Document
... The rates of enzyme-catalyzed reactions are altered by activators and inhibitors (a.k.a. effector molecules). (1) Allosteric enzymes: have more than one site, where effector binding at one site induces a conformational change in the enzyme, altering its affinity for a substrate. An allosteric activa ...
... The rates of enzyme-catalyzed reactions are altered by activators and inhibitors (a.k.a. effector molecules). (1) Allosteric enzymes: have more than one site, where effector binding at one site induces a conformational change in the enzyme, altering its affinity for a substrate. An allosteric activa ...
The ADP-dependent sugar kinase family
... duplication event (7). Although it is a very suggestive hypothesis, it was never demonstrated. Recent studies about the evolution of this protein family using the Bayesian method of phylogenetic inference and real value evolutionary trace showed that the evolutionary story of this family is much mor ...
... duplication event (7). Although it is a very suggestive hypothesis, it was never demonstrated. Recent studies about the evolution of this protein family using the Bayesian method of phylogenetic inference and real value evolutionary trace showed that the evolutionary story of this family is much mor ...
Supplementary Data
... T161A: Thr161 (Arg19) is located at the same interface as Asp159 (previous mutation). Replacement by alanine may incur the loss of a stabilizing hydrogen bond, destabilizing the enzyme. D190V: Replacing Asp190 (Asp47) by valine places an unfavorable, hydrophobic residue onto the surface of eALAS, de ...
... T161A: Thr161 (Arg19) is located at the same interface as Asp159 (previous mutation). Replacement by alanine may incur the loss of a stabilizing hydrogen bond, destabilizing the enzyme. D190V: Replacing Asp190 (Asp47) by valine places an unfavorable, hydrophobic residue onto the surface of eALAS, de ...
key
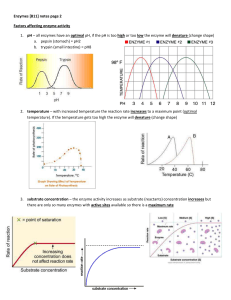
... 1. pH – all enzymes have an optimal pH, if the pH is too high or too low the enzyme will denature (change shape) a. pepsin (stomach) = pH2 ...
... 1. pH – all enzymes have an optimal pH, if the pH is too high or too low the enzyme will denature (change shape) a. pepsin (stomach) = pH2 ...
Enzymes
... There are a great many factors which affect the activity of enzymes. • They are denatured by high temperatures and extremes of pH, both of which alter the structure of the active site, preventing the substrate from binding with the enzyme. • The presence of inhibitors can also have an effect on enzy ...
... There are a great many factors which affect the activity of enzymes. • They are denatured by high temperatures and extremes of pH, both of which alter the structure of the active site, preventing the substrate from binding with the enzyme. • The presence of inhibitors can also have an effect on enzy ...
Document
... • The fact that metabolic enzymes are not well conserved does not mean that they were not there! • Scaffolds (pre-RNA, primitive metabolic reactions) may have disappeared without leaving a trace behind!!! • A more synthetic approach is needed • General evolutionary mechanisms must be sought ...
... • The fact that metabolic enzymes are not well conserved does not mean that they were not there! • Scaffolds (pre-RNA, primitive metabolic reactions) may have disappeared without leaving a trace behind!!! • A more synthetic approach is needed • General evolutionary mechanisms must be sought ...
Three Dimensional Protein Structures
... The positive cooperativity of O2 binding to Hb The effect of the ligand-binding state of one heme on the ligand-binding affinity of another. The Fe iron is about 0.6 Å out of the heme plane in the deoxy state. When oxygen binds it pulls the iron back into the heme plane. Since the proximal His F8 i ...
... The positive cooperativity of O2 binding to Hb The effect of the ligand-binding state of one heme on the ligand-binding affinity of another. The Fe iron is about 0.6 Å out of the heme plane in the deoxy state. When oxygen binds it pulls the iron back into the heme plane. Since the proximal His F8 i ...
Inborn Errors of Metabolism
... but rather later in childhood. Non-life threatening if controlled. – If not, brain damage can occur. ...
... but rather later in childhood. Non-life threatening if controlled. – If not, brain damage can occur. ...
Gene Section ADAM17 (ADAM metallopeptidase domain 17) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... thought to be important in regulation of the enzyme activity because of its potential tyrosine phosphorylation site, but recent studies showed that overexpressed ADAM17 lacking its cytoplasmic domain was able to cleave TNFalpha upon phorbolester stimulation (Reddy et al., 2000; Horiuchi et al., 2007 ...
... thought to be important in regulation of the enzyme activity because of its potential tyrosine phosphorylation site, but recent studies showed that overexpressed ADAM17 lacking its cytoplasmic domain was able to cleave TNFalpha upon phorbolester stimulation (Reddy et al., 2000; Horiuchi et al., 2007 ...
Interfering with enzymes (poisons and drugs)
... • “A non-protein organic molecule that forms a permanent part of a functioning protein molecule.” • E.g. zinc-based prosthetic group in carbonic anhydrase – where have we met this enzyme? ...
... • “A non-protein organic molecule that forms a permanent part of a functioning protein molecule.” • E.g. zinc-based prosthetic group in carbonic anhydrase – where have we met this enzyme? ...
Enzyme_Activity_and_Regulation_Internet_Activity updated 1
... Directions: You are going to view a series of on-line animations to help you better understand enzymes. Log onto http://www.4teachers.org/ and click onto Track Star icon along the right margin. View Track # 240347. The password is “ferg”. You should view the track in text. Visit each of the sites; t ...
