review - StudentAlumniAmbassadors
... birth help researchers determine the effects of genetic and environmental factors on human development? If genetic testing revealed that you had what is almost always a fatal disease, what use would the information have for you? Would it change your career goals? Chosen partner? Choice of ...
... birth help researchers determine the effects of genetic and environmental factors on human development? If genetic testing revealed that you had what is almost always a fatal disease, what use would the information have for you? Would it change your career goals? Chosen partner? Choice of ...
POPULATION GENETICS – 3/27/07
... If they don’t meet those five conditions, what will happen to the population? They will evolve! 3. What are the four causes of microevolution? Genetic drift Natural selection Migration (gene flow) Mutation What are the main ones? Genetic drift and natural selection. 4. What is genetic drift? Changes ...
... If they don’t meet those five conditions, what will happen to the population? They will evolve! 3. What are the four causes of microevolution? Genetic drift Natural selection Migration (gene flow) Mutation What are the main ones? Genetic drift and natural selection. 4. What is genetic drift? Changes ...
Nitrogen Base Pairs
... 9.What is a mutation? Are they always harmful? Permanent change to an organism No create variety ...
... 9.What is a mutation? Are they always harmful? Permanent change to an organism No create variety ...
lecture7
... populations • The principles of population genetics underpin the analysis of genetics of normal biological variation • As an extension, these same principles underpin the analysis of the genetic variation associated with human genetic disease • In the next two weeks, focus on analysis of the genetic ...
... populations • The principles of population genetics underpin the analysis of genetics of normal biological variation • As an extension, these same principles underpin the analysis of the genetic variation associated with human genetic disease • In the next two weeks, focus on analysis of the genetic ...
Human Genome PPT 2013
... Co-dominant alleles: Disorder manifested when two dominant alleles are inherited. Ex: AB (Sickle ...
... Co-dominant alleles: Disorder manifested when two dominant alleles are inherited. Ex: AB (Sickle ...
A-4 Notes
... find out how much of our mixed traits are from nature and how much from nurture. This has led to certain people becoming very sensitive and angry about the findings. ...
... find out how much of our mixed traits are from nature and how much from nurture. This has led to certain people becoming very sensitive and angry about the findings. ...
Genetic Principles
... • The probability of a fit this good by chance is .00007 • Possible that Mendel’s sample size was larger than he reported. ...
... • The probability of a fit this good by chance is .00007 • Possible that Mendel’s sample size was larger than he reported. ...
Name________________ Where does variation come from
... Name________________ Where does variation come from? - Guided Notes _____________ are controlled by genes. Individuals within a population are not _____________, there is _______________ or differences within the populations genes. ________________________: process by which organisms with traits bes ...
... Name________________ Where does variation come from? - Guided Notes _____________ are controlled by genes. Individuals within a population are not _____________, there is _______________ or differences within the populations genes. ________________________: process by which organisms with traits bes ...
Artemis P. Simopoulos, M.D.
... constitution (what today we would call genetics) and of the powers of various foods, both those natural to them and those resulting from human skill (today’s processed food). But eating alone is not enough for health. There must also be exercise, of which the effects must likewise be known. The comb ...
... constitution (what today we would call genetics) and of the powers of various foods, both those natural to them and those resulting from human skill (today’s processed food). But eating alone is not enough for health. There must also be exercise, of which the effects must likewise be known. The comb ...
Exam practice answers 8
... (b) Gametes are sex cells produced for sexual reproduction. During fertilisation, two gametes fuse and restore the diploid number of chromosomes (2n). 4 (a) When a selective force places pressure on the species and the frequency of alleles changes as a result. This changes the phenotype, making the ...
... (b) Gametes are sex cells produced for sexual reproduction. During fertilisation, two gametes fuse and restore the diploid number of chromosomes (2n). 4 (a) When a selective force places pressure on the species and the frequency of alleles changes as a result. This changes the phenotype, making the ...
Chapter 11.2 (Pg. 313-318): Applying Mendel*s Principles
... The Principle of Independent Assortment - Genes for different traits can segregate independently during formation of gametes - Traits that segregate independently do not influence each other’s inheritance - The gene that determines seed shape does not affect gene for seed color ...
... The Principle of Independent Assortment - Genes for different traits can segregate independently during formation of gametes - Traits that segregate independently do not influence each other’s inheritance - The gene that determines seed shape does not affect gene for seed color ...
Candidate Gene Approach
... 1. Maternally supplied genes i.e. the reason why maternal effect screen had to be conducted separately. 2. Involved in patterning/differentiation of internal structures 3. Only first instance of essential function may be scored ...
... 1. Maternally supplied genes i.e. the reason why maternal effect screen had to be conducted separately. 2. Involved in patterning/differentiation of internal structures 3. Only first instance of essential function may be scored ...
3chap23guidedreadingVideo
... 10. What is the relationship between mutation rates and generation span? ...
... 10. What is the relationship between mutation rates and generation span? ...
