid Metabolism
... and leucine yielding CO2, and acyl-CoA derivatives. • Shares ancestry with pyruvate dehydrogenase complex, -KG dehydrogenase complex – another example of gene duplication ...
... and leucine yielding CO2, and acyl-CoA derivatives. • Shares ancestry with pyruvate dehydrogenase complex, -KG dehydrogenase complex – another example of gene duplication ...
No Slide Title - Palm Beach State College
... hazards of ionizing radiation. – Distinguish between ions, electrolytes, and free radials. – Define the types of chemical bonds. ...
... hazards of ionizing radiation. – Distinguish between ions, electrolytes, and free radials. – Define the types of chemical bonds. ...
LECT02 thermo
... “A spontaneous reaction is one that favors movement from order to disorder…occurs with a positive change in entropy” “To go from disorder back to order requires input of energy” Take Home: Living system take chemicals from their disordered environment and assemble them into ordered ...
... “A spontaneous reaction is one that favors movement from order to disorder…occurs with a positive change in entropy” “To go from disorder back to order requires input of energy” Take Home: Living system take chemicals from their disordered environment and assemble them into ordered ...
complete
... Glycogen synthase – active when dephosphorylated, inactive when phosphorylated; insulin vs. glucagon ...
... Glycogen synthase – active when dephosphorylated, inactive when phosphorylated; insulin vs. glucagon ...
Cellular-Respiration Student
... One CO2 is removed from each pyruvate released as a waste product Remaining 2-carbon portions are oxidized by NAD+ ...
... One CO2 is removed from each pyruvate released as a waste product Remaining 2-carbon portions are oxidized by NAD+ ...
Metabolism

Metabolism (from Greek: μεταβολή metabolē, ""change"") is the set of life-sustaining chemical transformations within the cells of living organisms. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. The word metabolism can also refer to all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transport of substances into and between different cells, in which case the set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary metabolism or intermediate metabolism.Metabolism is usually divided into two categories: catabolism, the breaking down of organic matter by way of cellular respiration, and anabolism, the building up of components of cells such as proteins and nucleic acids. Usually, breaking down releases energy and building up consumes energy.The chemical reactions of metabolism are organized into metabolic pathways, in which one chemical is transformed through a series of steps into another chemical, by a sequence of enzymes. Enzymes are crucial to metabolism because they allow organisms to drive desirable reactions that require energy that will not occur by themselves, by coupling them to spontaneous reactions that release energy. Enzymes act as catalysts that allow the reactions to proceed more rapidly. Enzymes also allow the regulation of metabolic pathways in response to changes in the cell's environment or to signals from other cells.The metabolic system of a particular organism determines which substances it will find nutritious and which poisonous. For example, some prokaryotes use hydrogen sulfide as a nutrient, yet this gas is poisonous to animals. The speed of metabolism, the metabolic rate, influences how much food an organism will require, and also affects how it is able to obtain that food.A striking feature of metabolism is the similarity of the basic metabolic pathways and components between even vastly different species. For example, the set of carboxylic acids that are best known as the intermediates in the citric acid cycle are present in all known organisms, being found in species as diverse as the unicellular bacterium Escherichia coli and huge multicellular organisms like elephants. These striking similarities in metabolic pathways are likely due to their early appearance in evolutionary history, and their retention because of their efficacy.