Problem Set 3
... that this amino acid is not placed very well by Mutate and Auto Fit… You can use Real Space Refine Zone to fix this manually. Sometimes you may find it useful to move one atom at a time rather than an entire amino acid. Hold down the control key while moving (left mouse button down) to move just one ...
... that this amino acid is not placed very well by Mutate and Auto Fit… You can use Real Space Refine Zone to fix this manually. Sometimes you may find it useful to move one atom at a time rather than an entire amino acid. Hold down the control key while moving (left mouse button down) to move just one ...
18.2 Protein Structure and Function: An Overview
... ► Proteins have four levels of structure, each of which is explored later in this chapter. ► Primary structure is the sequence of amino acids in a protein chain (Section 18.7). ► Secondary structure is the regular and repeating spatial organization of neighboring segments of single protein chains ( ...
... ► Proteins have four levels of structure, each of which is explored later in this chapter. ► Primary structure is the sequence of amino acids in a protein chain (Section 18.7). ► Secondary structure is the regular and repeating spatial organization of neighboring segments of single protein chains ( ...
Enzyme
... raising the concentration of the substrate. • Most frequently, in competitive inhibition the inhibitor, I, binds to the substrate-binding portion of the active site and blocks access by the substrate. • The structures of most classic competitive inhibitors therefore tend to resemble the structures o ...
... raising the concentration of the substrate. • Most frequently, in competitive inhibition the inhibitor, I, binds to the substrate-binding portion of the active site and blocks access by the substrate. • The structures of most classic competitive inhibitors therefore tend to resemble the structures o ...
ID_4450_General principles of metaboli_English_sem_5
... Simple end product, energy Energy is carried from catabolic to anabolic reactions in the form of ADP Coenzymes Inorganic phosphate Oxygen High-energy ATP bonds Which term most precisely describes the general process of breaking down large molecules into smaller ones? Anabolism Dehydration Catalysis ...
... Simple end product, energy Energy is carried from catabolic to anabolic reactions in the form of ADP Coenzymes Inorganic phosphate Oxygen High-energy ATP bonds Which term most precisely describes the general process of breaking down large molecules into smaller ones? Anabolism Dehydration Catalysis ...
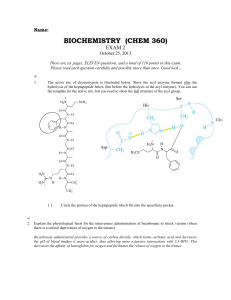
BIOCHEMISTRY (CHEM 360)
... Bicarbonate administered provides a source of carbon dioxide, which forms carbonic acid and decreases the pH of blood (makes it more acidic); thus allowing more extensive interactions with 2,3-BPG. This decreases the affinity of hemoglobin for oxygen and facilitates the release of oxygen to the tiss ...
... Bicarbonate administered provides a source of carbon dioxide, which forms carbonic acid and decreases the pH of blood (makes it more acidic); thus allowing more extensive interactions with 2,3-BPG. This decreases the affinity of hemoglobin for oxygen and facilitates the release of oxygen to the tiss ...
Unit 2 - PGS Science
... Due to hydrogen bonding, ethanol and propanoic acid are soluble in water whereas the ester produced is insoluble. In each of the boxes below, draw a molecule of water and use a dotted line to show where a hydrogen bond could exist between the organic molecule and the water molecule. ...
... Due to hydrogen bonding, ethanol and propanoic acid are soluble in water whereas the ester produced is insoluble. In each of the boxes below, draw a molecule of water and use a dotted line to show where a hydrogen bond could exist between the organic molecule and the water molecule. ...
A gene fusion consisting of 960 base pairs of 5`
... The studies described in this report demonstrate that the first 89 amino acids of the a-factor precursor encoded by the MFal gene are sufficient to direct secretion of a heterologous protein when attached to this prepro sequence. Approximately half of the interferon produced by cells containing a hy ...
... The studies described in this report demonstrate that the first 89 amino acids of the a-factor precursor encoded by the MFal gene are sufficient to direct secretion of a heterologous protein when attached to this prepro sequence. Approximately half of the interferon produced by cells containing a hy ...
