Model Description Sheet
... (PROG) to form 17-OH pregnenolone (17-OH PREG) and 17-OH progesterone (17-OH PROG), respectively. Most interestingly, it can further process the 17-OH PREG by catalyzing the cleavage of the carbon 17, 20 bond as a next step, which is the first committed step in androgen biosynthesis. While the enzym ...
... (PROG) to form 17-OH pregnenolone (17-OH PREG) and 17-OH progesterone (17-OH PROG), respectively. Most interestingly, it can further process the 17-OH PREG by catalyzing the cleavage of the carbon 17, 20 bond as a next step, which is the first committed step in androgen biosynthesis. While the enzym ...
09_Lectures_PPT
... connect to many other metabolic pathways • Gycolysis and the citric acid cycle are major intersections to various catabolic and anabolic pathways ...
... connect to many other metabolic pathways • Gycolysis and the citric acid cycle are major intersections to various catabolic and anabolic pathways ...
Protein Structure
... each peptide carbonyl group is H-bonded to a peptide amino group 4 amino acids later in the chain (amino acids n and n + 4 are linked). The polypeptide backbone lies in the core of the helix. The amino acid side chains project to the outside and coat its surface. Because the side chains project to t ...
... each peptide carbonyl group is H-bonded to a peptide amino group 4 amino acids later in the chain (amino acids n and n + 4 are linked). The polypeptide backbone lies in the core of the helix. The amino acid side chains project to the outside and coat its surface. Because the side chains project to t ...
Print - Circulation Research
... Interactions of the malate-aspartate cycle, the glycolytic pathway, and the citric acid cycle which allow indirect oxidation of cytosolic NADH, rapid alteration of citric acid cycle intermediate levels, and fine coordination of cytosolic and mitochondrial energy metabolism. The malate-a-ketoglutarat ...
... Interactions of the malate-aspartate cycle, the glycolytic pathway, and the citric acid cycle which allow indirect oxidation of cytosolic NADH, rapid alteration of citric acid cycle intermediate levels, and fine coordination of cytosolic and mitochondrial energy metabolism. The malate-a-ketoglutarat ...
astrochemistry_caselli
... The molecule AB* must loose the internal energy. In the Earth atmosphere, where the number of particles per cubic centimeter (cc) is very large (~1019), the molecule looses its energy via three-body reactions: ...
... The molecule AB* must loose the internal energy. In the Earth atmosphere, where the number of particles per cubic centimeter (cc) is very large (~1019), the molecule looses its energy via three-body reactions: ...
Cell Respiration
... Proteins are utilized by deaminating their amino acids, and then metabolizing the product. • Fats are utilized by beta-oxidation. ...
... Proteins are utilized by deaminating their amino acids, and then metabolizing the product. • Fats are utilized by beta-oxidation. ...
PROTEIN
... acids Amino acids bind to each other to form protein Amino acids bound --> peptide bound Protein Nitrogen (PN) Non Protein Nitrogen (NPN) ...
... acids Amino acids bind to each other to form protein Amino acids bound --> peptide bound Protein Nitrogen (PN) Non Protein Nitrogen (NPN) ...
Metabolism - Diet & Nutrition Lecture PowerPoint
... • The SPO Virtual Classrooms offer many educational resources, including practice test questions, review questions, lecture PowerPoints, video tutorials, sample assignments and course syllabi. New materials are continually being developed, so check back frequently, or follow us on Facebook (Science ...
... • The SPO Virtual Classrooms offer many educational resources, including practice test questions, review questions, lecture PowerPoints, video tutorials, sample assignments and course syllabi. New materials are continually being developed, so check back frequently, or follow us on Facebook (Science ...
Lesson 4.Protein
... are listed in Enzyme Nomenclature, the standard reference volume on enzyme classification. Enzymes are catalysts that accelerate the rates of biological reactions. Each enzyme is very specific in its function and acts only in a particular metabolic reaction. Virtually every step in metabolism is cat ...
... are listed in Enzyme Nomenclature, the standard reference volume on enzyme classification. Enzymes are catalysts that accelerate the rates of biological reactions. Each enzyme is very specific in its function and acts only in a particular metabolic reaction. Virtually every step in metabolism is cat ...
Lactic Acid : Brief History
... cycle (TCA cycle), or the Krebs cycle, is a series of chemical reactions used by all aerobic organisms to generate energy through the oxidation ...
