Pharmacology 34: Bacterial and Mycobacterial Infections (Cell Wall
... Activation step -> TP attacks D-Ala-D-Ala amide bond on glycan polymer (releasing alanine) Coupling step -> free amino group (Gram-positive) or DAP (Gram-negative) attacks intermediate = new amide bond cross-link o Penicillin mimics D-Ala-D-Ala binding TP active site forming enzyme-penicillin comple ...
... Activation step -> TP attacks D-Ala-D-Ala amide bond on glycan polymer (releasing alanine) Coupling step -> free amino group (Gram-positive) or DAP (Gram-negative) attacks intermediate = new amide bond cross-link o Penicillin mimics D-Ala-D-Ala binding TP active site forming enzyme-penicillin comple ...
Statistical Selection of Amino Acids Fortifying a Minimal Defined
... As another approach, a minimal defined medium fortified with specific amino acids was designed to develop a defined medium without any additional YE. To assess the effect of each amino acid on cell growth, a statistical method, the Plackett-Burman design, was used [12]. Each flask contained a certai ...
... As another approach, a minimal defined medium fortified with specific amino acids was designed to develop a defined medium without any additional YE. To assess the effect of each amino acid on cell growth, a statistical method, the Plackett-Burman design, was used [12]. Each flask contained a certai ...
ch04-Cellular-Metabolism-Anatomy
... Energy for Metabolic Reactions Energy • ability to do work or change something • heat, light, sound, electricity, mechanical energy, chemical energy • changed from one form to another • involved in all metabolic reactions Release of chemical energy • most metabolic processes depend on chemical ener ...
... Energy for Metabolic Reactions Energy • ability to do work or change something • heat, light, sound, electricity, mechanical energy, chemical energy • changed from one form to another • involved in all metabolic reactions Release of chemical energy • most metabolic processes depend on chemical ener ...
Enzymes and Metabolism - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... Metabolism – all chemical reactions necessary to maintain life Cellular respiration – food fuels are broken down within cells and some of the energy is captured to produce ATP Anabolic reactions – synthesis of larger molecules from smaller ones Catabolic reactions – hydrolysis of complex str ...
... Metabolism – all chemical reactions necessary to maintain life Cellular respiration – food fuels are broken down within cells and some of the energy is captured to produce ATP Anabolic reactions – synthesis of larger molecules from smaller ones Catabolic reactions – hydrolysis of complex str ...
Cellular Respiration
... process that uses energy to extract energy (ATP) from macromolecules (glucose). Catabolic: Rxn that breaks molecules down Makes CO2 and H2O as well as energy (ATP) ...
... process that uses energy to extract energy (ATP) from macromolecules (glucose). Catabolic: Rxn that breaks molecules down Makes CO2 and H2O as well as energy (ATP) ...
Journal of Biotechnology Evaluation of 13C isotopic tracers for
... as the flux values themselves (Antoniewicz et al., 2006). Stationary MFA is conducted when the labeled substrate is at isotopic steady state and does not utilize pool size or transient data; as such, this technique is especially reliant upon the specific tracer used. Depending on the particular biorea ...
... as the flux values themselves (Antoniewicz et al., 2006). Stationary MFA is conducted when the labeled substrate is at isotopic steady state and does not utilize pool size or transient data; as such, this technique is especially reliant upon the specific tracer used. Depending on the particular biorea ...
Fatty Acid Synthesis
... The conversion of stearoyl-CoA to oleoyl-CoA in eukaryotes is catalyzed by stearoyl-CoA desaturase in a reaction sequence that also involves cytochrome b5 and cytochrome b5 reductase. Two electrons are passed from NADH through the chain of reactions as shown, and two electrons are also derived from ...
... The conversion of stearoyl-CoA to oleoyl-CoA in eukaryotes is catalyzed by stearoyl-CoA desaturase in a reaction sequence that also involves cytochrome b5 and cytochrome b5 reductase. Two electrons are passed from NADH through the chain of reactions as shown, and two electrons are also derived from ...
medical chemistry and biochemistry
... Illustrate the central roles of transaminases (aminotranferases), of glutamate dehydrogenase, and of glutaminase in human nitrogen metabolism. Write the equation for an aminotransferase reaction and illustrate the role played by the coenzyme. Represent the reactions that convert NH3, CO2 and the ami ...
... Illustrate the central roles of transaminases (aminotranferases), of glutamate dehydrogenase, and of glutaminase in human nitrogen metabolism. Write the equation for an aminotransferase reaction and illustrate the role played by the coenzyme. Represent the reactions that convert NH3, CO2 and the ami ...
