Lezione 10 - Dipartimento di Informatica e Automazione
... From: David S. Goodsell, The machinery of life, Springer, 1998. ...
... From: David S. Goodsell, The machinery of life, Springer, 1998. ...
Pod photosynthesis and seed dark CO2 fixation support oil
... of radio-labelled substrates into fatty acids by leucoplasts isolated from endosperm of developing castor oil seeds. Compared to pyruvate and acetate, exogenous malate was found to support very high rates of fatty acid synthesis in these preparations. Furthermore, they could detect significant activ ...
... of radio-labelled substrates into fatty acids by leucoplasts isolated from endosperm of developing castor oil seeds. Compared to pyruvate and acetate, exogenous malate was found to support very high rates of fatty acid synthesis in these preparations. Furthermore, they could detect significant activ ...
Document
... C. Antibody fights against infectious agents. D. Trypsin act as an enzyme 11. Write the chemical composition of cell. Ans. Water : 70-90% Proteins: 10-15% Carbohydrates : 3% Lipids : 2% Nucleic acids : 5-7% Ions: 1% 12. What are polysaccharides? Give any two examples. Ans. Polysaccharides are long c ...
... C. Antibody fights against infectious agents. D. Trypsin act as an enzyme 11. Write the chemical composition of cell. Ans. Water : 70-90% Proteins: 10-15% Carbohydrates : 3% Lipids : 2% Nucleic acids : 5-7% Ions: 1% 12. What are polysaccharides? Give any two examples. Ans. Polysaccharides are long c ...
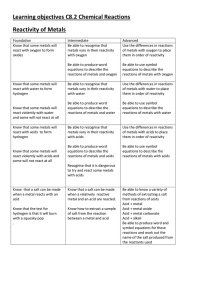
Learning objectives C8.2 Chemical Reactions Reactivity of Metals
... of a metal is linked to the method by which it is extracted Understand that the value of the voltage cell depends on the difference in reactivity of the 2 metals used ...
... of a metal is linked to the method by which it is extracted Understand that the value of the voltage cell depends on the difference in reactivity of the 2 metals used ...
Evolutionary relationship and application of a superfamily of cyclic
... ABSTRACT: Cyclic amidohydrolases belong to a superfamily of enzymes that catalyze the hydrolysis of cyclic C¶N bonds. They are commonly found in nucleotide metabolism of purine and pyrimidine. These enzymes share similar catalytic mechanisms and show considerable structural homologies, suggesting th ...
... ABSTRACT: Cyclic amidohydrolases belong to a superfamily of enzymes that catalyze the hydrolysis of cyclic C¶N bonds. They are commonly found in nucleotide metabolism of purine and pyrimidine. These enzymes share similar catalytic mechanisms and show considerable structural homologies, suggesting th ...
Jumbo_2860g_strawberry_2014 copy - Supplements
... powder with protein, carbohydrates, sugars, creatine, amino acids, AKG, magnesium and Bioperine® ...
... powder with protein, carbohydrates, sugars, creatine, amino acids, AKG, magnesium and Bioperine® ...
Protein oxidation and cellular homeostasis: Emphasis
... As mentioned previously there are several mechanisms by which ROS may be generated including aerobic respiration, nitric oxide synthesis, and NADPH oxidase pathways during inflammation. In aerobic respiration, the mitochondrial respiratory chain produces ROS as it transfers electrons during the redu ...
... As mentioned previously there are several mechanisms by which ROS may be generated including aerobic respiration, nitric oxide synthesis, and NADPH oxidase pathways during inflammation. In aerobic respiration, the mitochondrial respiratory chain produces ROS as it transfers electrons during the redu ...
An operon encoding a novel ABC-type transport
... three ORFs (orfl, orf2 and orf3), probably organized in a single transcriptional unit, were found. The nucleotide sequence of or-7, or--2 and orf3 is given in Fig. 2. The 804 bp long orfl potentially codes for a protein of 268 amino acids whereas orf2 is 702 bp in length (protein of 234 amino acids) ...
... three ORFs (orfl, orf2 and orf3), probably organized in a single transcriptional unit, were found. The nucleotide sequence of or-7, or--2 and orf3 is given in Fig. 2. The 804 bp long orfl potentially codes for a protein of 268 amino acids whereas orf2 is 702 bp in length (protein of 234 amino acids) ...
Protein Structure
... The helix is a right handed twist of the backbone - notice when we are looking at this the side groups are NOT considered Notice where the amino acids are. Hydrogen bonding occurs between the carbonyl and the amino group four residues away. The bonding takes place within the same chain. A run of pro ...
... The helix is a right handed twist of the backbone - notice when we are looking at this the side groups are NOT considered Notice where the amino acids are. Hydrogen bonding occurs between the carbonyl and the amino group four residues away. The bonding takes place within the same chain. A run of pro ...