... cycle (TCA cycle), or the Krebs cycle, is a series of chemical reactions used by all aerobic organisms to generate energy through the oxidation ...
biochemistry - Textbooks Online
... water, water tends to flow from the latter to the former. The property of the movement of solvent particles is called as osmosis. Osmosis is the net diffusion of water from the dilute solution to the concentrated solution. Osmosis is a colligative property of solution that depends on the number of m ...
... water, water tends to flow from the latter to the former. The property of the movement of solvent particles is called as osmosis. Osmosis is the net diffusion of water from the dilute solution to the concentrated solution. Osmosis is a colligative property of solution that depends on the number of m ...
Anaerobic Respiration
... • During periods of vigorous exercise, an animal may not be able to provide enough oxygen to the muscles. The muscles will continue to work using ATP from the anerobic breakdown of glucose to pyruvate. • Lactic acid accumulates in the muscles and soon fatigue sets in. Lactic acid accumulation can ca ...
... • During periods of vigorous exercise, an animal may not be able to provide enough oxygen to the muscles. The muscles will continue to work using ATP from the anerobic breakdown of glucose to pyruvate. • Lactic acid accumulates in the muscles and soon fatigue sets in. Lactic acid accumulation can ca ...
Chapter 20. Proteins
... whole human body contains about 100,000 different proteins. Proteins are the backbone of enzymes, certain hormones, an some blood components and tissues. Proteins are the most abundant substances in nearly all cells accounting for about 15% of a cell's overall mass. Proteins contain the elements car ...
... whole human body contains about 100,000 different proteins. Proteins are the backbone of enzymes, certain hormones, an some blood components and tissues. Proteins are the most abundant substances in nearly all cells accounting for about 15% of a cell's overall mass. Proteins contain the elements car ...
Citrate Cycle Supplemental Reading Key Concepts
... What role does NADH and FADH2 have in connecting the citrate cycle to ATP synthesis? Why is the citrate cycle considered the hub of metabolism? Biochemical Applications of the Citrate Cycle: Fluoroacetate is found in poisonous plants and it is the active ingredient in "compound 1080" which is used b ...
... What role does NADH and FADH2 have in connecting the citrate cycle to ATP synthesis? Why is the citrate cycle considered the hub of metabolism? Biochemical Applications of the Citrate Cycle: Fluoroacetate is found in poisonous plants and it is the active ingredient in "compound 1080" which is used b ...
Resume - TILT - Colorado State University
... generated a library of molecules based on the 4-alkoxydiphenylmethanones which contain tertiary, secondary amines and hydrazines. Regioselective alkylations of the hydrazine derivatives are achieved by using the (2,6-dichloro-4-methoxyphenyl)(2,4dichlorophenyl)methoxycarboxyl resin. Heterocycles 200 ...
... generated a library of molecules based on the 4-alkoxydiphenylmethanones which contain tertiary, secondary amines and hydrazines. Regioselective alkylations of the hydrazine derivatives are achieved by using the (2,6-dichloro-4-methoxyphenyl)(2,4dichlorophenyl)methoxycarboxyl resin. Heterocycles 200 ...
University of Lincoln RIF Studentships 2014 PROJECT DETAILS
... arising from the long-term use of antibiotics. In a clinical setting these strains proliferate under antibacterial treatment, resulting in sepsis and often life-threatening levels of infection. As part of the measures required to counteract this, new antimicrobial compounds are needed. Due to their ...
... arising from the long-term use of antibiotics. In a clinical setting these strains proliferate under antibacterial treatment, resulting in sepsis and often life-threatening levels of infection. As part of the measures required to counteract this, new antimicrobial compounds are needed. Due to their ...
Lecture 6
... – Describe energy-releasing and energyrequiring reactions. – Use the creation and use of ATP for cellular work as examples of these reactions. – Be sure to use the word “entropy.” ...
... – Describe energy-releasing and energyrequiring reactions. – Use the creation and use of ATP for cellular work as examples of these reactions. – Be sure to use the word “entropy.” ...
Dinazyme C/S
... This class of enzymes catalyzes the transfer of groups of atoms (radicals) from one molecule to another. Aminotransferases or transaminases promote the transfer of an amino group from one amino acid to an alpha-keto-acid. ...
... This class of enzymes catalyzes the transfer of groups of atoms (radicals) from one molecule to another. Aminotransferases or transaminases promote the transfer of an amino group from one amino acid to an alpha-keto-acid. ...