Diapositiva 1 - UniFI
... groups are exchangeable. This means that they will back-exchange to 1H when the protein is purified in normal aqueous solution. In this way, many of the normal NHbased experiments can be carried out on triple-labelled protein. ...
... groups are exchangeable. This means that they will back-exchange to 1H when the protein is purified in normal aqueous solution. In this way, many of the normal NHbased experiments can be carried out on triple-labelled protein. ...
Mouse anti- Acetyl CoA Carboxylase 1
... Important Licensing Information - These products may be covered by one or more Limited Use Label Licenses (see the Invitrogen Catalog or our website, www.invitrogen.com). By use of these products you accept the terms and conditions of all applicable Limited Use Label Licenses. Unless otherwise indic ...
... Important Licensing Information - These products may be covered by one or more Limited Use Label Licenses (see the Invitrogen Catalog or our website, www.invitrogen.com). By use of these products you accept the terms and conditions of all applicable Limited Use Label Licenses. Unless otherwise indic ...
Metabolism & Enzymes
... each enzyme works with a specific substrate chemical fit between active site & substrate H bonds & ionic bonds ...
... each enzyme works with a specific substrate chemical fit between active site & substrate H bonds & ionic bonds ...
CH # 9-3
... Lactic acid fermentation can supply enough ATP to last about 90 seconds. However, extra oxygen is required to get rid of the lactic acid produced. Following intense exercise, a person will huff and puff for several minutes in order to pay back the built-up “oxygen debt” and clear the lactic acid fro ...
... Lactic acid fermentation can supply enough ATP to last about 90 seconds. However, extra oxygen is required to get rid of the lactic acid produced. Following intense exercise, a person will huff and puff for several minutes in order to pay back the built-up “oxygen debt” and clear the lactic acid fro ...
Chapter 9 PP - Jones-Bio
... Processing Proteins and Fats as Fuel • Proteins, carbohydrates, and fats can all furnish substrates for cellular respiration. – Enzymes routinely break down fats to form glycerol, which enters the glycolytic pathway, and acetyl CoA, which enters the citric acid cycle. – Enzymes remove the amino grou ...
... Processing Proteins and Fats as Fuel • Proteins, carbohydrates, and fats can all furnish substrates for cellular respiration. – Enzymes routinely break down fats to form glycerol, which enters the glycolytic pathway, and acetyl CoA, which enters the citric acid cycle. – Enzymes remove the amino grou ...
Fermentation - Spencer Community Schools
... Lactic acid fermentation can supply enough ATP to last about 90 seconds. However, extra oxygen is required to get rid of the lactic acid produced. Following intense exercise, a person will huff and puff for several minutes in order to pay back the built-up “oxygen debt” and clear the lactic acid fro ...
... Lactic acid fermentation can supply enough ATP to last about 90 seconds. However, extra oxygen is required to get rid of the lactic acid produced. Following intense exercise, a person will huff and puff for several minutes in order to pay back the built-up “oxygen debt” and clear the lactic acid fro ...
Amino Acids - Building Blocks of Proteins
... recognized that the structure of a finch’s beak was related to the food it ate. This fundamental structure-function relationship is also true at all levels below the Potassium macro level, including proteins and other structures at the molecular Ion level. For two examples of proteins and their func ...
... recognized that the structure of a finch’s beak was related to the food it ate. This fundamental structure-function relationship is also true at all levels below the Potassium macro level, including proteins and other structures at the molecular Ion level. For two examples of proteins and their func ...
EnteraLite Infinity Feeding Pump Combats Metabolic Hypoglycemia
... Deficiency of G-6-P blocks the final steps of glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis resulting in severe hypoglycemia and is one of the few genetic-biochemical causes of hypoglycemia in newborns. Height and growth rate are usually subnormal. At seven months of age, A.N. was at the 85th percentile for we ...
... Deficiency of G-6-P blocks the final steps of glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis resulting in severe hypoglycemia and is one of the few genetic-biochemical causes of hypoglycemia in newborns. Height and growth rate are usually subnormal. At seven months of age, A.N. was at the 85th percentile for we ...
Enhancing the Six Phase II Detoxification
... The detoxification system of the body consists of three phases that process toxins for excretion from the body. The Phase I detoxification pathway is responsible for breaking fat-soluble toxins down and then sending the metabolites to the Phase II detoxification pathways, which builds new substances fr ...
