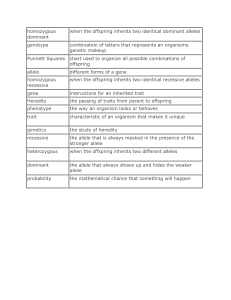
Notes and Study Guide for weeks 8
... chromosome are both considered sex-linked traits. Why is that? Fig. 7.24. If a man has a particular allele for a gene on his Y chromosome, will all of his sons inherit this allele? Will any of his daughters inherit this allele? K. Genes that are located close together on a chromosome are less likely ...
... chromosome are both considered sex-linked traits. Why is that? Fig. 7.24. If a man has a particular allele for a gene on his Y chromosome, will all of his sons inherit this allele? Will any of his daughters inherit this allele? K. Genes that are located close together on a chromosome are less likely ...
iNTRO TO GENETICS PowerPoint
... • Genes for different traits can segregate independently during the formation of gametes (sex cells). • Mendel wondered if the gene for one trait, such as pea color, had anything to do with another trait such as pea shape. ...
... • Genes for different traits can segregate independently during the formation of gametes (sex cells). • Mendel wondered if the gene for one trait, such as pea color, had anything to do with another trait such as pea shape. ...
PSYC 2314 Chapter 3
... • X-linked Genes: genes that are on the X chromosome. – If an X-linked gene is recessive—as are the genes for most forms of color-blindness, many allergies, several diseases, and some learning disabilities—the fact that it is on the X chromosome is critical. ...
... • X-linked Genes: genes that are on the X chromosome. – If an X-linked gene is recessive—as are the genes for most forms of color-blindness, many allergies, several diseases, and some learning disabilities—the fact that it is on the X chromosome is critical. ...
Mendelian Genetics Objectives (Chapter 14)
... and genotypic ratios of the F2 generation Predict the results of genetic crosses involving three or more unlinked genes Give an example of incomplete dominance and explain how it differs from "blending inheritance" Describe inheritance within the ABO blood group system Define and give an example of ...
... and genotypic ratios of the F2 generation Predict the results of genetic crosses involving three or more unlinked genes Give an example of incomplete dominance and explain how it differs from "blending inheritance" Describe inheritance within the ABO blood group system Define and give an example of ...
Understanding Inheritance A. 1.
... 2. Mendel’s factors are parts of chromosomes, and each cell in the offspring contains chromosomes from both ...
... 2. Mendel’s factors are parts of chromosomes, and each cell in the offspring contains chromosomes from both ...
File
... accomplished by controlling transcription initiation • Regulatory proteins bind to DNA to either block or stimulate transcription, depending on how they interact with RNA polymerase ...
... accomplished by controlling transcription initiation • Regulatory proteins bind to DNA to either block or stimulate transcription, depending on how they interact with RNA polymerase ...
Modern theory of Evolution…Part4
... – Ex: homo sapiens in Hawaii – Ex: Stray cats at Kalaheo High School ...
... – Ex: homo sapiens in Hawaii – Ex: Stray cats at Kalaheo High School ...
Memphis/Le Bonheur CF Family Day - The Cystic Fibrosis Center at
... – “a little bit of restored function will go a long way” ...
... – “a little bit of restored function will go a long way” ...
Diapositive 1
... characterize retinal genes. This protocol has been applied to the design of the preliminary list of RetChip and validated on an larger pool of genes (Genoret Genes). To query these information, querying forms have been developed allowing the user to retrieve the Genoret Gene Identity Card (GIC) by g ...
... characterize retinal genes. This protocol has been applied to the design of the preliminary list of RetChip and validated on an larger pool of genes (Genoret Genes). To query these information, querying forms have been developed allowing the user to retrieve the Genoret Gene Identity Card (GIC) by g ...
Disruption of Genetic Equilibrium
... Immigration and emigration can change gene frequencies Gene flow is the process of genes moving from one population to another ...
... Immigration and emigration can change gene frequencies Gene flow is the process of genes moving from one population to another ...
Lecture 4 Gene Products
... to convert tyrosine to DOPA in the melanin pathway. Without melanin, individuals have white skin and hair, and red eyes due to lack of pigmentation in the iris. This enzyme defficiency is also found in a large number of animals. ...