... Directions: You are going to view a series of on-line animations to help you better understand enzymes. Log onto http://www.4teachers.org/ and click onto Track Star icon along the right margin. View Track # 240347. The password is “ferg”. You should view the track in text. Visit each of the sites; t ...
Chapter 12. Strategies for metabolic control and their application to
... The structure of Types I-III isozymes consists of two globular halves -the N-terminal and C-terminal regions- held together by a connecting helix and a few hydrogen bonds (100 kDa). The structure of each half is similar to that of yeast hexokinase, which consists of two regions, i.e. the large and t ...
... The structure of Types I-III isozymes consists of two globular halves -the N-terminal and C-terminal regions- held together by a connecting helix and a few hydrogen bonds (100 kDa). The structure of each half is similar to that of yeast hexokinase, which consists of two regions, i.e. the large and t ...
Table S2 Candidate drug target genes. Gene symbol Gene title
... and Ty1 expression; Ste12p activation of most filamentation gene promoters depends on Tec1p and Tec1p transcriptional activity is dependent on its association with Ste12p; binds to TCS elements upstream of filamentation genes, which are regulated by Tec1p/Ste12p/Dig1p complex; competes with Dig2p fo ...
... and Ty1 expression; Ste12p activation of most filamentation gene promoters depends on Tec1p and Tec1p transcriptional activity is dependent on its association with Ste12p; binds to TCS elements upstream of filamentation genes, which are regulated by Tec1p/Ste12p/Dig1p complex; competes with Dig2p fo ...
Enzymes - CynthiaJankowski
... reactants of the reaction that it is catalyzing. • The reactant an enzyme works on is called a substrate. • The substrate binds to the active site to make the enzyme active. • Factors such as temperature, and pH affect enzyme activity. ...
... reactants of the reaction that it is catalyzing. • The reactant an enzyme works on is called a substrate. • The substrate binds to the active site to make the enzyme active. • Factors such as temperature, and pH affect enzyme activity. ...
Reading GuideMetabolismchapter6
... idea of the big picture of metabolism, what pathways are operating within a type of metabolism (fermentation, aerobic respiration, or anaerobic respiration) and the final products from each of them. This chapter covers the processes involved in bacterial metabolism, both catabolic and anabolic react ...
... idea of the big picture of metabolism, what pathways are operating within a type of metabolism (fermentation, aerobic respiration, or anaerobic respiration) and the final products from each of them. This chapter covers the processes involved in bacterial metabolism, both catabolic and anabolic react ...
Enzymes HW Key
... 4. Define active site, allosteric site, substrate, ligand. Active site: where the substrate binds to the enzyme. where the reaction takes place. allosteric site: a site other than the active site where regulatory molecules bind to the enzyme. substrate: the reactant of the enzyme reaction. binds to ...
... 4. Define active site, allosteric site, substrate, ligand. Active site: where the substrate binds to the enzyme. where the reaction takes place. allosteric site: a site other than the active site where regulatory molecules bind to the enzyme. substrate: the reactant of the enzyme reaction. binds to ...
chapter 20
... of the reaction as the available enzyme molecules become saturated with substrate? 6. Discuss differences between competitive and noncompetitive inhibitors of enzymes, and reversible and irreversible inhibitors of enzymes. 7. Enzyme activity is controlled by means of zymogens and feedback control. D ...
... of the reaction as the available enzyme molecules become saturated with substrate? 6. Discuss differences between competitive and noncompetitive inhibitors of enzymes, and reversible and irreversible inhibitors of enzymes. 7. Enzyme activity is controlled by means of zymogens and feedback control. D ...
Cell Physiology
... Other substances may bind to the enzyme and modify its behavior; either as an activator or inhibitor If the substance competes with the substrate for the active site; it is a competitive inhibitor If it binds elsewhere and changes the enzymes shape at its active site then it is a noncompetitive inhi ...
... Other substances may bind to the enzyme and modify its behavior; either as an activator or inhibitor If the substance competes with the substrate for the active site; it is a competitive inhibitor If it binds elsewhere and changes the enzymes shape at its active site then it is a noncompetitive inhi ...
Kubota - Rice CAAM Department
... spines. In this project, we simulate intracellular environment and chemical interactions between Ca2+ signaling molecules and understand the possible mechanism that controls molecular diffusions in neurons. In addition, we will construct mathematical framework of anomalous diffusions in neuronal cel ...
... spines. In this project, we simulate intracellular environment and chemical interactions between Ca2+ signaling molecules and understand the possible mechanism that controls molecular diffusions in neurons. In addition, we will construct mathematical framework of anomalous diffusions in neuronal cel ...
Enzyme_Classificn
... ENZYME CLASSIFICATION ANSWERS TO IN-CLASS EXERCISE (1) TRANSFERASE (HEXOKINASE) (2) OXIDOREDUCTASE (ALCOHOL DEHYDROGENASE) (3) HYDROLASE (ATPase) (4) LYASE (PYRUVATE DECARBOXYLASE) (5) LIGASE (PYRUVATE CARBOXYLASE) (6) ISOMERASE (MALEATE ISOMERASE) (7) HYDROLASE (PHOSPHOENOLPYRUVATE ...
... ENZYME CLASSIFICATION ANSWERS TO IN-CLASS EXERCISE (1) TRANSFERASE (HEXOKINASE) (2) OXIDOREDUCTASE (ALCOHOL DEHYDROGENASE) (3) HYDROLASE (ATPase) (4) LYASE (PYRUVATE DECARBOXYLASE) (5) LIGASE (PYRUVATE CARBOXYLASE) (6) ISOMERASE (MALEATE ISOMERASE) (7) HYDROLASE (PHOSPHOENOLPYRUVATE ...