Handout
... All matter will exist in one of three different states depending on the environmental conditions: 1.) solid – has a definite shape and volume. 2.) liquid – has a definite volume but takes the shape of its container. 3.) gas – has no definite shape or volume and can be compressed (both shape and volu ...
... All matter will exist in one of three different states depending on the environmental conditions: 1.) solid – has a definite shape and volume. 2.) liquid – has a definite volume but takes the shape of its container. 3.) gas – has no definite shape or volume and can be compressed (both shape and volu ...
Protein Synthesis Notes
... (the “chefs”) to send these recipes to the ribosomes (“kitchen”) so they can be made. 1. The basic unit of a protein is an amino acid a. we use 20 amino acids to make all of our proteins 2. A chain of amino acids together is a protein 3. Types of proteins include: hormones, enzymes, structural prote ...
... (the “chefs”) to send these recipes to the ribosomes (“kitchen”) so they can be made. 1. The basic unit of a protein is an amino acid a. we use 20 amino acids to make all of our proteins 2. A chain of amino acids together is a protein 3. Types of proteins include: hormones, enzymes, structural prote ...
Lab 1 activity, AMINO ACIDS - Cal State LA
... Planar peptide groups in a protein • Rotation around C-N bond is restricted due to 40% double-bond nature of the resonance hybrid form • Peptide groups (blue planes) are therefore planar; restrict conformations possible in protein chains ...
... Planar peptide groups in a protein • Rotation around C-N bond is restricted due to 40% double-bond nature of the resonance hybrid form • Peptide groups (blue planes) are therefore planar; restrict conformations possible in protein chains ...
Organisms are highly organized, and other
... You think they’re eating… They’re harvesting energy! ...
... You think they’re eating… They’re harvesting energy! ...
BIOL103 Review Questions for Midterm 2 SP16
... 8. Why is high fructose corn syrup associated with weight gain? 9. What is HFCS90 made up of? 10. Describe in detail how soluble fiber and insoluble fiber help lower risks for cardiovascular disease, obes ...
... 8. Why is high fructose corn syrup associated with weight gain? 9. What is HFCS90 made up of? 10. Describe in detail how soluble fiber and insoluble fiber help lower risks for cardiovascular disease, obes ...
3.2 Metabolism of cardiac muscle cell
... The latter participates in contraction as a regulatory protein. During diastole, the troponin-tropomyosin complex is firmly bound on actin and thus inhibits chemical interaction between actin and myosin. The surface of troponin contains a receptor which is able to bind calcium. Providing this site is ...
... The latter participates in contraction as a regulatory protein. During diastole, the troponin-tropomyosin complex is firmly bound on actin and thus inhibits chemical interaction between actin and myosin. The surface of troponin contains a receptor which is able to bind calcium. Providing this site is ...
5.2 Molecular Models for Fungi Growing: Digestion and
... Digest STARCH molecules by cutting the starch into individual glucose monomers. Notice that after you cut the starch apart there are bonds without atoms. Cut up water molecules to tape an –H and –OH to every glucose. ...
... Digest STARCH molecules by cutting the starch into individual glucose monomers. Notice that after you cut the starch apart there are bonds without atoms. Cut up water molecules to tape an –H and –OH to every glucose. ...
Bio Chem webquest
... 11. Describe how glycolysis and photosynthesis are related. 12. Why do you need to build molecules? 13. What is ATP? Click on 14. What IS a carbohydrate? 15. What is the function of a carbohydrate? 16. What is a monosaccharide? 17. What is a disaccharide? 18. What is a polysaccharide? 19. What is gl ...
... 11. Describe how glycolysis and photosynthesis are related. 12. Why do you need to build molecules? 13. What is ATP? Click on 14. What IS a carbohydrate? 15. What is the function of a carbohydrate? 16. What is a monosaccharide? 17. What is a disaccharide? 18. What is a polysaccharide? 19. What is gl ...
Text S1.
... peroxidase (GPX), and catalase (CAT) (Table S11). The CCMP1779 genome has genes likely encoding SOD and GPX that might participate in enzymatic ROS scavenging pathways. Thus, CCMP1779 likely shares basic stress responses with flowering plants. ...
... peroxidase (GPX), and catalase (CAT) (Table S11). The CCMP1779 genome has genes likely encoding SOD and GPX that might participate in enzymatic ROS scavenging pathways. Thus, CCMP1779 likely shares basic stress responses with flowering plants. ...
Cell Biology
... o If oxygen available, pyruvate fed into TCA cycle where it generates some ATP and more NADH(H+) and FADH2 are used to generate ATP by oxidative phosphorylation and chemiosmotic coupling via ETS. Oxidized to carbon dioxide. o If there is no oxygen available or cannot be used another way to regenerat ...