Topic 1: Statistical analysis (2 hours)
... Skeletal muscle fibres are larger / have many nuclei / are not typical cells; fungal hyphae are (sometimes) not divided up into individual cells; unicellular organisms can be considered acellular; because they are larger than a typical cell / carry out all life functions; some tissues / organs conta ...
... Skeletal muscle fibres are larger / have many nuclei / are not typical cells; fungal hyphae are (sometimes) not divided up into individual cells; unicellular organisms can be considered acellular; because they are larger than a typical cell / carry out all life functions; some tissues / organs conta ...
ESSENTIAL FATTY ACIDS FROM PHARMAX
... What are Omega-3 Essential Fatty Acids? Essential fatty acids (EFAs) are nutrients found in fish oils and some types of plants. EFAs can’t be made within the body and must be obtained from dietary intake. Omega-3s comprise a category of EFAs that includes eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), docosahexaenoi ...
... What are Omega-3 Essential Fatty Acids? Essential fatty acids (EFAs) are nutrients found in fish oils and some types of plants. EFAs can’t be made within the body and must be obtained from dietary intake. Omega-3s comprise a category of EFAs that includes eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), docosahexaenoi ...
Soyfoods and high quality protein
... Protein is an important nutrient needed for the growth and repair of all body cells including organs, muscles, tissues, skin and hair. It’s also required for hormones, enzymes and bodily fluids such as blood. All proteins are made up of chains of amino acids. Amino acids are the building blocks of p ...
... Protein is an important nutrient needed for the growth and repair of all body cells including organs, muscles, tissues, skin and hair. It’s also required for hormones, enzymes and bodily fluids such as blood. All proteins are made up of chains of amino acids. Amino acids are the building blocks of p ...
Insulin, Glucagon, and Diabetes Mellitus
... insulin increases transport of glucose into liver cells (glucose pyruvate acetylCoA fatty acids) excess of citrate and isocitrate ions formed by citric acid cycle when excess amounts of glucose are being used for energy activation of acetyl-CoA carboxylase formation of triglycerides and rele ...
... insulin increases transport of glucose into liver cells (glucose pyruvate acetylCoA fatty acids) excess of citrate and isocitrate ions formed by citric acid cycle when excess amounts of glucose are being used for energy activation of acetyl-CoA carboxylase formation of triglycerides and rele ...
Higher Human Biology Resource Guide - Glow Blogs
... many different body tissues such as the epithelium, bones, cartilage, muscle and blood. During cell division the nucleus of a somatic cell divides by mitosis to maintain the diploid chromosome number. Diploid cells have 23 pairs of homologous chromosomes. Any errors made during mitosis are not passe ...
... many different body tissues such as the epithelium, bones, cartilage, muscle and blood. During cell division the nucleus of a somatic cell divides by mitosis to maintain the diploid chromosome number. Diploid cells have 23 pairs of homologous chromosomes. Any errors made during mitosis are not passe ...
Krebs Cycle
... - Mitogenic signals (demanding energy production) such as insulin and Ca2+ reverse this inactivation by virtue of their ability to activate pyruvate dehydrogenase phosphatase (PDP)— which in turn dephosphorylates E1, thereby promoting its activation (3) Feedforth Activation—Accumulation of pyruvate ...
... - Mitogenic signals (demanding energy production) such as insulin and Ca2+ reverse this inactivation by virtue of their ability to activate pyruvate dehydrogenase phosphatase (PDP)— which in turn dephosphorylates E1, thereby promoting its activation (3) Feedforth Activation—Accumulation of pyruvate ...
cyt c - mustafaaltinisik.org.uk
... runs downhill to drive the synthesis of ATP • Electron transport is coupled with oxidative phosphorylation • It all happens in or at the inner mitochondrial membrane ...
... runs downhill to drive the synthesis of ATP • Electron transport is coupled with oxidative phosphorylation • It all happens in or at the inner mitochondrial membrane ...
Niacinamide - Douglas Laboratories
... provides 500 mg of niacinamide per capsule. Niacin (vitamin B3) occurs in the body as two metabolically active coenzymes, NAD (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) and NADP (NAD phosphate). The niacin coenzymes NAD and NADP have pervasive roles in energy-related and biosynthetic metabolic processes. A ...
... provides 500 mg of niacinamide per capsule. Niacin (vitamin B3) occurs in the body as two metabolically active coenzymes, NAD (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) and NADP (NAD phosphate). The niacin coenzymes NAD and NADP have pervasive roles in energy-related and biosynthetic metabolic processes. A ...
2. Citric acid cycle
... Fatty acids at coenzyme junction - becomes Acetyl CoA 2 carbons at a time via β-oxidation ...
