Ch. 6 - Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry
... nucleophilic anions, and this results in “naked” anions of the Nu⊖ and makes the e⊖ pair of the Nu⊖ more available ...
... nucleophilic anions, and this results in “naked” anions of the Nu⊖ and makes the e⊖ pair of the Nu⊖ more available ...
Organic Chemistry Fifth Edition
... substitution: they always react by the SN2 mechanism. Tertiary alkyl halides undergo nucleophilic substitution: they always react by the SN1 mechanism. Secondary alkyl halides undergo nucleophilic substitution: they react by the SN1 mechanism in the presence of a weak ...
... substitution: they always react by the SN2 mechanism. Tertiary alkyl halides undergo nucleophilic substitution: they always react by the SN1 mechanism. Secondary alkyl halides undergo nucleophilic substitution: they react by the SN1 mechanism in the presence of a weak ...
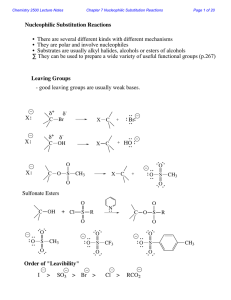
Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions
... SN1 reaction involve carbocation intermediates. So, the only substrates that undergo SN1 reactions are those that form stabilized carbocations. So - What makes a relatively stable carbocation? ...
... SN1 reaction involve carbocation intermediates. So, the only substrates that undergo SN1 reactions are those that form stabilized carbocations. So - What makes a relatively stable carbocation? ...
Elimination Reactions
... • E1 reactions occur under essentially neutral conditions with polar solvents, such as water, ethyl alcohol or acetic acid. • E1 reactions can also occur with strong bases, but only at low concentration, about 0.01 to 0.1 M or below. • E2 reactions require strong base in high concentration, about 1 ...
... • E1 reactions occur under essentially neutral conditions with polar solvents, such as water, ethyl alcohol or acetic acid. • E1 reactions can also occur with strong bases, but only at low concentration, about 0.01 to 0.1 M or below. • E2 reactions require strong base in high concentration, about 1 ...
(III) ion and a cobalt (II) - Iowa State University Digital Repository
... left-hand corner and continuing from left to right in equal sections with small overlaps. Each oversize page is available as one exposure on a standard 35 mm slide or as a 17" x 23" black and white photographic print for an additional charge. Photographs included in the original manuscript have been ...
... left-hand corner and continuing from left to right in equal sections with small overlaps. Each oversize page is available as one exposure on a standard 35 mm slide or as a 17" x 23" black and white photographic print for an additional charge. Photographs included in the original manuscript have been ...
Alkyl Halides02
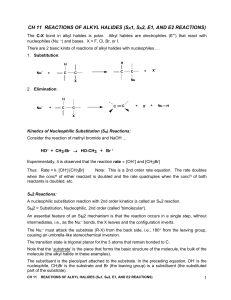
... when the concn of either reactant is doubled and the rate quadruples when the concn of both reactants is doubled, etc. SN2 Reactions: A nucleophilic substitution reaction with 2nd order kinetics is called an SN2 reaction. SN2 = Substitution, Nucleophilic, 2nd order (called 'bimolecular'). An essenti ...
... when the concn of either reactant is doubled and the rate quadruples when the concn of both reactants is doubled, etc. SN2 Reactions: A nucleophilic substitution reaction with 2nd order kinetics is called an SN2 reaction. SN2 = Substitution, Nucleophilic, 2nd order (called 'bimolecular'). An essenti ...
hydrogen peroxide disproportionation and organic
... [MnIV(Me3TACN)(OMe)3]PF6 .....................................................................57 Mn(IV) catalyst stability ..............................................................................57 Cis-trans Isomerization in the Manganese(II) Catalyzed Alkene Epoxidation ...61 Cis/Trans isomer ...
... [MnIV(Me3TACN)(OMe)3]PF6 .....................................................................57 Mn(IV) catalyst stability ..............................................................................57 Cis-trans Isomerization in the Manganese(II) Catalyzed Alkene Epoxidation ...61 Cis/Trans isomer ...
7: Reactions of Haloalkanes, Alcohols, and Amines. Nucleophilic
... case). Similarly, (CH3 )2 CH+ is a 2 (secondary) carbocation because it has 2 alkyl groups on the C+ center, while CH3 CH2 + with 1 alkyl group on C+ is a 1 (primary) carbocation. Using this general terminology, we can summarize this carbocation stability order as 3° > 2° > 1° > methyl. Other simple ...
... case). Similarly, (CH3 )2 CH+ is a 2 (secondary) carbocation because it has 2 alkyl groups on the C+ center, while CH3 CH2 + with 1 alkyl group on C+ is a 1 (primary) carbocation. Using this general terminology, we can summarize this carbocation stability order as 3° > 2° > 1° > methyl. Other simple ...