... o If oxygen available, pyruvate fed into TCA cycle where it generates some ATP and more NADH(H+) and FADH2 are used to generate ATP by oxidative phosphorylation and chemiosmotic coupling via ETS. Oxidized to carbon dioxide. o If there is no oxygen available or cannot be used another way to regenerat ...
6.1 ATOMS, ELEMENTS, and COMPOUNDS
... __________________ -- the substance that is dissolved in the solvent. (Ex: Sugar) In a heterogeneous mixture, the components remain distinct. a. In a __________________, the components will eventually settle to the bottom. b. In a __________________, the particles will not settle over time. Examples ...
... __________________ -- the substance that is dissolved in the solvent. (Ex: Sugar) In a heterogeneous mixture, the components remain distinct. a. In a __________________, the components will eventually settle to the bottom. b. In a __________________, the particles will not settle over time. Examples ...
Sample pages 1 PDF
... although the former is located within the membrane while the latter is found in the intermembrane space. The double-electron NAD dehydrogenase initiator changes to a conduit for univalent electron carriers (iron-sulfur proteins, cytochromes) and a four-electron channel in the last phase of oxygen re ...
... although the former is located within the membrane while the latter is found in the intermembrane space. The double-electron NAD dehydrogenase initiator changes to a conduit for univalent electron carriers (iron-sulfur proteins, cytochromes) and a four-electron channel in the last phase of oxygen re ...
Oxidative Phosphorylation
... Oxidative Phosphorylation • H+ transport results in an electrochemical gradient • Proton motive force: energy released by flow of H+ down its gradient is used for ATP synthesis • ATP synthase: H+ channel that couples energy from H+ flow with ATP synthesis ...
... Oxidative Phosphorylation • H+ transport results in an electrochemical gradient • Proton motive force: energy released by flow of H+ down its gradient is used for ATP synthesis • ATP synthase: H+ channel that couples energy from H+ flow with ATP synthesis ...
Lecture 8 - People Server at UNCW
... • Respiratory centers in the brain • Peripheral input to respirator centers ...
... • Respiratory centers in the brain • Peripheral input to respirator centers ...
Citric Acid Cycle - University of California, Berkeley
... electrons to an electron carrier, NAD+, via a tightly bound intermediary electron carrier, FAD. Dihydroxylipoyllysine + NAD+ Lipoyllysine + NADH FAD. The flavin group is the business end of FAD; it is not linked to ribose, but to ribitol—a reduced product of ribose. Then, it is linked to a pyropho ...
... electrons to an electron carrier, NAD+, via a tightly bound intermediary electron carrier, FAD. Dihydroxylipoyllysine + NAD+ Lipoyllysine + NADH FAD. The flavin group is the business end of FAD; it is not linked to ribose, but to ribitol—a reduced product of ribose. Then, it is linked to a pyropho ...
Chapter 9: Fermentation
... bacteria is used to make cheese and yogurt. •Muscle cells switch from aerobic respiration to lactic acid fermentation to generate ATP when O2 is scarce. •The waste product, lactate, may cause muscle fatigue, but ultimately it is converted back to pyruvate in the liver. ...
... bacteria is used to make cheese and yogurt. •Muscle cells switch from aerobic respiration to lactic acid fermentation to generate ATP when O2 is scarce. •The waste product, lactate, may cause muscle fatigue, but ultimately it is converted back to pyruvate in the liver. ...
Class XIX Tissues and organ systems I – Epithelial tissues To Grow
... 2. We learned how glucose and Na++ are absorbed by the intestinal epithelial cell. How are aminoacids, nucleotides, fats and other ions absorbed? 3. What is “transcytosis”? 4. Other than parietal cells, the epithelium of the stomach contains at least 4 other epithelial cells. What are these and what ...
... 2. We learned how glucose and Na++ are absorbed by the intestinal epithelial cell. How are aminoacids, nucleotides, fats and other ions absorbed? 3. What is “transcytosis”? 4. Other than parietal cells, the epithelium of the stomach contains at least 4 other epithelial cells. What are these and what ...
Pattern Matching: Organic Molecules
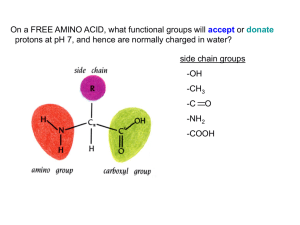
... Redraw the chain of amino acids linked in a chain as shown above. Title your drawing. Highlight the atoms of the backbone. Put a box around each individual amino acid (hint: there are 5). Each amino acid has a different side group that is represented by "R" in the generalized structure. The “R” grou ...
... Redraw the chain of amino acids linked in a chain as shown above. Title your drawing. Highlight the atoms of the backbone. Put a box around each individual amino acid (hint: there are 5). Each amino acid has a different side group that is represented by "R" in the generalized structure. The “R” grou ...
HERE - No Brain Too Small
... Stages of respiration include Glycolysis, where Glucose is broken down, the Krebs Cycle where CO2 is produced / hydrogen is produced and the electron transport chain where Hydrogen is used to make ATP. The purpose of respiration is to release energy from food. Energy is needed for metabolism, growth ...
