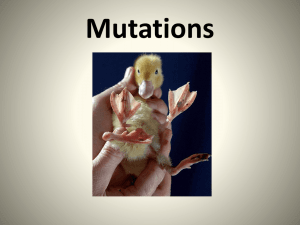
VOCAB- Evolution
... evolves into several different forms that live in different ways; rapid growth in the diversity of a group of organisms. COEVOLUTION- process by which two species evolve in response to changes in each other PUNCTUATED EQUILIBRIUM-pattern of evolution in which long stable periods are interrupted by b ...
... evolves into several different forms that live in different ways; rapid growth in the diversity of a group of organisms. COEVOLUTION- process by which two species evolve in response to changes in each other PUNCTUATED EQUILIBRIUM-pattern of evolution in which long stable periods are interrupted by b ...
Bio Quiz #4 Review Sheet
... Structures with the same function found in animals that have a different common ancestor Caused by random events that remove genes from a population Theory that living things come from other living things Structures found in organisms with common evolutionary ancestry Adaptation in which one animal ...
... Structures with the same function found in animals that have a different common ancestor Caused by random events that remove genes from a population Theory that living things come from other living things Structures found in organisms with common evolutionary ancestry Adaptation in which one animal ...
Gene Section P53 (protein 53 kDa) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... P53 is mutated in about 50% of human cancers, and the non-mutated allele is generally lost; the frequency and the type of mutation may vary from one tumor type to another; in general, mutations are found in the central part (exons 4-8) of the p53 gene; these mutations are missense, non-sense, deleti ...
... P53 is mutated in about 50% of human cancers, and the non-mutated allele is generally lost; the frequency and the type of mutation may vary from one tumor type to another; in general, mutations are found in the central part (exons 4-8) of the p53 gene; these mutations are missense, non-sense, deleti ...
18-2 Modern Evolutionary Classification
... lineage but not in its older members are called derived characters. Derived characters are used to construct a cladogram, a diagram that shows the evolutionary relationship among a group of organisms. ...
... lineage but not in its older members are called derived characters. Derived characters are used to construct a cladogram, a diagram that shows the evolutionary relationship among a group of organisms. ...
Structural and Functional Genomics of Tomato
... 2) Develop deep EST databases from various Solanaceae tissues and shotgun genomic sequencing of other Solanaceae with data integration. 4) Construct a set of interspecific introgression resources (e.g. introgression lines, backcross inbred lines etc.) for all Solanaceae crop species in order to ...
... 2) Develop deep EST databases from various Solanaceae tissues and shotgun genomic sequencing of other Solanaceae with data integration. 4) Construct a set of interspecific introgression resources (e.g. introgression lines, backcross inbred lines etc.) for all Solanaceae crop species in order to ...
GENETICS
... • Pure bred: breed true, offspring like parents • Hybrid: don’t breed true, offspring mixed • Homozygous: genotype with both genes the same (pure bred-DD or dd) • Heterozygous: genotype with one dominant and one recessive gene (hybrid--Dd) • Genotype: gene combo that produces the visible results (PP ...
... • Pure bred: breed true, offspring like parents • Hybrid: don’t breed true, offspring mixed • Homozygous: genotype with both genes the same (pure bred-DD or dd) • Heterozygous: genotype with one dominant and one recessive gene (hybrid--Dd) • Genotype: gene combo that produces the visible results (PP ...
Some No-Nonsense Facts on
... carried by all living organisms. This stored information is used as a "blueprint" or set of instructions for building and maintaining a living ...
... carried by all living organisms. This stored information is used as a "blueprint" or set of instructions for building and maintaining a living ...
Unit 1 DNA and the Genome Summary
... b) Single gene mutations involve the alteration of a DNA nucleotide sequence as a result of the substitution, insertion or deletion of nucleotides. - Single-nucleotide substitutions include: missense, nonsense and splice-site mutations. - Sickle cell anaemia and lactose intolerance are examples of p ...
... b) Single gene mutations involve the alteration of a DNA nucleotide sequence as a result of the substitution, insertion or deletion of nucleotides. - Single-nucleotide substitutions include: missense, nonsense and splice-site mutations. - Sickle cell anaemia and lactose intolerance are examples of p ...
Genetics and Heredity
... Contains the genes that code for inherited traits Stored in the nucleus of an organisms cells Organized into chromosomes Carried by DNA ...
... Contains the genes that code for inherited traits Stored in the nucleus of an organisms cells Organized into chromosomes Carried by DNA ...
Professor Jennifer A. Marshall Graves Fellow of the Australian
... weird because they work better, or is it the result of some horrible evolutionary accident? To follow the evolution of the human X and Y, we compare the chromosomes, genes and DNA in distantly related mammals, and even birds and reptiles. The genomes of Australia’s unique kangaroos and platypus, now ...
... weird because they work better, or is it the result of some horrible evolutionary accident? To follow the evolution of the human X and Y, we compare the chromosomes, genes and DNA in distantly related mammals, and even birds and reptiles. The genomes of Australia’s unique kangaroos and platypus, now ...
Patterns in Development
... • Identity of the segments are determined by homeotic genes – specify the appendages that form on the individual segments ...
... • Identity of the segments are determined by homeotic genes – specify the appendages that form on the individual segments ...
