Reading GuideBacterialGenetics(CH8)
... mutations, and how to select for mutants or use bacteria to study these mutations. We will focus on sections 8.1-8.5 for now. We will finish the last sections, 8.6-8.9, after talking about viruses. So let’s begin with a look at some key terms and the different types of mutations that can occur in ba ...
... mutations, and how to select for mutants or use bacteria to study these mutations. We will focus on sections 8.1-8.5 for now. We will finish the last sections, 8.6-8.9, after talking about viruses. So let’s begin with a look at some key terms and the different types of mutations that can occur in ba ...
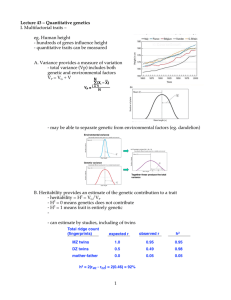
1 Lecture 43 â Quantitative genetics I. Multifactorial traits â eg
... - weight F2 fruit and genotype across genome “p/l” vs “l/l” - does weight differ? - For most genotypes, the answer is no but for a few it is yes (these are loci that contribute to the trait, in this case fruit size) - identified 28 loci responsible for fruit size B. How can we study QTLs in humans? ...
... - weight F2 fruit and genotype across genome “p/l” vs “l/l” - does weight differ? - For most genotypes, the answer is no but for a few it is yes (these are loci that contribute to the trait, in this case fruit size) - identified 28 loci responsible for fruit size B. How can we study QTLs in humans? ...
EMS-treated culture
... Most prokaryotic genes are regulated in units called operons (Jacob and Monod, 1960) Operon: a coordinated unit of gene expression consisting of one or more related genes and the operator and promoter sequences that regulate their transcription. The mRNAs thus produced are “polycistronic’—multiple g ...
... Most prokaryotic genes are regulated in units called operons (Jacob and Monod, 1960) Operon: a coordinated unit of gene expression consisting of one or more related genes and the operator and promoter sequences that regulate their transcription. The mRNAs thus produced are “polycistronic’—multiple g ...
Karotype Chromosomal Abnormalities
... In your groups, brainstorm 3 reasons why genetic diversity can be beneficial ...
... In your groups, brainstorm 3 reasons why genetic diversity can be beneficial ...
Intro to Genetics - MacWilliams Biology
... Law of Segregation -In a pair of alleles (e.g. blue and brown eye color) only ONE of the two are represented in a gamete. **Alleles SEGREGATE into different gametes during meiosis (ensures each parent only donates half of their genetic material to each offspring) ...
... Law of Segregation -In a pair of alleles (e.g. blue and brown eye color) only ONE of the two are represented in a gamete. **Alleles SEGREGATE into different gametes during meiosis (ensures each parent only donates half of their genetic material to each offspring) ...
GENETICS Read chapters 14 and 15 in Campbell. Key Terms: F1 F
... 2. Differentiate between the two terms in each of the following pairs: dominant recessive, allele - gene, F1 - F2, homozygous - heterozygous, phenotype genotype, monohybrid - dihybrid. 3. Explain how incomplete dominance differs from complete dominance. 4. Use a Punnett square or the multiplication ...
... 2. Differentiate between the two terms in each of the following pairs: dominant recessive, allele - gene, F1 - F2, homozygous - heterozygous, phenotype genotype, monohybrid - dihybrid. 3. Explain how incomplete dominance differs from complete dominance. 4. Use a Punnett square or the multiplication ...
Genetics - TeacherWeb
... -The degree of crossing over of any 2 loci is proportional to the distance between them. -In complete linkage only the parental type gametes are produced -In gametes produced by crossing over, two new combinations appear (the result of nonsister chromatids exchanging segments) along with the parenta ...
... -The degree of crossing over of any 2 loci is proportional to the distance between them. -In complete linkage only the parental type gametes are produced -In gametes produced by crossing over, two new combinations appear (the result of nonsister chromatids exchanging segments) along with the parenta ...
