charlietalk
... • Cell is a dynamical system • Somewhat modularized (into pathways) • Given pathway elements, how do they communicate? – Protein modification – Gene expression changes ...
... • Cell is a dynamical system • Somewhat modularized (into pathways) • Given pathway elements, how do they communicate? – Protein modification – Gene expression changes ...
Supplementary data
... acquire nutrients and evade immune defences [1,2]. Direct protein-protein interactions (PPIs) between pathogen and host proteins play a key role in such strategies [3]. Identifying PPIs between B. dentium Bd1 and its host will therefore provide valuable information on the pathogenic activities of th ...
... acquire nutrients and evade immune defences [1,2]. Direct protein-protein interactions (PPIs) between pathogen and host proteins play a key role in such strategies [3]. Identifying PPIs between B. dentium Bd1 and its host will therefore provide valuable information on the pathogenic activities of th ...
Self-adaptation of Genome Size in Artificial Organisms | SpringerLink
... When all mutation rates are increased, the acquired genomic structure is quickly displaced by a new, shorter one, more robust but less fit. This shows that the shrinkage effect can be surprisingly strong, compared to the pressure for individual adaptation. When, on the contrary, all mutation rates are ...
... When all mutation rates are increased, the acquired genomic structure is quickly displaced by a new, shorter one, more robust but less fit. This shows that the shrinkage effect can be surprisingly strong, compared to the pressure for individual adaptation. When, on the contrary, all mutation rates are ...
DNA Technology
... Either plasmids or bacteriophages can serve as vectors (carriers) to introduce recombinant DNA molecules into host cells. Recombinant DNA is made by inserting a piece of DNA containing a gene of interest into the plasmid or phage DNA that has been clipped by restriction enzymes. In either case, gene ...
... Either plasmids or bacteriophages can serve as vectors (carriers) to introduce recombinant DNA molecules into host cells. Recombinant DNA is made by inserting a piece of DNA containing a gene of interest into the plasmid or phage DNA that has been clipped by restriction enzymes. In either case, gene ...
Mutations
... Genetic code redundancy - a change in the sequence may not alter the amino acid (eg. UUU and UUC both result in phenylalanine) ...
... Genetic code redundancy - a change in the sequence may not alter the amino acid (eg. UUU and UUC both result in phenylalanine) ...
Dear Sir - PhagesDB
... Glimmer. The difference between our annotation and the Glimmer call is ~90 bp. Interestingly, NCBI BLAST indicates Gomashi uses an earlier start site, while PhagesDB BLAST indicates Gomashi uses a later start site. Furthermore, the earlier start site (29489, called by glimmer) only allows 8 bp for t ...
... Glimmer. The difference between our annotation and the Glimmer call is ~90 bp. Interestingly, NCBI BLAST indicates Gomashi uses an earlier start site, while PhagesDB BLAST indicates Gomashi uses a later start site. Furthermore, the earlier start site (29489, called by glimmer) only allows 8 bp for t ...
lecture 20 notes
... – also tends to cause a small duplication at the site • RNA transposons (retrotransposons) and some DNA transposons ...
... – also tends to cause a small duplication at the site • RNA transposons (retrotransposons) and some DNA transposons ...
DNA FRQ practice
... • Allows for Complexity ______allows for more genes ______evolution of new genes can occur/transposons ______intron/ exon allows for alternate splicing ...
... • Allows for Complexity ______allows for more genes ______evolution of new genes can occur/transposons ______intron/ exon allows for alternate splicing ...
07Lab_MitoMei - Biology Learning Center at the University of
... •Human genome is ~1 meter of DNA *Includes control regions & stuff that won’t make it into the final product **We keep finding stuff that matters ...
... •Human genome is ~1 meter of DNA *Includes control regions & stuff that won’t make it into the final product **We keep finding stuff that matters ...
Genetic Engineering
... SM1 was placed under control of a promoter controlled by feeding in the mosquito genome Mosquitoes with SM1 were unable to transmit malaria to mice To effectively eliminate transmission transgenic mosquitoes must be able to survive as well or better than wildtype mosquitoes ...
... SM1 was placed under control of a promoter controlled by feeding in the mosquito genome Mosquitoes with SM1 were unable to transmit malaria to mice To effectively eliminate transmission transgenic mosquitoes must be able to survive as well or better than wildtype mosquitoes ...
wk1_day1_introduction_2010
... Genome is fragmented and cloned Random sequencing of both ends of cloned DNA High numbers of random sequences It statistically ensures the whole genome is ...