... The detoxification system of the body consists of three phases that process toxins for excretion from the body. The Phase I detoxification pathway is responsible for breaking fat-soluble toxins down and then sending the metabolites to the Phase II detoxification pathways, which builds new substances fr ...
Lecture on PROTEIN FOLDING
... Proteins are very rickety; their shape is easily distorted. Mother Nature uses this to control enzymes (bind something to an enzyme, and distort the enzyme, turn it off or on) Proteins are rickety because their 3-D shape is largely due to weak bonds (not strong covalent bonds) Biomolecules/drugs bin ...
... Proteins are very rickety; their shape is easily distorted. Mother Nature uses this to control enzymes (bind something to an enzyme, and distort the enzyme, turn it off or on) Proteins are rickety because their 3-D shape is largely due to weak bonds (not strong covalent bonds) Biomolecules/drugs bin ...
Nutritional Impact on Protein Metabolism of Muscle and
... The word protein was coined by Jons J. Berzselius, The famous Swedish chemist in 1838 and derived from the Greek work Proteios (meaning of the first rank). Proteins include several important cell constituents such as enzymes, peptide hormones, antibodies, transport molecules and components of cell s ...
... The word protein was coined by Jons J. Berzselius, The famous Swedish chemist in 1838 and derived from the Greek work Proteios (meaning of the first rank). Proteins include several important cell constituents such as enzymes, peptide hormones, antibodies, transport molecules and components of cell s ...
Carlson, Scott M.: Sequence Motifs are Necessary but not Sufficient for Predicting Post-translational Modifications
... determine under what conditions a protein will be post-translationally modified. In addition to enzyme-substrate recognition, PTMs depend on the presence of their enzyme and often on the presence of particular chemical factors that activate that enzyme. Determining the presence of an enzyme is a pro ...
... determine under what conditions a protein will be post-translationally modified. In addition to enzyme-substrate recognition, PTMs depend on the presence of their enzyme and often on the presence of particular chemical factors that activate that enzyme. Determining the presence of an enzyme is a pro ...
lec-04-transcript
... because of its partial double bond characters, which arises due to resonance structure present in peptide bond. There could be two forms- cis form and trans form. But peptide bonds in proteins exist in the trans form. If you see the top panel the trans configuration, there are two C-α on the opposit ...
... because of its partial double bond characters, which arises due to resonance structure present in peptide bond. There could be two forms- cis form and trans form. But peptide bonds in proteins exist in the trans form. If you see the top panel the trans configuration, there are two C-α on the opposit ...
Metabolism

Metabolism (from Greek: μεταβολή metabolē, ""change"") is the set of life-sustaining chemical transformations within the cells of living organisms. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. The word metabolism can also refer to all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transport of substances into and between different cells, in which case the set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary metabolism or intermediate metabolism.Metabolism is usually divided into two categories: catabolism, the breaking down of organic matter by way of cellular respiration, and anabolism, the building up of components of cells such as proteins and nucleic acids. Usually, breaking down releases energy and building up consumes energy.The chemical reactions of metabolism are organized into metabolic pathways, in which one chemical is transformed through a series of steps into another chemical, by a sequence of enzymes. Enzymes are crucial to metabolism because they allow organisms to drive desirable reactions that require energy that will not occur by themselves, by coupling them to spontaneous reactions that release energy. Enzymes act as catalysts that allow the reactions to proceed more rapidly. Enzymes also allow the regulation of metabolic pathways in response to changes in the cell's environment or to signals from other cells.The metabolic system of a particular organism determines which substances it will find nutritious and which poisonous. For example, some prokaryotes use hydrogen sulfide as a nutrient, yet this gas is poisonous to animals. The speed of metabolism, the metabolic rate, influences how much food an organism will require, and also affects how it is able to obtain that food.A striking feature of metabolism is the similarity of the basic metabolic pathways and components between even vastly different species. For example, the set of carboxylic acids that are best known as the intermediates in the citric acid cycle are present in all known organisms, being found in species as diverse as the unicellular bacterium Escherichia coli and huge multicellular organisms like elephants. These striking similarities in metabolic pathways are likely due to their early appearance in evolutionary history, and their retention because of their efficacy.