Mutations
... How are mutations inherited? Only mutations that occur in gametes, or were present when the organism was fertilized, are passed onto offspring. Mutations that occur in body cells (somatic cells) (after an organism has developed) only affect the organism in which they occur and are not passed on. ...
... How are mutations inherited? Only mutations that occur in gametes, or were present when the organism was fertilized, are passed onto offspring. Mutations that occur in body cells (somatic cells) (after an organism has developed) only affect the organism in which they occur and are not passed on. ...
Document
... completely dominant nor completely recessive – Heterozygous phenotype is intermediate between the two homozygous phenotypes ...
... completely dominant nor completely recessive – Heterozygous phenotype is intermediate between the two homozygous phenotypes ...
Genetics --- introduction
... - Sex linkage (problem: how to get a white-eyed female) - Inheritance and probability - Independent Assortment - Mendelian genetics in humans - Linkage - Gene mapping ...
... - Sex linkage (problem: how to get a white-eyed female) - Inheritance and probability - Independent Assortment - Mendelian genetics in humans - Linkage - Gene mapping ...
Genetics: Phenotype and Genotype - science 6
... word allelos meaning each other) is one of two or more forms of the DNA sequence of a particular gene. Homozygous- having 2 identical alleles of a particular gene Heterozygous (a.k.a. hybrids)- having 2 different alleles of a particular gene ...
... word allelos meaning each other) is one of two or more forms of the DNA sequence of a particular gene. Homozygous- having 2 identical alleles of a particular gene Heterozygous (a.k.a. hybrids)- having 2 different alleles of a particular gene ...
Mutagenesis Lab Biology 322 Fall 2003
... 1. The number of viable cells/ml for the untreated and EMS-treated cultures. 2. The number of rifamycin-resistant cells/total cells plated and the number of laccells/total cells plated for both untreated and EMS-treated cultures. These are the mutation frequencies for these phenotypes. 3. The revers ...
... 1. The number of viable cells/ml for the untreated and EMS-treated cultures. 2. The number of rifamycin-resistant cells/total cells plated and the number of laccells/total cells plated for both untreated and EMS-treated cultures. These are the mutation frequencies for these phenotypes. 3. The revers ...
probability and genetics
... - ABO blood system = multiple alleles (genes that have more that 2 alleles) - ABO blood types – both alleles are expressed in heterozygotes - When more than 2 alleles exist for a given locus, a “multiple allele system” PROBABILITY AND GENETICS - geneticists use probability to predict outcomes of cro ...
... - ABO blood system = multiple alleles (genes that have more that 2 alleles) - ABO blood types – both alleles are expressed in heterozygotes - When more than 2 alleles exist for a given locus, a “multiple allele system” PROBABILITY AND GENETICS - geneticists use probability to predict outcomes of cro ...
GENETICS
... • Sex (X) linked traits: found in guys – Genes on the X chromosome – Guys only have one X – They can get recessive traits with one recessive gene – Hemophilia, baldness, color blindness ...
... • Sex (X) linked traits: found in guys – Genes on the X chromosome – Guys only have one X – They can get recessive traits with one recessive gene – Hemophilia, baldness, color blindness ...
- Fairview High School
... Any trait that enhances an individual’s fitness (ability to survive and reproduce in a particular environment) is called an adaptive trait. Survival of the fittest? ...
... Any trait that enhances an individual’s fitness (ability to survive and reproduce in a particular environment) is called an adaptive trait. Survival of the fittest? ...
Epistasis

Epistasis is a phenomenon that consists of the effect of one gene being dependent on the presence of one or more 'modifier genes' (genetic background). Similarly, epistatic mutations have different effects in combination than individually. It was originally a concept from genetics but is now used in biochemistry, population genetics, computational biology and evolutionary biology. It arises due to interactions, either between genes, or within them leading to non-additive effects. Epistasis has a large influence on the shape of evolutionary landscapes which leads to profound consequences for evolution and evolvability of traits.