... Genome is fragmented and cloned Random sequencing of both ends of cloned DNA High numbers of random sequences It statistically ensures the whole genome is ...
genome - Microme
... TrEMBL contains functional annotations which often come from automatic procedures only: ‘IPMed?’ is used for proteins that may have an experimentally validated function. ...
... TrEMBL contains functional annotations which often come from automatic procedures only: ‘IPMed?’ is used for proteins that may have an experimentally validated function. ...
Biotechnology Notes
... Gene Therapy • Is the replacement of faulty genes • Gene therapy replaces defective or missing genes, or adds new genes, to treat a disease. ...
... Gene Therapy • Is the replacement of faulty genes • Gene therapy replaces defective or missing genes, or adds new genes, to treat a disease. ...
Genit 2
... This type of mutations happens in 1% of each cell division, and this will result in early abortion of the fetus carrying the abnormality. - Single chromosome mutations: in this case we have normal number of chromosomes, but they may have abnormal structures. For example, translocation of segments of ...
... This type of mutations happens in 1% of each cell division, and this will result in early abortion of the fetus carrying the abnormality. - Single chromosome mutations: in this case we have normal number of chromosomes, but they may have abnormal structures. For example, translocation of segments of ...
9.1 - How Do Populations Evolve SG
... Gene flow: the net movement of alleles from one population to another due to the migration of individuals. Non-random mating: mating among individuals on the basis of mate selection for a particular phenotype or due to breeding. Genetic drift: the change in frequencies of alleles due to chance event ...
... Gene flow: the net movement of alleles from one population to another due to the migration of individuals. Non-random mating: mating among individuals on the basis of mate selection for a particular phenotype or due to breeding. Genetic drift: the change in frequencies of alleles due to chance event ...
References - Proceedings of the Royal Society B
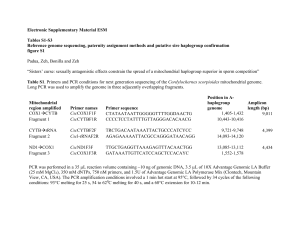
... adults was extracted as described above and PCR was conducted using the ND2 mitochondrial DNA locus forward (5’ – TGTAAGTCTTAAAAYAAAGAAAACC – 3’) and reverse primers (5’ – AAGTCATCGAATAGARACRTTAGC – 3’). PCR reactions were performed, as described above, except that the conditions of the 34 cycles we ...
... adults was extracted as described above and PCR was conducted using the ND2 mitochondrial DNA locus forward (5’ – TGTAAGTCTTAAAAYAAAGAAAACC – 3’) and reverse primers (5’ – AAGTCATCGAATAGARACRTTAGC – 3’). PCR reactions were performed, as described above, except that the conditions of the 34 cycles we ...
Proteins to Phenotype
... Alleles: Different forms of a gene at same location on chromosome. Polymorphism: Existence of many common variants (alleles) of a gene in a population. Morph = allele = variant Each organism normally has two alleles for each gene! High number of different alleles leads to genetic variance in populat ...
... Alleles: Different forms of a gene at same location on chromosome. Polymorphism: Existence of many common variants (alleles) of a gene in a population. Morph = allele = variant Each organism normally has two alleles for each gene! High number of different alleles leads to genetic variance in populat ...
Chapter 3 - The Nature and Nurture of Behavior
... • Each sperm and each ovum contains 23 chromosomes. • The chromosomes contain the genes. • The fertilized egg (zygote) and all the body cells that develop from it (except the sperm cells and the ova) contain 46 chromosomes. ...
... • Each sperm and each ovum contains 23 chromosomes. • The chromosomes contain the genes. • The fertilized egg (zygote) and all the body cells that develop from it (except the sperm cells and the ova) contain 46 chromosomes. ...
Genome evolution

Genome evolution is the process by which a genome changes in structure (sequence) or size over time. The study of genome evolution involves multiple fields such as structural analysis of the genome, the study of genomic parasites, gene and ancient genome duplications, polyploidy, and comparative genomics. Genome evolution is a constantly changing and evolving field due to the steadily growing number of sequenced genomes, both prokaryotic and eukaryotic, available to the scientific community and the public at large.