PHYS 1311: Advanced Intro. Physics I
... teacher.pas.rochester.edu/phy_labs/appendixe/appendixe.html) ...
... teacher.pas.rochester.edu/phy_labs/appendixe/appendixe.html) ...
Document
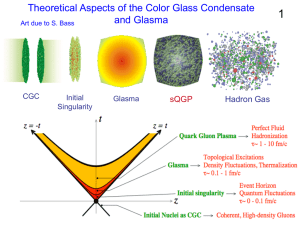
... What is the Color Glass Condensate? Glue at large x generates glue at small x Glue at small x is classical field Time dilation -> Classical field is glassy High phase space density -> Condensate ...
... What is the Color Glass Condensate? Glue at large x generates glue at small x Glue at small x is classical field Time dilation -> Classical field is glassy High phase space density -> Condensate ...
TALK - ECM
... The basic idea is the same as in Kolmogorov Heisenberg turbulence theory: a mode of the field with wave number k lives in the environment provided by all modes with wave number k' > k The dynamics of the relevant mode is obtained by tracing over the environment. This generally leaves the relevant m ...
... The basic idea is the same as in Kolmogorov Heisenberg turbulence theory: a mode of the field with wave number k lives in the environment provided by all modes with wave number k' > k The dynamics of the relevant mode is obtained by tracing over the environment. This generally leaves the relevant m ...
Spectrum of electron in quantum well with continuous position
... physical processes in multilayered heterostructures which are the elementary basis of modern nanodevices. For the deep understanding it is necessary do develop the adequate theory of quasiparticles states in nanoheterostructures in which the realistic models are to be used, in particular, the contin ...
... physical processes in multilayered heterostructures which are the elementary basis of modern nanodevices. For the deep understanding it is necessary do develop the adequate theory of quasiparticles states in nanoheterostructures in which the realistic models are to be used, in particular, the contin ...
a S
... evolution, but not the absolute value of aS Perturbative effects, varying as ~ 1/lnQ Non-perturbative effects, varying as ~ 1/Q Test: measure different processes, energies Intuitive techniques in e+eaS ...
... evolution, but not the absolute value of aS Perturbative effects, varying as ~ 1/lnQ Non-perturbative effects, varying as ~ 1/Q Test: measure different processes, energies Intuitive techniques in e+eaS ...
Geometry, Physics, and Representation Theory Traces of intertwiners for quantum affine and
... Felder-Varchenko functions Abstract. This talk concerns two approaches for studying a family of special functions occurring in the study of the q-Knizhnik-Zamolodchikov-Bernard (q-KZB) equation. The philosophy of KZ-type equations predicts that it admits solutions via (1) traces of intertwining oper ...
... Felder-Varchenko functions Abstract. This talk concerns two approaches for studying a family of special functions occurring in the study of the q-Knizhnik-Zamolodchikov-Bernard (q-KZB) equation. The philosophy of KZ-type equations predicts that it admits solutions via (1) traces of intertwining oper ...
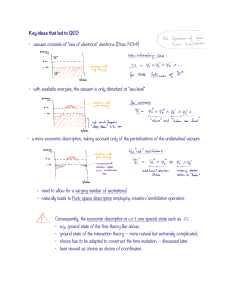
Key ideas that led to QED vacuum consists of "sea of electrons
... Many symbolic manipulations have to conducted on the integrant such as: • normal ordering due to the infinitely many charges in the Dirac sea; • mass renormalization due to the ultraviolet/infrared divergence of the photon field; • charge renormalization, again due to the infinitely many charges in ...
... Many symbolic manipulations have to conducted on the integrant such as: • normal ordering due to the infinitely many charges in the Dirac sea; • mass renormalization due to the ultraviolet/infrared divergence of the photon field; • charge renormalization, again due to the infinitely many charges in ...
Physics 411: Introduction to Quantum Mechanics
... sophistication. A familiarity with linear algebra and differential equations is essential for success in this course. ...
... sophistication. A familiarity with linear algebra and differential equations is essential for success in this course. ...
PHYS 1111 Mechanics, Waves, & Thermodynamics
... Geometry, and Basic Chemistry Course is NOT for physical science majors (PHYS 1211) ...
... Geometry, and Basic Chemistry Course is NOT for physical science majors (PHYS 1211) ...