Protein
... tRNA’s line up one after the other with amino acids Amino acids form peptide bonds to make the primary sequence of the protein Protein then coils to form the secondary and tertiary structure ...
... tRNA’s line up one after the other with amino acids Amino acids form peptide bonds to make the primary sequence of the protein Protein then coils to form the secondary and tertiary structure ...
Cyclooxygenase (depicted above) inhibited by Salicylic Acid
... Sodium Bicarbonate unknown that it is “organic” in the sense of containing the element carbon. • In 1846 two New York bakers, John Dwight and Austin Church, established the first factory using Leblanc’s method. ...
... Sodium Bicarbonate unknown that it is “organic” in the sense of containing the element carbon. • In 1846 two New York bakers, John Dwight and Austin Church, established the first factory using Leblanc’s method. ...
Influence of genomic G+ C content on average amino
... The most important absolute variations of aminoacid frequencies in the biological range (from 25% to 75%) were for Ala (+10.9%), Ile (-10.5%), Phe (-5.4%), and Gly (+5.3%) in IMP, and for Ala (+9.3%), Lys ( - 8.6%), Asn (-6.2%), Arg (+6.0%) and Ile (-5.8%) in non-IMP. For these amino acids, the abso ...
... The most important absolute variations of aminoacid frequencies in the biological range (from 25% to 75%) were for Ala (+10.9%), Ile (-10.5%), Phe (-5.4%), and Gly (+5.3%) in IMP, and for Ala (+9.3%), Lys ( - 8.6%), Asn (-6.2%), Arg (+6.0%) and Ile (-5.8%) in non-IMP. For these amino acids, the abso ...
lecture CH23 chem131pikul
... • Metabolism is the sum of all the chemical reactions that take place in an organism. • Catabolism is the breakdown of large molecules into smaller ones; energy is ...
... • Metabolism is the sum of all the chemical reactions that take place in an organism. • Catabolism is the breakdown of large molecules into smaller ones; energy is ...
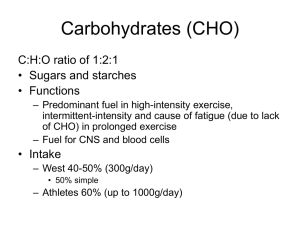
Carbohydrates (CHO)
... – Main role is to maintain blood glucose – stored as glycogen glucose and released – 80-100g, but reduced to <20g after overnight fast – Also produces glucose via gluconeogenesis fom lactate, glycerol , pyruvate, alanine, glutamine +other amino acids ...
... – Main role is to maintain blood glucose – stored as glycogen glucose and released – 80-100g, but reduced to <20g after overnight fast – Also produces glucose via gluconeogenesis fom lactate, glycerol , pyruvate, alanine, glutamine +other amino acids ...
Metabolism

Metabolism (from Greek: μεταβολή metabolē, ""change"") is the set of life-sustaining chemical transformations within the cells of living organisms. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. The word metabolism can also refer to all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transport of substances into and between different cells, in which case the set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary metabolism or intermediate metabolism.Metabolism is usually divided into two categories: catabolism, the breaking down of organic matter by way of cellular respiration, and anabolism, the building up of components of cells such as proteins and nucleic acids. Usually, breaking down releases energy and building up consumes energy.The chemical reactions of metabolism are organized into metabolic pathways, in which one chemical is transformed through a series of steps into another chemical, by a sequence of enzymes. Enzymes are crucial to metabolism because they allow organisms to drive desirable reactions that require energy that will not occur by themselves, by coupling them to spontaneous reactions that release energy. Enzymes act as catalysts that allow the reactions to proceed more rapidly. Enzymes also allow the regulation of metabolic pathways in response to changes in the cell's environment or to signals from other cells.The metabolic system of a particular organism determines which substances it will find nutritious and which poisonous. For example, some prokaryotes use hydrogen sulfide as a nutrient, yet this gas is poisonous to animals. The speed of metabolism, the metabolic rate, influences how much food an organism will require, and also affects how it is able to obtain that food.A striking feature of metabolism is the similarity of the basic metabolic pathways and components between even vastly different species. For example, the set of carboxylic acids that are best known as the intermediates in the citric acid cycle are present in all known organisms, being found in species as diverse as the unicellular bacterium Escherichia coli and huge multicellular organisms like elephants. These striking similarities in metabolic pathways are likely due to their early appearance in evolutionary history, and their retention because of their efficacy.