Chapter Seven - U of L Class Index
... CH3 Br CH3 CH 2 Br CH3 CH 2 CH 2 Br CH3 CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 Br ...
... CH3 Br CH3 CH 2 Br CH3 CH 2 CH 2 Br CH3 CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 Br ...
Alkyl Halides SN and E reactions
... 3. Consider the nature of the solvent: For SN1 reactions, the solvent affects the rate only if it influences the stability of the charged transition state, i.e., the C+. The Nu:- is not involved in the rate determining step so solvent effects on the Nu:- do not affect the rate of SN1 reactions. ...
... 3. Consider the nature of the solvent: For SN1 reactions, the solvent affects the rate only if it influences the stability of the charged transition state, i.e., the C+. The Nu:- is not involved in the rate determining step so solvent effects on the Nu:- do not affect the rate of SN1 reactions. ...
Reactions of Alkyl Halides (SN1, SN2, E1, and E2 reactions)
... 3. Consider the nature of the solvent: For SN1 reactions, the solvent affects the rate only if it influences the stability of the charged transition state, i.e., the C+. The Nu:- is not involved in the rate determining step so solvent effects on the Nu:- do not affect the rate of SN1 reactions. ...
... 3. Consider the nature of the solvent: For SN1 reactions, the solvent affects the rate only if it influences the stability of the charged transition state, i.e., the C+. The Nu:- is not involved in the rate determining step so solvent effects on the Nu:- do not affect the rate of SN1 reactions. ...
Reactions of Alkyl Halides (SN1, SN2, E1, and E2 reactions)
... 3. Consider the nature of the solvent: For SN1 reactions, the solvent affects the rate only if it influences the stability of the charged transition state, i.e., the C+. The Nu:- is not involved in the rate determining step so solvent effects on the Nu:- do not affect the rate of SN1 reactions. ...
... 3. Consider the nature of the solvent: For SN1 reactions, the solvent affects the rate only if it influences the stability of the charged transition state, i.e., the C+. The Nu:- is not involved in the rate determining step so solvent effects on the Nu:- do not affect the rate of SN1 reactions. ...
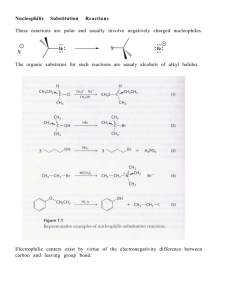
Organic Chemistry - UCR Chemistry
... We will learn below that, because of the different structures of their alkyl groups, nucleophilic substitution on bromomethane (CH3-Br) occurs only by SN2 mechanisms, while t-butyl bromide (2-bromo-2-methylpropane) ((CH3)3C-Br) undergoes nucleophilic substitution only by SN1 mechanisms. H2O versus - ...
... We will learn below that, because of the different structures of their alkyl groups, nucleophilic substitution on bromomethane (CH3-Br) occurs only by SN2 mechanisms, while t-butyl bromide (2-bromo-2-methylpropane) ((CH3)3C-Br) undergoes nucleophilic substitution only by SN1 mechanisms. H2O versus - ...
Boron and boron isotope systematics in the peralkaline Ilímaussaq
... Minerals investigated in earlier studies include clinopyroxene, orthopyroxene, plagioclase, amphibole and garnet. Some of these minerals are relevant for granitic and syenitic rocks the present study deals with. However, it remains to be tested, whether compatibilities in peralkaline magmatic system ...
... Minerals investigated in earlier studies include clinopyroxene, orthopyroxene, plagioclase, amphibole and garnet. Some of these minerals are relevant for granitic and syenitic rocks the present study deals with. However, it remains to be tested, whether compatibilities in peralkaline magmatic system ...
Kinetics and Reaction Pathways for Propane Dehydrogenation and
... kinetic model was used to describe experimental rates based on these observations and to obtain rate constants for individual reaction steps as a function of Co content and H2 concentration. H2 inhibits propane dehydrogenation to propene and alkene conversion to aromatics, and increases the rate and ...
... kinetic model was used to describe experimental rates based on these observations and to obtain rate constants for individual reaction steps as a function of Co content and H2 concentration. H2 inhibits propane dehydrogenation to propene and alkene conversion to aromatics, and increases the rate and ...
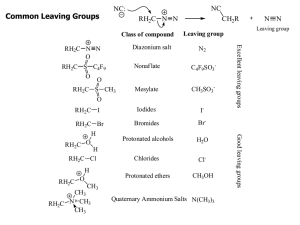
Common Leaving Groups
... •To favour E1 over SN1 for alcohols, use an acid with a non-nucleophilic conjugate base (H2SO4, H3PO4). To favour SN1 over E1, use a good nucleophile. •To favour E2 over SN2, use a strong, bulky non-nucleophilic base. To favour SN2 over E2, use good nucleophiles that are relatively weak bases. •It i ...