Marvin_Weinstein
... required, just a choice of coupling constant. Question: What do we hold fixed ? My choice is the energy of the zero momentum two-particle state. This immediately shows why this theory is trivial in four dimensions. ...
... required, just a choice of coupling constant. Question: What do we hold fixed ? My choice is the energy of the zero momentum two-particle state. This immediately shows why this theory is trivial in four dimensions. ...
Quantum Physics 2005 Notes-6 Solving the Time Independent Schrodinger Equation
... A specific example #For a finite square well of width L, we expect the energies to be h2$ 2 of order: E0 = and useful lengths to be of order L. ...
... A specific example #For a finite square well of width L, we expect the energies to be h2$ 2 of order: E0 = and useful lengths to be of order L. ...
Exercises in Statistical Mechanics
... rate in terms of σ(ω) and Ea (ω). Compare with Ohm’s law. What is the symmetry of Reσ(ω) when ω changes sign? (b) Use the fluctuation dissipation theorem to show the (classical) Kubo formula: Z ∞ ...
... rate in terms of σ(ω) and Ea (ω). Compare with Ohm’s law. What is the symmetry of Reσ(ω) when ω changes sign? (b) Use the fluctuation dissipation theorem to show the (classical) Kubo formula: Z ∞ ...
Problem Set 00 - UCSD Department of Physics
... the groundstate energies of each of these oscillators. Changing the boundary conditions on the field, we change the allowed modes; this results in a finite, measurable force on the walls of the box. ...
... the groundstate energies of each of these oscillators. Changing the boundary conditions on the field, we change the allowed modes; this results in a finite, measurable force on the walls of the box. ...
File - SPHS Devil Physics
... a. The electron microscope and the tunnelling electron microscope rely on the findings from studies in quantum physics b. Probability is treated in a mathematical sense in Mathematical studies SL sub-topics 3.6–3.7 9. Aims: a. Aim 1: study of quantum phenomena introduces students to an exciting new ...
... a. The electron microscope and the tunnelling electron microscope rely on the findings from studies in quantum physics b. Probability is treated in a mathematical sense in Mathematical studies SL sub-topics 3.6–3.7 9. Aims: a. Aim 1: study of quantum phenomena introduces students to an exciting new ...
see flyer - Centre for Research in String Theory
... "The strong nuclear force binding the nucleus is described very well by Quantum Chromo-Dynamics (QCD) which has been directly tested in high energy collisions of elementary particles. However, extracting quantitative predictions from QCD for low energy or macroscopic phenomena is one of the outstand ...
... "The strong nuclear force binding the nucleus is described very well by Quantum Chromo-Dynamics (QCD) which has been directly tested in high energy collisions of elementary particles. However, extracting quantitative predictions from QCD for low energy or macroscopic phenomena is one of the outstand ...
Renormalization group

In theoretical physics, the renormalization group (RG) refers to a mathematical apparatus that allows systematic investigation of the changes of a physical system as viewed at different distance scales. In particle physics, it reflects the changes in the underlying force laws (codified in a quantum field theory) as the energy scale at which physical processes occur varies, energy/momentum and resolution distance scales being effectively conjugate under the uncertainty principle (cf. Compton wavelength).A change in scale is called a ""scale transformation"". The renormalization group is intimately related to ""scale invariance"" and ""conformal invariance"", symmetries in which a system appears the same at all scales (so-called self-similarity). (However, note that scale transformations are included in conformal transformations, in general: the latter including additional symmetry generators associated with special conformal transformations.)As the scale varies, it is as if one is changing the magnifying power of a notional microscope viewing the system. In so-called renormalizable theories, the system at one scale will generally be seen to consist of self-similar copies of itself when viewed at a smaller scale, with different parameters describing the components of the system. The components, or fundamental variables, may relate to atoms, elementary particles, atomic spins, etc. The parameters of the theory typically describe the interactions of the components. These may be variable ""couplings"" which measure the strength of various forces, or mass parameters themselves. The components themselves may appear to be composed of more of the self-same components as one goes to shorter distances.For example, in quantum electrodynamics (QED), an electron appears to be composed of electrons, positrons (anti-electrons) and photons, as one views it at higher resolution, at very short distances. The electron at such short distances has a slightly different electric charge than does the ""dressed electron"" seen at large distances, and this change, or ""running,"" in the value of the electric charge is determined by the renormalization group equation.