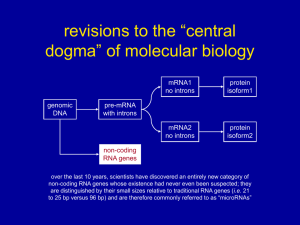
Global Transposon Mutagenesis and a Minimal Mycoplasma Genome
... One approach to estimating the total number of nonessential M. genitalium genes is to determine the number of dispensable orthologs of these genes in M. pneumoniae (see Table 2). We obtain similar estimates of nonessential M. genitalium orthologs whether we use data from all genes disrupted in M. pn ...
... One approach to estimating the total number of nonessential M. genitalium genes is to determine the number of dispensable orthologs of these genes in M. pneumoniae (see Table 2). We obtain similar estimates of nonessential M. genitalium orthologs whether we use data from all genes disrupted in M. pn ...
Study Guide 3 Bio 4 C
... restriction fragments, gene therapy, DNA ligase, gel electrophoresis, what is PCR and how is it used?, RFLP, applications of RFLP, forensic uses of DNA technology, DNA fingerprinting, agricultural uses of DNA technology, safety and ethical issues (p.422-423) and other areas of this chapter), genomic ...
... restriction fragments, gene therapy, DNA ligase, gel electrophoresis, what is PCR and how is it used?, RFLP, applications of RFLP, forensic uses of DNA technology, DNA fingerprinting, agricultural uses of DNA technology, safety and ethical issues (p.422-423) and other areas of this chapter), genomic ...
Evolution and Biology II
... Recent work on caloric restriction suggests it may lengthen life, perhaps in similar ways, by slowing metabolism ...
... Recent work on caloric restriction suggests it may lengthen life, perhaps in similar ways, by slowing metabolism ...
lecture24_RnaInterfe.. - University of Alberta
... gene silencing phenomena; in 1998, Fire and Mello compared the silencing activity of singlestranded RNAs (ssRNAs) (sense or antisense) with double-stranded (dsRNAs) hybrids; marginal silencing was achieved by injecting C. elegans with ssRNAs, but potent and specific silencing was achieved by injecti ...
... gene silencing phenomena; in 1998, Fire and Mello compared the silencing activity of singlestranded RNAs (ssRNAs) (sense or antisense) with double-stranded (dsRNAs) hybrids; marginal silencing was achieved by injecting C. elegans with ssRNAs, but potent and specific silencing was achieved by injecti ...
Complementary DNA Sequencing: Expressed Sequence Tags and
... Of cDNA libraries, random-primed and partial cDNA clones are more informative in identifying genes and constructing a more useful EST database than sequencing from the ends of full-length cDNAs. Therefore, obtain coding sequences in order to take advantage of more sensitive peptide sequences and for ...
... Of cDNA libraries, random-primed and partial cDNA clones are more informative in identifying genes and constructing a more useful EST database than sequencing from the ends of full-length cDNAs. Therefore, obtain coding sequences in order to take advantage of more sensitive peptide sequences and for ...
Genetics Unit Test
... 12. ___________________The kind of organisms he first used to study heredity. 13. ___________________the branch of Biology that studies heredity 14. ___________________ is the transmission of traits from parents to offspring 15. ______________What instrument you use to perform a testcross ...
... 12. ___________________The kind of organisms he first used to study heredity. 13. ___________________the branch of Biology that studies heredity 14. ___________________ is the transmission of traits from parents to offspring 15. ______________What instrument you use to perform a testcross ...
gene control regions?
... What is the structure of a chromosome and how does that relate to function? ...
... What is the structure of a chromosome and how does that relate to function? ...
Teacher`s Guide - Discovery Education
... Context: DNA in the human genome is arranged into 24 chromosomes. DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) Definition: The chemical inside a cell’s nucleus that carries the instructions for everything the cell does; made up of four chemical sub-units referred to as bases Context: The human genome contains 600,00 ...