Health Quiz
... • They are the result of the interaction of several genes. • For instance, phenotypes like high blood pressure (hypertension) are not the result of a single "blood pressure" gene with many alleles (a 120/80allele, a 100/70 allele, a 170/95 allele, etc.) • The phenotype is an interaction between a pe ...
... • They are the result of the interaction of several genes. • For instance, phenotypes like high blood pressure (hypertension) are not the result of a single "blood pressure" gene with many alleles (a 120/80allele, a 100/70 allele, a 170/95 allele, etc.) • The phenotype is an interaction between a pe ...
Name: : ______ Notes 11.3 – Other Patterns of Inheritance THINK
... MULTIPLE ALLELES 11. A gene with more than _______ alleles is said to have _____________ ___________. 12. Fill in the blanks….. ...
... MULTIPLE ALLELES 11. A gene with more than _______ alleles is said to have _____________ ___________. 12. Fill in the blanks….. ...
Genetic Change - Minneota Public Schools
... a. the movement of alleles into and out of a population 2. gene flow b. one of the most powerful agents of genetic change 3. nonrandom mating c. eliminates individuals with average phenotype values 4. genetic drift d. a change in allele frequency because of random occurrences 5. mutation e. the stat ...
... a. the movement of alleles into and out of a population 2. gene flow b. one of the most powerful agents of genetic change 3. nonrandom mating c. eliminates individuals with average phenotype values 4. genetic drift d. a change in allele frequency because of random occurrences 5. mutation e. the stat ...
Directed Reading 17.2 - Blair Community Schools
... _____ 1. genetic equilibrium a. the movement of alleles into and out of a population _____ 2. gene flow b. one of the most powerful agents of genetic change _____ 3. nonrandom mating c. eliminates individuals with average phenotype values _____ 4. genetic drift d. a change in allele frequency becaus ...
... _____ 1. genetic equilibrium a. the movement of alleles into and out of a population _____ 2. gene flow b. one of the most powerful agents of genetic change _____ 3. nonrandom mating c. eliminates individuals with average phenotype values _____ 4. genetic drift d. a change in allele frequency becaus ...
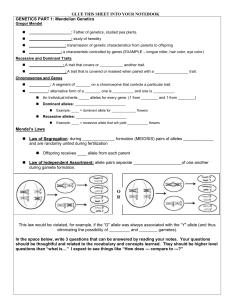
Fill-in Handout - Liberty Union High School District
... This law would be violated, for example, if the “G" allele was always associated with the “Y" allele (and thus eliminating the possibility of _________ and ________ gametes). In the space below, write 3 questions that can be answered by reading your notes. Your questions should be thoughtful and rel ...
... This law would be violated, for example, if the “G" allele was always associated with the “Y" allele (and thus eliminating the possibility of _________ and ________ gametes). In the space below, write 3 questions that can be answered by reading your notes. Your questions should be thoughtful and rel ...
BIOL 6617
... Course description in English: “Discussion of selected topics in genetics.” This course provides exposure to advanced topics in the field of genetics which are not otherwise covered in departmental courses. An emphasis is given to the area of complex genetic interactions between genes and their envi ...
... Course description in English: “Discussion of selected topics in genetics.” This course provides exposure to advanced topics in the field of genetics which are not otherwise covered in departmental courses. An emphasis is given to the area of complex genetic interactions between genes and their envi ...
A genome wide association experiment for gallstone
... The disease: Gallstones represent a frequent and costly health problem: 10 - 15% of the population are affected and over 170,000 cholecystectomies are performed annually in Germany. Essentially, the causal mechanisms of gallstone generation are not well understood and thus no real treatment options ...
... The disease: Gallstones represent a frequent and costly health problem: 10 - 15% of the population are affected and over 170,000 cholecystectomies are performed annually in Germany. Essentially, the causal mechanisms of gallstone generation are not well understood and thus no real treatment options ...
Biology Notes Evolution
... 1. Genotype variation (& isolation caused by type one) leading to phenotype variation o Eg. Galapagos island finches 2. Inbreeding o The mating of closely related individuals o Can happen due to geographic isolation (type 1) or a genetic bottleneck o Religious and sociocultural reasons for this in h ...
... 1. Genotype variation (& isolation caused by type one) leading to phenotype variation o Eg. Galapagos island finches 2. Inbreeding o The mating of closely related individuals o Can happen due to geographic isolation (type 1) or a genetic bottleneck o Religious and sociocultural reasons for this in h ...
Figure S1. Architecture of genetic elements in bacteria different of K
... We performed the same analysis as for E. coli strain K-12 MG1655 in E. coli strains K-12 W3110 and BL21 (DE3), in Salmonella typhimurium SL1344, and in Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains PA14 and PAO1 (see, Table S2 and S3). A) Consensus architecture of E. coli K12 MG1655, B) Summary o ...
... We performed the same analysis as for E. coli strain K-12 MG1655 in E. coli strains K-12 W3110 and BL21 (DE3), in Salmonella typhimurium SL1344, and in Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains PA14 and PAO1 (see, Table S2 and S3). A) Consensus architecture of E. coli K12 MG1655, B) Summary o ...