... to convert tyrosine to DOPA in the melanin pathway. Without melanin, individuals have white skin and hair, and red eyes due to lack of pigmentation in the iris. This enzyme defficiency is also found in a large number of animals. ...
CHAPTER 10
... An adaptation is a trait that is favored by natural selection and increases an individual’s fitness in a particular environment. Fitness is the relative survival and reproduction of one variant compared to others in the same population. Natural Selection is the process by which individuals wi ...
... An adaptation is a trait that is favored by natural selection and increases an individual’s fitness in a particular environment. Fitness is the relative survival and reproduction of one variant compared to others in the same population. Natural Selection is the process by which individuals wi ...
Directed Reading 17.2 - Blair Community Schools
... _____ 1. genetic equilibrium a. the movement of alleles into and out of a population _____ 2. gene flow b. one of the most powerful agents of genetic change _____ 3. nonrandom mating c. eliminates individuals with average phenotype values _____ 4. genetic drift d. a change in allele frequency becaus ...
... _____ 1. genetic equilibrium a. the movement of alleles into and out of a population _____ 2. gene flow b. one of the most powerful agents of genetic change _____ 3. nonrandom mating c. eliminates individuals with average phenotype values _____ 4. genetic drift d. a change in allele frequency becaus ...
Genetic Change - Minneota Public Schools
... a. the movement of alleles into and out of a population 2. gene flow b. one of the most powerful agents of genetic change 3. nonrandom mating c. eliminates individuals with average phenotype values 4. genetic drift d. a change in allele frequency because of random occurrences 5. mutation e. the stat ...
... a. the movement of alleles into and out of a population 2. gene flow b. one of the most powerful agents of genetic change 3. nonrandom mating c. eliminates individuals with average phenotype values 4. genetic drift d. a change in allele frequency because of random occurrences 5. mutation e. the stat ...
No Slide Title
... The conundrum: to account for ~1011 different IgG specificities - cannot be separate gene for each (i.e., more different antibodies than base pairs in genome!) ...
... The conundrum: to account for ~1011 different IgG specificities - cannot be separate gene for each (i.e., more different antibodies than base pairs in genome!) ...
document
... 4. ego-1 and ego-3 are epistatic to a glp-1(gf) allele Overall, enhancement is a way to recover lof mutations identifying new players in a common process. 5. ego-1 encodes an RNA-dependent RNA polymerase that has a role in germline RNAi. 6. ego-2 encodes a Bro1 domain protein facilitates ligand prod ...
... 4. ego-1 and ego-3 are epistatic to a glp-1(gf) allele Overall, enhancement is a way to recover lof mutations identifying new players in a common process. 5. ego-1 encodes an RNA-dependent RNA polymerase that has a role in germline RNAi. 6. ego-2 encodes a Bro1 domain protein facilitates ligand prod ...
You, From A to T - Macmillan Learning
... color, the length of your nose, and your susceptibility to certain diseases. On average, the genomes of two people are 99.9% identical, meaning that they differ at about 3 million sites. Oftentimes, those individual differences have no impact on health. In some cases, however, a particular genetic s ...
... color, the length of your nose, and your susceptibility to certain diseases. On average, the genomes of two people are 99.9% identical, meaning that they differ at about 3 million sites. Oftentimes, those individual differences have no impact on health. In some cases, however, a particular genetic s ...
Types of Dominance
... • How could you figure out it’s genotype? – Assume that you do not have access to the technology to sequence the alleles ...
... • How could you figure out it’s genotype? – Assume that you do not have access to the technology to sequence the alleles ...
Epistasis

Epistasis is a phenomenon that consists of the effect of one gene being dependent on the presence of one or more 'modifier genes' (genetic background). Similarly, epistatic mutations have different effects in combination than individually. It was originally a concept from genetics but is now used in biochemistry, population genetics, computational biology and evolutionary biology. It arises due to interactions, either between genes, or within them leading to non-additive effects. Epistasis has a large influence on the shape of evolutionary landscapes which leads to profound consequences for evolution and evolvability of traits.