... Context: DNA in the human genome is arranged into 24 chromosomes. DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) Definition: The chemical inside a cell’s nucleus that carries the instructions for everything the cell does; made up of four chemical sub-units referred to as bases Context: The human genome contains 600,00 ...
Human Genome
... in the GC rich regions and that these ‘selfish’ elements may benefit their human hosts 8. The mutation rate is about twice as high in maleas in female meiosis. Thus, most mutation occurs in males 9. Large GC-poor regions are strongly correlated with ‘dark G-bands’ in karyotypes ...
... in the GC rich regions and that these ‘selfish’ elements may benefit their human hosts 8. The mutation rate is about twice as high in maleas in female meiosis. Thus, most mutation occurs in males 9. Large GC-poor regions are strongly correlated with ‘dark G-bands’ in karyotypes ...
Transcriptome - Nematode bioinformatics. Analysis tools and data
... • In many cases, the patterns of differential expression are the target (as opposed to specific genes) – Clustering or other approaches for pattern identification - find genes which behave similarly across all experiments or experiments which behave similarly across all genes – Classification - iden ...
... • In many cases, the patterns of differential expression are the target (as opposed to specific genes) – Clustering or other approaches for pattern identification - find genes which behave similarly across all experiments or experiments which behave similarly across all genes – Classification - iden ...
Questions - Vanier College
... D) cut the DNA again with restriction enzyme Y and insert these fragments into the plasmid cut with the same enzyme. E) insert the fragments cut with restriction enzyme X directly into the plasmid without cutting the plasmid. 8. A principal problem with inserting an unmodified mammalian gene into a ...
... D) cut the DNA again with restriction enzyme Y and insert these fragments into the plasmid cut with the same enzyme. E) insert the fragments cut with restriction enzyme X directly into the plasmid without cutting the plasmid. 8. A principal problem with inserting an unmodified mammalian gene into a ...
lecture 2
... Occurs, for example in Bacillus subtilis, Haemophilus influenzae, Streptococcus pneumoniae Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Likely to occur at a low level in most bacterial species. Mechanism of transformation varies between species. a. Competence usually occurs at a specific stage of growth, typically late l ...
... Occurs, for example in Bacillus subtilis, Haemophilus influenzae, Streptococcus pneumoniae Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Likely to occur at a low level in most bacterial species. Mechanism of transformation varies between species. a. Competence usually occurs at a specific stage of growth, typically late l ...
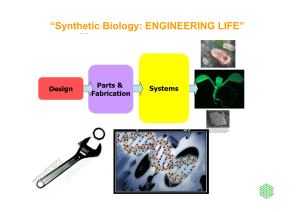
Synthetic Biology: ENGINEERING LIFE
... Filed last October and published by the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office on 31 May, the application describes "a minimal set of protein-coding genes which provides the information required for replication of a free-living organism in a rich bacterial culture medium." The application cites work by Ha ...
... Filed last October and published by the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office on 31 May, the application describes "a minimal set of protein-coding genes which provides the information required for replication of a free-living organism in a rich bacterial culture medium." The application cites work by Ha ...
GENETICS - St. Bonaventure University
... same in all people! (This still leaves about 3 million base pairs that differ among any two individuals) Focus on the similarities… The genome is full of non-coding or “Junk” or repetitive DNA – but even this can be useful for DNA Fingerprinting. ...
... same in all people! (This still leaves about 3 million base pairs that differ among any two individuals) Focus on the similarities… The genome is full of non-coding or “Junk” or repetitive DNA – but even this can be useful for DNA Fingerprinting. ...
Chapter 14 * The Human Genome
... nutrition and exercise These environmental effects are not inherited; genes are Genes may be denied a proper environment in which to reach full expression in one generation, but given the right environment can be seen more in later generations ...
... nutrition and exercise These environmental effects are not inherited; genes are Genes may be denied a proper environment in which to reach full expression in one generation, but given the right environment can be seen more in later generations ...
