Mapping Life
... convert feed to meat or produce a more nutritious meat can be made more efficient. Human genomics shows great promise in health and medicine. At the present time we know about some mutations that can cause health problems. Genomics offers the possibility of correcting defective genes and eliminating ...
... convert feed to meat or produce a more nutritious meat can be made more efficient. Human genomics shows great promise in health and medicine. At the present time we know about some mutations that can cause health problems. Genomics offers the possibility of correcting defective genes and eliminating ...
WORKING WITH THE FIGURES 1. Examining Figure 20
... other hand, nonsynonymous substitutions do change the amino acid sequence and potentially have a wide range of affects on phenotype. These effects are subject to natural selection. Most nonsynonymous substitutions will be at least slightly harmful and selected against, reducing their frequency, whil ...
... other hand, nonsynonymous substitutions do change the amino acid sequence and potentially have a wide range of affects on phenotype. These effects are subject to natural selection. Most nonsynonymous substitutions will be at least slightly harmful and selected against, reducing their frequency, whil ...
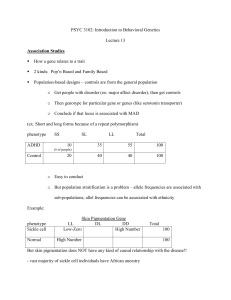
Lecture 13
... 9 to 1 ratio of men to women with violent crimes In this sense the Y chromosome has a VERY high association with violent crimes, it is a genetic marker in this sense But, does the Y chromosome cause crime????? This is just a statistical association HOW do genes and environment interact? Y is a predi ...
... 9 to 1 ratio of men to women with violent crimes In this sense the Y chromosome has a VERY high association with violent crimes, it is a genetic marker in this sense But, does the Y chromosome cause crime????? This is just a statistical association HOW do genes and environment interact? Y is a predi ...
Basic principles of DT40
... • Good model for genome stability in mammals • Complementation by human genes • Good database ...
... • Good model for genome stability in mammals • Complementation by human genes • Good database ...
Name: Block: ______ Lab Biology Chapter 16 The Evolution of
... Fifty percent of an experimental population of four o’clock flowers are red flowered plants, and 50 percent are white flowered plants. What is the frequency of the r ...
... Fifty percent of an experimental population of four o’clock flowers are red flowered plants, and 50 percent are white flowered plants. What is the frequency of the r ...
Molecular Basis of Lung Disease
... Tumorigenesis requires loss of function of both copies of tumor suppressor ...
... Tumorigenesis requires loss of function of both copies of tumor suppressor ...
13.3_201-204
... means. Errors can be made during replication. Environmental conditions may increase the rate of mutation. Mutagens are chemical or physical agents in the environment that cause mutations. The effects of mutations on genes vary widely: Some mutations have little or no effect. Some mutations produce b ...
... means. Errors can be made during replication. Environmental conditions may increase the rate of mutation. Mutagens are chemical or physical agents in the environment that cause mutations. The effects of mutations on genes vary widely: Some mutations have little or no effect. Some mutations produce b ...
13.3 Study Workbook
... means. Errors can be made during replication. Environmental conditions may increase the rate of mutation. Mutagens are chemical or physical agents in the environment that cause mutations. The effects of mutations on genes vary widely: Some mutations have little or no effect. Some mutations produce b ...
... means. Errors can be made during replication. Environmental conditions may increase the rate of mutation. Mutagens are chemical or physical agents in the environment that cause mutations. The effects of mutations on genes vary widely: Some mutations have little or no effect. Some mutations produce b ...
Ch 4 Extensions of Mendelian Genetics
... Epistasis – One gene’s alleles mask the effects of another gene’s alleles Epistasis: A gene interaction where the allele of one gene masks/hides the effects of alleles of another gene. -The gene doing the masking is epistatic to the gene being masked (hypostatic gene) -Bombay phenotype is an example ...
... Epistasis – One gene’s alleles mask the effects of another gene’s alleles Epistasis: A gene interaction where the allele of one gene masks/hides the effects of alleles of another gene. -The gene doing the masking is epistatic to the gene being masked (hypostatic gene) -Bombay phenotype is an example ...
Book Review Mutation Driven Evolution
... When it comes to his criticisms of “beanbag genetics,” Nei is not a naive iconoclast. In Chapter 2 and in an appendix, he very clearly presents the mathematical theories of population genetics but finds them essentially meaningless, for example, models with just two alleles or models assuming const ...
... When it comes to his criticisms of “beanbag genetics,” Nei is not a naive iconoclast. In Chapter 2 and in an appendix, he very clearly presents the mathematical theories of population genetics but finds them essentially meaningless, for example, models with just two alleles or models assuming const ...
Lecture 5-Variation
... Importance of genetic variations in evolution • Mutations are usually lethal so that they are naturally removed from a population. • Recombination (and crossing over) alone will generate a large number of variations • They only mix characters. A large number variants with slight changes are produce ...
... Importance of genetic variations in evolution • Mutations are usually lethal so that they are naturally removed from a population. • Recombination (and crossing over) alone will generate a large number of variations • They only mix characters. A large number variants with slight changes are produce ...