... Fatty acids at coenzyme junction - becomes Acetyl CoA 2 carbons at a time via β-oxidation ...
amino acids M
... -Proteins with the same function from different organisms have similar primary structures -Amino-acid sequence determines the 3-D structure in which the protein folds and its biological function. -Proteins can have very different sizes (from 30 to ~ 100,000 residues) ...
... -Proteins with the same function from different organisms have similar primary structures -Amino-acid sequence determines the 3-D structure in which the protein folds and its biological function. -Proteins can have very different sizes (from 30 to ~ 100,000 residues) ...
Cellular Respiration Harvesting Chemical Energy
... – about 146 ATP (energy molecules) from a triglyceride • Proteins are least likely to be broken down to make ATP. – amino acids not usually needed for energy – about the same amount of energy as a carbohydrate ...
... – about 146 ATP (energy molecules) from a triglyceride • Proteins are least likely to be broken down to make ATP. – amino acids not usually needed for energy – about the same amount of energy as a carbohydrate ...
Vitamins
... Health Effects of Sugars Diabetes Hormonal regulation or obesity (in case of type 2 diabetes) causes diabetes - not sugar Carbohydrate intake, including sugar, may be modified as part of the treatment for diabetes but it is not a cause For people with diabetes, attention is first given to t ...
... Health Effects of Sugars Diabetes Hormonal regulation or obesity (in case of type 2 diabetes) causes diabetes - not sugar Carbohydrate intake, including sugar, may be modified as part of the treatment for diabetes but it is not a cause For people with diabetes, attention is first given to t ...
Minimal Reaction Sets for Escherichia Coli Metabolism under
... dehydrogenase are zero while succinyl-CoA synthetase operates in its reverse direction suggesting a less demanding energetic state under the submaximal growth demands. Acetate is now secreted as a byproduct along with carbon dioxide. Fluxes through two additional TCA cycle reactions, fumarase and ma ...
... dehydrogenase are zero while succinyl-CoA synthetase operates in its reverse direction suggesting a less demanding energetic state under the submaximal growth demands. Acetate is now secreted as a byproduct along with carbon dioxide. Fluxes through two additional TCA cycle reactions, fumarase and ma ...
Glycolysis reaction (Investment phase)
... 2. Now that you have two paper clips, you must take one H from the matrix and move it across the inner membrane through the proton pump into the intermembrane space. 3. Once you push the H across, pass the paper clips to Cytochrome A3. ...
... 2. Now that you have two paper clips, you must take one H from the matrix and move it across the inner membrane through the proton pump into the intermembrane space. 3. Once you push the H across, pass the paper clips to Cytochrome A3. ...
Chapter 23 Gluconeogenesis Gluconeogenesis, con`t.
... Gluconeogenesis, con’t. • Brain and muscle consume most of the glucose. • Liver and kidney are the main sites of gluconeogenesis. • Substrates include pyruvate, lactate, glycerol, most amino acids, and all TCA intermediates. • Fatty acids cannot be converted to glucose in animals. • (They can in pla ...
... Gluconeogenesis, con’t. • Brain and muscle consume most of the glucose. • Liver and kidney are the main sites of gluconeogenesis. • Substrates include pyruvate, lactate, glycerol, most amino acids, and all TCA intermediates. • Fatty acids cannot be converted to glucose in animals. • (They can in pla ...
Metabolism

Metabolism (from Greek: μεταβολή metabolē, ""change"") is the set of life-sustaining chemical transformations within the cells of living organisms. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. The word metabolism can also refer to all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transport of substances into and between different cells, in which case the set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary metabolism or intermediate metabolism.Metabolism is usually divided into two categories: catabolism, the breaking down of organic matter by way of cellular respiration, and anabolism, the building up of components of cells such as proteins and nucleic acids. Usually, breaking down releases energy and building up consumes energy.The chemical reactions of metabolism are organized into metabolic pathways, in which one chemical is transformed through a series of steps into another chemical, by a sequence of enzymes. Enzymes are crucial to metabolism because they allow organisms to drive desirable reactions that require energy that will not occur by themselves, by coupling them to spontaneous reactions that release energy. Enzymes act as catalysts that allow the reactions to proceed more rapidly. Enzymes also allow the regulation of metabolic pathways in response to changes in the cell's environment or to signals from other cells.The metabolic system of a particular organism determines which substances it will find nutritious and which poisonous. For example, some prokaryotes use hydrogen sulfide as a nutrient, yet this gas is poisonous to animals. The speed of metabolism, the metabolic rate, influences how much food an organism will require, and also affects how it is able to obtain that food.A striking feature of metabolism is the similarity of the basic metabolic pathways and components between even vastly different species. For example, the set of carboxylic acids that are best known as the intermediates in the citric acid cycle are present in all known organisms, being found in species as diverse as the unicellular bacterium Escherichia coli and huge multicellular organisms like elephants. These striking similarities in metabolic pathways are likely due to their early appearance in evolutionary history, and their retention because of their efficacy.