... Stages of respiration include Glycolysis, where Glucose is broken down, the Krebs Cycle where CO2 is produced / hydrogen is produced and the electron transport chain where Hydrogen is used to make ATP. The purpose of respiration is to release energy from food. Energy is needed for metabolism, growth ...
Pattern Matching: Organic Molecules
... Redraw the chain of amino acids linked in a chain as shown above. Title your drawing. Highlight the atoms of the backbone. Put a box around each individual amino acid (hint: there are 5). Each amino acid has a different side group that is represented by "R" in the generalized structure. The “R” grou ...
... Redraw the chain of amino acids linked in a chain as shown above. Title your drawing. Highlight the atoms of the backbone. Put a box around each individual amino acid (hint: there are 5). Each amino acid has a different side group that is represented by "R" in the generalized structure. The “R” grou ...
Chemistry, Photosynthesis, Respiration Review
... B—glucose C--light reaction D and E—Chrorophyll and chloroplast F—Electrons from water G—Energy transfer H--Chemiosmosis I—NADPH J—ATP K—Calvin Cycle L—made into PGA M—RuBp N—Glucose ...
... B—glucose C--light reaction D and E—Chrorophyll and chloroplast F—Electrons from water G—Energy transfer H--Chemiosmosis I—NADPH J—ATP K—Calvin Cycle L—made into PGA M—RuBp N—Glucose ...
Chapter 6 – How Cells Harvest Chemical Energy Standard 1.g
... 1. The movement of electrons along an electron transport chain creates a proton gradient across the inner membrane. The protons diffuse back across the membrane through ATP synthase releasing energy that is used to make ATP by 2. ATP can also be made by transferring phosphate groups from organic mol ...
... 1. The movement of electrons along an electron transport chain creates a proton gradient across the inner membrane. The protons diffuse back across the membrane through ATP synthase releasing energy that is used to make ATP by 2. ATP can also be made by transferring phosphate groups from organic mol ...
File
... Esters are organic “salts” formed from the reaction of a carboxylic acid and an alcohol. Consequently, the name of an ester has two parts. The first part is the name of the alkyl group from the alcohol used in the esterification reaction. The second part comes from the acid. The ending of the acid n ...
... Esters are organic “salts” formed from the reaction of a carboxylic acid and an alcohol. Consequently, the name of an ester has two parts. The first part is the name of the alkyl group from the alcohol used in the esterification reaction. The second part comes from the acid. The ending of the acid n ...
2nd Nine Weeks Exam Review Unit 5
... During DNA replication, a complementary strand of DNA is made for each original DNA strand. If a portion of the original strand is TCAGAA, then the new strand that bonds with it would be… A. UCGGAA C. ACGGTT B. AGTCTT D. AGCCUU Genetic information usually flows in one specific direction. Which of th ...
... During DNA replication, a complementary strand of DNA is made for each original DNA strand. If a portion of the original strand is TCAGAA, then the new strand that bonds with it would be… A. UCGGAA C. ACGGTT B. AGTCTT D. AGCCUU Genetic information usually flows in one specific direction. Which of th ...
Metabolism

Metabolism (from Greek: μεταβολή metabolē, ""change"") is the set of life-sustaining chemical transformations within the cells of living organisms. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. The word metabolism can also refer to all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transport of substances into and between different cells, in which case the set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary metabolism or intermediate metabolism.Metabolism is usually divided into two categories: catabolism, the breaking down of organic matter by way of cellular respiration, and anabolism, the building up of components of cells such as proteins and nucleic acids. Usually, breaking down releases energy and building up consumes energy.The chemical reactions of metabolism are organized into metabolic pathways, in which one chemical is transformed through a series of steps into another chemical, by a sequence of enzymes. Enzymes are crucial to metabolism because they allow organisms to drive desirable reactions that require energy that will not occur by themselves, by coupling them to spontaneous reactions that release energy. Enzymes act as catalysts that allow the reactions to proceed more rapidly. Enzymes also allow the regulation of metabolic pathways in response to changes in the cell's environment or to signals from other cells.The metabolic system of a particular organism determines which substances it will find nutritious and which poisonous. For example, some prokaryotes use hydrogen sulfide as a nutrient, yet this gas is poisonous to animals. The speed of metabolism, the metabolic rate, influences how much food an organism will require, and also affects how it is able to obtain that food.A striking feature of metabolism is the similarity of the basic metabolic pathways and components between even vastly different species. For example, the set of carboxylic acids that are best known as the intermediates in the citric acid cycle are present in all known organisms, being found in species as diverse as the unicellular bacterium Escherichia coli and huge multicellular organisms like elephants. These striking similarities in metabolic pathways are likely due to their early appearance in evolutionary history, and their retention because of their efficacy.