File
... a. Where does the carbon “go” that is removed? _____________________________________________________________________________________ b. What is the major FUNCTION of the Kreb’s cycle? _____________________________________________________________________________________ c. What are the roles of NAD+ ...
... a. Where does the carbon “go” that is removed? _____________________________________________________________________________________ b. What is the major FUNCTION of the Kreb’s cycle? _____________________________________________________________________________________ c. What are the roles of NAD+ ...
Isolation and Purification of RP2-L, a Nuclear Protein Fraction of the
... amino acids, and molecular weight. In early stud ies on the proteins of the nucleus of tumor cells, it was found that each gram of tumor (wet weight) contained approximately 13 mg. of acid-soluble nuclear proteins and that RP2-L comprised ap proximately 14 per cent of the total weight. Since studies ...
... amino acids, and molecular weight. In early stud ies on the proteins of the nucleus of tumor cells, it was found that each gram of tumor (wet weight) contained approximately 13 mg. of acid-soluble nuclear proteins and that RP2-L comprised ap proximately 14 per cent of the total weight. Since studies ...
Grade 9 Chemistry – Unit Plan - HSBIOLOGY-PHYSICS-2010
... Substrate level phosphorylation vs oxidative phosphorylation Glycolysis (ATP in/out, NADH in/out) Energy Inventory Structure and function of the mitochondrion Location of Glycolysis, Krebs Cycle, and the Electron Transport Chain Endosymbiosis hypothesis The Krebs Cycle (ADP in/ATP out, NAD in ...
... Substrate level phosphorylation vs oxidative phosphorylation Glycolysis (ATP in/out, NADH in/out) Energy Inventory Structure and function of the mitochondrion Location of Glycolysis, Krebs Cycle, and the Electron Transport Chain Endosymbiosis hypothesis The Krebs Cycle (ADP in/ATP out, NAD in ...
fatty acids: straight-chain saturated
... in membrane lipids, for example. They are absent from most vegetable fats, but with important exceptions. Thus, they are major components of such seed oils as coconut oil, palm kernel oil and Cuphea species. Odd-chain fatty acids from 13:0 to 19:0 are found in esterified form in the lipids of many b ...
... in membrane lipids, for example. They are absent from most vegetable fats, but with important exceptions. Thus, they are major components of such seed oils as coconut oil, palm kernel oil and Cuphea species. Odd-chain fatty acids from 13:0 to 19:0 are found in esterified form in the lipids of many b ...
Problem Sets / Exams - Department of Chemistry ::: CALTECH
... hydrogen-deuterium exchange and mass spectrometry to determine folding intermediates of the protein ribonuclease H. i. (2 points) In the experiment, the authors unfold ribonuclease H in the presence of D2O and then refold the protein in the presence of H2O. If an amino acid residue shows a high D:H ...
... hydrogen-deuterium exchange and mass spectrometry to determine folding intermediates of the protein ribonuclease H. i. (2 points) In the experiment, the authors unfold ribonuclease H in the presence of D2O and then refold the protein in the presence of H2O. If an amino acid residue shows a high D:H ...
Enzyme Mechanisms
... We’ve discussed its significance as an energy currency It’s one of two energy-rich products of the conversion of light energy into chemical energy in phototrophs ATP then provides drivers for almost everything else other than redox ...
... We’ve discussed its significance as an energy currency It’s one of two energy-rich products of the conversion of light energy into chemical energy in phototrophs ATP then provides drivers for almost everything else other than redox ...
O 2
... ATP is made directly from a “substrate” The Substrate is phosphorylated, oxidized and ATP is made from ADP The 4 ATP made in Glycolysis are made this way ...
... ATP is made directly from a “substrate” The Substrate is phosphorylated, oxidized and ATP is made from ADP The 4 ATP made in Glycolysis are made this way ...
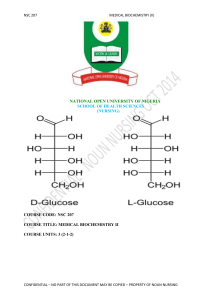
NSC 207 - National Open University of Nigeria
... laboratory. The interactive online activities will be available to you on the course link on the Website of NOUN. There are activities and assignments online for every unit every week. It is important that you visit the course sites weekly and do all assignments to meet deadlines and to contribute ...