A Closer Look at Conception
... several genes. Genes: the unit that determine the child's inherited characteristics. Genes makeup chromosomes as beads make up a necklace. For every inherited characteristic, a person receives 2 copies- 1 from mom and 1 from dad. ...
... several genes. Genes: the unit that determine the child's inherited characteristics. Genes makeup chromosomes as beads make up a necklace. For every inherited characteristic, a person receives 2 copies- 1 from mom and 1 from dad. ...
intro to inheritance
... • The two copies of the gene are called ALLELES- they may be the same or different • Variation is caused by the different alleles • Examples in humans- eye colour, hair colour • Examples in plants- petal colour, leaf shape ...
... • The two copies of the gene are called ALLELES- they may be the same or different • Variation is caused by the different alleles • Examples in humans- eye colour, hair colour • Examples in plants- petal colour, leaf shape ...
Supplementary Information (docx 341K)
... Supplementary Figure 1. Topologically associating domains (TADs) disrupted by DGAP242’s chromosomal translocation and genes predicted to show haploinsufficiency (HI). The top row is the chromosome section, containing the banding patterns of the 6 Mb chromosome region surrounding the breakpoint (red ...
... Supplementary Figure 1. Topologically associating domains (TADs) disrupted by DGAP242’s chromosomal translocation and genes predicted to show haploinsufficiency (HI). The top row is the chromosome section, containing the banding patterns of the 6 Mb chromosome region surrounding the breakpoint (red ...
Document
... b. map the location of only the most important genes on each chromosome. c. clone the entire human genome in bacteria. d. determine the nucleotide sequence of the entire human genome. _____ 2. One of the surprising discoveries of the Human Genome Project was that a. the human genome consists of only ...
... b. map the location of only the most important genes on each chromosome. c. clone the entire human genome in bacteria. d. determine the nucleotide sequence of the entire human genome. _____ 2. One of the surprising discoveries of the Human Genome Project was that a. the human genome consists of only ...
File
... group of genetically related organisms that make up a single step in the line of descent (passing of traits) ...
... group of genetically related organisms that make up a single step in the line of descent (passing of traits) ...
Final Exam Study Guide
... 8. What are the nucleotides found in DNA? Deoxyribose + phosphate group + cytosine 9. The overall structure of DNA can be described as? Double helix or two strands that are twisted 10. Explain the process of translation. The ribosomes use information from mRNA to produce proteins 11. Why is crossing ...
... 8. What are the nucleotides found in DNA? Deoxyribose + phosphate group + cytosine 9. The overall structure of DNA can be described as? Double helix or two strands that are twisted 10. Explain the process of translation. The ribosomes use information from mRNA to produce proteins 11. Why is crossing ...
Liu Drosophila Library Overview
... resistance), and sgRNA populations between control and treated populations compared by high throughput sequencing. It is important to maintain coverage of the library throughout the screening process, and ideally 500-1000 cells should be screened per sgRNA (20-40 million cells) in order that it is p ...
... resistance), and sgRNA populations between control and treated populations compared by high throughput sequencing. It is important to maintain coverage of the library throughout the screening process, and ideally 500-1000 cells should be screened per sgRNA (20-40 million cells) in order that it is p ...
Module - Discovering the Genome
... http://www.dnai.org/c/index.html (Select Genome / Tour) Video on how gene duplication can lead to ...
... http://www.dnai.org/c/index.html (Select Genome / Tour) Video on how gene duplication can lead to ...
GMO and gene therapy - Hicksville Public Schools / Homepage
... What are the benefits to genetically modified plants and animals? 1)To make pesticide __________ resistant plants. 2)GM plants can produce natural __________. pesticide ...
... What are the benefits to genetically modified plants and animals? 1)To make pesticide __________ resistant plants. 2)GM plants can produce natural __________. pesticide ...
4 - On Cells, DNA, Proteins, and Populations
... How is the variation present within a species at any time affected by the environment? ...
... How is the variation present within a species at any time affected by the environment? ...