Cross-Curricular Discussion
... 4. Would evolution still happen if there were no transposons, retrotransposons or retroviruses messing with the genome? [Yes, but it would probably be slower, relying on ordinary mutations that arise during DNA replication when cells divide or genetic recombination of chromosomes in a new generati ...
... 4. Would evolution still happen if there were no transposons, retrotransposons or retroviruses messing with the genome? [Yes, but it would probably be slower, relying on ordinary mutations that arise during DNA replication when cells divide or genetic recombination of chromosomes in a new generati ...
May 27, 2017 The Difference Makers
... 4. Would evolution still happen if there were no transposons, retrotransposons or retroviruses messing with the genome? [Yes, but it would probably be slower, relying on ordinary mutations that arise during DNA replication when cells divide or genetic recombination of chromosomes in a new generati ...
... 4. Would evolution still happen if there were no transposons, retrotransposons or retroviruses messing with the genome? [Yes, but it would probably be slower, relying on ordinary mutations that arise during DNA replication when cells divide or genetic recombination of chromosomes in a new generati ...
Gene Clustering - Bioinformatics at School of Informatics, Indiana
... This DB has grouped genes based on the operons they belongs too.Each Uber_Operon gropu represent a rich set of footprints of operon evolution. ...
... This DB has grouped genes based on the operons they belongs too.Each Uber_Operon gropu represent a rich set of footprints of operon evolution. ...
What Darwin Never Knew Hout
... 21.) How many genes are in the human genome? 22.) Research on the fruit fly showed there are “switches” in DNA. What are switches? 23.) How did the lake stickleback fish lose its spikes? 24.) Finch beaks are all made by the same gene, so why are there different shaped beaks? 25.) Define transitional ...
... 21.) How many genes are in the human genome? 22.) Research on the fruit fly showed there are “switches” in DNA. What are switches? 23.) How did the lake stickleback fish lose its spikes? 24.) Finch beaks are all made by the same gene, so why are there different shaped beaks? 25.) Define transitional ...
bchm6280_lect1_16
... • You will be asked to choose 3 genes from your gene lists that you would follow-up on at the bench. – You will be asked to give a rationale for making the choices ...
... • You will be asked to choose 3 genes from your gene lists that you would follow-up on at the bench. – You will be asked to give a rationale for making the choices ...
Presentation
... or more isolated populations. While they are separated, natural selection operates to adapt each population to its environment. If this generates enough change, the two populations may become so different that they cannot interbreed. Similar organisms that have recently evolved into separate species ...
... or more isolated populations. While they are separated, natural selection operates to adapt each population to its environment. If this generates enough change, the two populations may become so different that they cannot interbreed. Similar organisms that have recently evolved into separate species ...
Arrays
... Many microarray experiments have been performed with Yeast. • Genome is completely sequenced and well annotated. • Select a PCR primer pair that amplifies each ORF. • My arrays- all yeast genes represented (70mers). ...
... Many microarray experiments have been performed with Yeast. • Genome is completely sequenced and well annotated. • Select a PCR primer pair that amplifies each ORF. • My arrays- all yeast genes represented (70mers). ...
The Human Genome
... • All people are different • but the DNA of different people only varies for 0.2% or less • So, only up to 2 letters in 1000 are expected to be different. • Evidence in current genomics studies (Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms or SNPs) imply that • on average only 1 letter out of 1400 is different b ...
... • All people are different • but the DNA of different people only varies for 0.2% or less • So, only up to 2 letters in 1000 are expected to be different. • Evidence in current genomics studies (Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms or SNPs) imply that • on average only 1 letter out of 1400 is different b ...
“Command Center” because it houses all the genetic material in every
... Genetic Code: Arrangement of the 4 chemical “letters” on a DNA molecule that can be arranged into words, creating the instructions for an organism ...
... Genetic Code: Arrangement of the 4 chemical “letters” on a DNA molecule that can be arranged into words, creating the instructions for an organism ...
1pt - adamsapbio
... DNA sequences called ___ increase the rate of RNA synthesis after initiation of ...
... DNA sequences called ___ increase the rate of RNA synthesis after initiation of ...
src
... The first gene studied responsible for transformation is src—sarcoma by using experimental strategies, such as hybridization and column chromatography. cDNAsarc corresponded to approximately 16 percent of the viral genome(1600 nucleotides out of a total genomic length of 10,000 nucleotides). This cD ...
... The first gene studied responsible for transformation is src—sarcoma by using experimental strategies, such as hybridization and column chromatography. cDNAsarc corresponded to approximately 16 percent of the viral genome(1600 nucleotides out of a total genomic length of 10,000 nucleotides). This cD ...
Mendel`s Laws of Segregation
... 3. “If the two alleles differ, then one, the dominant allele, is fully expressed in the organism's appearance; the other, the recessive allele, has no noticeable effect on the organism's appearance.” ...
... 3. “If the two alleles differ, then one, the dominant allele, is fully expressed in the organism's appearance; the other, the recessive allele, has no noticeable effect on the organism's appearance.” ...
Genome evolution

Genome evolution is the process by which a genome changes in structure (sequence) or size over time. The study of genome evolution involves multiple fields such as structural analysis of the genome, the study of genomic parasites, gene and ancient genome duplications, polyploidy, and comparative genomics. Genome evolution is a constantly changing and evolving field due to the steadily growing number of sequenced genomes, both prokaryotic and eukaryotic, available to the scientific community and the public at large.