... laboratory. The interactive online activities will be available to you on the course link on the Website of NOUN. There are activities and assignments online for every unit every week. It is important that you visit the course sites weekly and do all assignments to meet deadlines and to contribute ...
Lecture 4 - Biological Molecules Part II
... Enzymes: a type of protein • Enzymes are a type of protein that acts as a catalyst to speed up chemical reactions • Enzymes can perform their functions repeatedly without being used up in a reaction, functioning as workhorses that carry out the processes of life • An enzyme is denoted by the suffix ...
... Enzymes: a type of protein • Enzymes are a type of protein that acts as a catalyst to speed up chemical reactions • Enzymes can perform their functions repeatedly without being used up in a reaction, functioning as workhorses that carry out the processes of life • An enzyme is denoted by the suffix ...
Q43to47
... GS can respond to G6P in both liver and muscle – but this is irrelevant to release of glucose ...
... GS can respond to G6P in both liver and muscle – but this is irrelevant to release of glucose ...
C - 鄭智美的Homepage
... There are three main processes in this metabolic enterprise Electron shuttles span membrane ...
... There are three main processes in this metabolic enterprise Electron shuttles span membrane ...
Preview as PDF - Pearson Higher Education
... comes from the sun. In photosynthesis, the energy of sunlight is used to rearrange the atoms of carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O), producing organic molecules and releasing oxygen (O2). In cellular respiration, O2 is consumed as organic molecules are broken down to CO2 and H2O, and the cell captu ...
... comes from the sun. In photosynthesis, the energy of sunlight is used to rearrange the atoms of carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O), producing organic molecules and releasing oxygen (O2). In cellular respiration, O2 is consumed as organic molecules are broken down to CO2 and H2O, and the cell captu ...
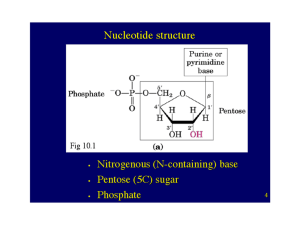
Purine metabolism - mustafaaltinisik.org.uk
... Nucleotides play key roles in many, many cellular processes 1. Activated precursors of RNA and DNA ...
... Nucleotides play key roles in many, many cellular processes 1. Activated precursors of RNA and DNA ...
Learn More - Montgomery County Community College
... Describe the structure of the Carbon atom, its bonding capabilities and hydrocarbon molecular arrangements. B. Distinguish between organic and inorganic molecules. C. Recognize common functional groups such as: hydrogen, hydroxyl, carboxyl, amine, phosphate. D. Describe possible origins of biologica ...
... Describe the structure of the Carbon atom, its bonding capabilities and hydrocarbon molecular arrangements. B. Distinguish between organic and inorganic molecules. C. Recognize common functional groups such as: hydrogen, hydroxyl, carboxyl, amine, phosphate. D. Describe possible origins of biologica ...
Metabolism

Metabolism (from Greek: μεταβολή metabolē, ""change"") is the set of life-sustaining chemical transformations within the cells of living organisms. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. The word metabolism can also refer to all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transport of substances into and between different cells, in which case the set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary metabolism or intermediate metabolism.Metabolism is usually divided into two categories: catabolism, the breaking down of organic matter by way of cellular respiration, and anabolism, the building up of components of cells such as proteins and nucleic acids. Usually, breaking down releases energy and building up consumes energy.The chemical reactions of metabolism are organized into metabolic pathways, in which one chemical is transformed through a series of steps into another chemical, by a sequence of enzymes. Enzymes are crucial to metabolism because they allow organisms to drive desirable reactions that require energy that will not occur by themselves, by coupling them to spontaneous reactions that release energy. Enzymes act as catalysts that allow the reactions to proceed more rapidly. Enzymes also allow the regulation of metabolic pathways in response to changes in the cell's environment or to signals from other cells.The metabolic system of a particular organism determines which substances it will find nutritious and which poisonous. For example, some prokaryotes use hydrogen sulfide as a nutrient, yet this gas is poisonous to animals. The speed of metabolism, the metabolic rate, influences how much food an organism will require, and also affects how it is able to obtain that food.A striking feature of metabolism is the similarity of the basic metabolic pathways and components between even vastly different species. For example, the set of carboxylic acids that are best known as the intermediates in the citric acid cycle are present in all known organisms, being found in species as diverse as the unicellular bacterium Escherichia coli and huge multicellular organisms like elephants. These striking similarities in metabolic pathways are likely due to their early appearance in evolutionary history, and their retention because of their efficacy.