... •To favour E1 over SN1 for alcohols, use an acid with a non-nucleophilic conjugate base (H2SO4, H3PO4). To favour SN1 over E1, use a good nucleophile. •To favour E2 over SN2, use a strong, bulky non-nucleophilic base. To favour SN2 over E2, use good nucleophiles that are relatively weak bases. •It i ...
Drawing Organic Structures Functional Groups Constitutional Isomers
... • X eliminated from one carbon • H eliminated from adjacent carbon • Compete with substitution reactions ...
... • X eliminated from one carbon • H eliminated from adjacent carbon • Compete with substitution reactions ...
Chemical reactivity of ultracold polar molecules: investigation of H+
... with values differing by 3 orders of magnitude for v = 1, and 2 orders of magnitude for v = 2 at an incident kinetic energy of 10−7 eV. For energies below 10−4 eV, cross sections reach the Wigner regime [64] where they vary inversely as the velocity and their ratios become constant. For the v = 0, j ...
... with values differing by 3 orders of magnitude for v = 1, and 2 orders of magnitude for v = 2 at an incident kinetic energy of 10−7 eV. For energies below 10−4 eV, cross sections reach the Wigner regime [64] where they vary inversely as the velocity and their ratios become constant. For the v = 0, j ...
10. Alkyl Halides
... Some nucleophiles are more nucleophilic than others. Their reaction rates with the same alkyl halide are faster. *Stronger Nucleophiles react faster in an SN2 reaction Negative Nucleophiles result in a neutral organic product Neutral Nucleophiles result in a positive organic product ...
... Some nucleophiles are more nucleophilic than others. Their reaction rates with the same alkyl halide are faster. *Stronger Nucleophiles react faster in an SN2 reaction Negative Nucleophiles result in a neutral organic product Neutral Nucleophiles result in a positive organic product ...
CHEMICAL REACTIVITY AND MECHANISMS, AND SUBSTITUTION REACTIONS 1.
... From your knowledge of the mechanism, predict and interpret experimental results for SN1 and SN2 reactions. Be prepared to draw mechanisms with arrows that show electron movement. For a summary of important factors that influence reaction rates, see the study guide on the next page. ...
... From your knowledge of the mechanism, predict and interpret experimental results for SN1 and SN2 reactions. Be prepared to draw mechanisms with arrows that show electron movement. For a summary of important factors that influence reaction rates, see the study guide on the next page. ...
Alkyl halide
... Protic solvents solvate the nucleophile, thereby lowering its ground-state energy, increasing ∆G‡, and decreasing SN2 reaction rate Polar aprotic solvents surround the accompanying cation but not the nucleophilic anion, thereby raising the groundstate energy of the nucleophile, decreasing ∆G‡ and in ...
... Protic solvents solvate the nucleophile, thereby lowering its ground-state energy, increasing ∆G‡, and decreasing SN2 reaction rate Polar aprotic solvents surround the accompanying cation but not the nucleophilic anion, thereby raising the groundstate energy of the nucleophile, decreasing ∆G‡ and in ...
Resolution of Diols via Catalytic Asymmetric Acetalization
... of different aldehydes revealed that efficient kinetic resolution of diol rac-2a can be achieved in the presence of only 1−2 mol% of 1a to give a variety of 1,3-dioxolanes 4 with excellent enantioselectivities and diastereoselectivities (Table 1). Replacing isovaleraldehyde with less bulky n-pentanal o ...
... of different aldehydes revealed that efficient kinetic resolution of diol rac-2a can be achieved in the presence of only 1−2 mol% of 1a to give a variety of 1,3-dioxolanes 4 with excellent enantioselectivities and diastereoselectivities (Table 1). Replacing isovaleraldehyde with less bulky n-pentanal o ...
Reaction Kinetics Basics
... emitted to the troposphere, and their ratio changes dependent on the type of ...
... emitted to the troposphere, and their ratio changes dependent on the type of ...
184
... geometry and frequencies of some transition states are sensitive to the level of theory, in the present work we use the zeropoint energy calculated at the MP2/6-31G(d) scaled by 0.964620 for all structures (minima and transition states) rather than the HF/6-31G(d) zero-point energy scaled by 0.8929. ...
... geometry and frequencies of some transition states are sensitive to the level of theory, in the present work we use the zeropoint energy calculated at the MP2/6-31G(d) scaled by 0.964620 for all structures (minima and transition states) rather than the HF/6-31G(d) zero-point energy scaled by 0.8929. ...