Supplementary Fig S7: A Schematic Figure of the Key Driver Analysis
... Supplementary Fig S7: A Schematic Figure of the Key Driver Analysis (KDA). In order to test if gene G (shown in red) is a KD or not, the subnetwork of G is first extracted by retrieving its 1st to 3rdlayer neighbor genes in the network. Subsequently, the enrichment of genes in a given BP gene set (s ...
... Supplementary Fig S7: A Schematic Figure of the Key Driver Analysis (KDA). In order to test if gene G (shown in red) is a KD or not, the subnetwork of G is first extracted by retrieving its 1st to 3rdlayer neighbor genes in the network. Subsequently, the enrichment of genes in a given BP gene set (s ...
Blue Biology Review Second Semester
... 18. What feature of Darwin’s finches is an example of an adaptation that illustrates natural selection? 19. Why do population geneticists determine gene frequencies? 20. If a geneticist finds 25% of a population to be phenotypic for a recessive trait, he can reasonably conclude what % of the populat ...
... 18. What feature of Darwin’s finches is an example of an adaptation that illustrates natural selection? 19. Why do population geneticists determine gene frequencies? 20. If a geneticist finds 25% of a population to be phenotypic for a recessive trait, he can reasonably conclude what % of the populat ...
Worksheet #6: Epistasis Practice 1. In man, the gene D is necessary
... Worksheet #6: Epistasis Practice 1. In man, the gene D is necessary for normal ear cochlea and gene E is necessary for a normal auditory nerve. In the absence of either of these factors, the individual is deaf (that is ee or dd make you deaf). Do the following crosses and give the phenotypic ratios ...
... Worksheet #6: Epistasis Practice 1. In man, the gene D is necessary for normal ear cochlea and gene E is necessary for a normal auditory nerve. In the absence of either of these factors, the individual is deaf (that is ee or dd make you deaf). Do the following crosses and give the phenotypic ratios ...
Cystic fibrosis
... Northern European descent, but can be found in all ethnic groups with varying frequency. CF is characterized by production of thick mucous that clogs respiratory airways. The mucous provides a breeding ground for infections and subsequent damage of lung tissue, which can result in respiratory failur ...
... Northern European descent, but can be found in all ethnic groups with varying frequency. CF is characterized by production of thick mucous that clogs respiratory airways. The mucous provides a breeding ground for infections and subsequent damage of lung tissue, which can result in respiratory failur ...
Pathology Chapter 5 pg 137-140 [10-22
... Like monogenic disease they are uncommon but associated with high penetrance. ...
... Like monogenic disease they are uncommon but associated with high penetrance. ...
Lecture#31 – Evolution and cis
... - the phenomenon of a single gene being responsible for a number of distinct and seemingly unrelated phenotypic effects. - Consequence: mutations in the gene’s protein coding sequence will have a simultaneous affect on multiple traits -> drastic, severe (dead) -> selected against Concept: - Mutation ...
... - the phenomenon of a single gene being responsible for a number of distinct and seemingly unrelated phenotypic effects. - Consequence: mutations in the gene’s protein coding sequence will have a simultaneous affect on multiple traits -> drastic, severe (dead) -> selected against Concept: - Mutation ...
File
... Not everything can be inherited from parent to child. Scientists used a chart called a pedigree to study how something is inherited in a family. A person that has one allele for a disease but is not affected by it is called a carrier. Some mutations, or changes in DNA have resulted in genetic disord ...
... Not everything can be inherited from parent to child. Scientists used a chart called a pedigree to study how something is inherited in a family. A person that has one allele for a disease but is not affected by it is called a carrier. Some mutations, or changes in DNA have resulted in genetic disord ...
Variation exists within individuals, within populations, and among
... Review guidelines for discussion test in WFB 224 Examples of types of questions are given in italics Basic terminology – review terms in genetics (Hardy-Weinberg, Mendel, molecular genetics); you should not only be able to define the terms, but understand the concepts behind them Define F1, homozygo ...
... Review guidelines for discussion test in WFB 224 Examples of types of questions are given in italics Basic terminology – review terms in genetics (Hardy-Weinberg, Mendel, molecular genetics); you should not only be able to define the terms, but understand the concepts behind them Define F1, homozygo ...
Crossbreeding terminology
... Allele One of two or more forms of a gene at a particular location on a chromosome. For example, blue and brown eyes are determined by different alleles of the gene for eye colour. Chromosomes rod-like structures that are found in the nucleus of all cells. These structures contain genetic informatio ...
... Allele One of two or more forms of a gene at a particular location on a chromosome. For example, blue and brown eyes are determined by different alleles of the gene for eye colour. Chromosomes rod-like structures that are found in the nucleus of all cells. These structures contain genetic informatio ...
Epistasis

Epistasis is a phenomenon that consists of the effect of one gene being dependent on the presence of one or more 'modifier genes' (genetic background). Similarly, epistatic mutations have different effects in combination than individually. It was originally a concept from genetics but is now used in biochemistry, population genetics, computational biology and evolutionary biology. It arises due to interactions, either between genes, or within them leading to non-additive effects. Epistasis has a large influence on the shape of evolutionary landscapes which leads to profound consequences for evolution and evolvability of traits.