6.2.5 Capacitors
... In teams of two to three, you will charge and discharge capacitors to simulate a camera flash. Make notes and build the circuit as shown in the Capacitors presentation. There are many kinds of capacitors, but they all do the same thing: __________________________. The simplest capacitor is two _____ ...
... In teams of two to three, you will charge and discharge capacitors to simulate a camera flash. Make notes and build the circuit as shown in the Capacitors presentation. There are many kinds of capacitors, but they all do the same thing: __________________________. The simplest capacitor is two _____ ...
- University of Bath Opus
... The properties of standard components are categorised using an automated test rig that places a charge on the components being tested and then measures the residual charge at a fixed frequency over time. The residual charge information is passed to MATLAB where the information is processed to produc ...
... The properties of standard components are categorised using an automated test rig that places a charge on the components being tested and then measures the residual charge at a fixed frequency over time. The residual charge information is passed to MATLAB where the information is processed to produc ...
Electric Force - Parkland College
... -In the very short term, you can treat the capacitor like a wire. R=0 -In the long term, you can treat the capacitor like a break. R = Infinite ...
... -In the very short term, you can treat the capacitor like a wire. R=0 -In the long term, you can treat the capacitor like a break. R = Infinite ...
ConcepTest 25.1 Capacitors
... a potential difference of 400 V and is then disconnected from the charging battery. If the plate spacing is now doubled (without changing Q), what is the new value of the voltage? Once the battery is disconnected, Q has to remain constant, constant since no charge can flow either to or from the batt ...
... a potential difference of 400 V and is then disconnected from the charging battery. If the plate spacing is now doubled (without changing Q), what is the new value of the voltage? Once the battery is disconnected, Q has to remain constant, constant since no charge can flow either to or from the batt ...
Process
... capacitor. When electric insulation of inner element or aluminum case is required, proper materials shall be selected. ...
... capacitor. When electric insulation of inner element or aluminum case is required, proper materials shall be selected. ...
VARIABLE CAPACITOR BASICS - IDC
... In mechanically controlled variable capacitors, the distance between the plates, or the amount of plate surface area which overlaps, can be changed. The most common form arranges a group of semicircular metal plates on a rotary axis (“rotor”) that are positioned in the gaps between a set of stationa ...
... In mechanically controlled variable capacitors, the distance between the plates, or the amount of plate surface area which overlaps, can be changed. The most common form arranges a group of semicircular metal plates on a rotary axis (“rotor”) that are positioned in the gaps between a set of stationa ...
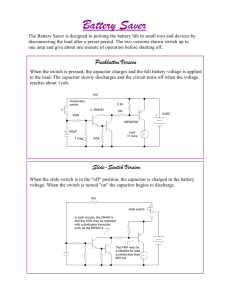
Battery Saver
... When the switch is pressed, the capacitor charges and the full battery voltage is applied to the load. The capacitor slowly discharges and the circuit turns off when the voltage ...
... When the switch is pressed, the capacitor charges and the full battery voltage is applied to the load. The capacitor slowly discharges and the circuit turns off when the voltage ...
Chap. 17 Conceptual Modules Giancoli
... voltage across C1 is 10 V and the voltage across C2 and C3 each is 5 V. Since Q = CV and C is the same for all the capacitors, then since V1 > V2 therefore Q1 > Q2. ...
... voltage across C1 is 10 V and the voltage across C2 and C3 each is 5 V. Since Q = CV and C is the same for all the capacitors, then since V1 > V2 therefore Q1 > Q2. ...
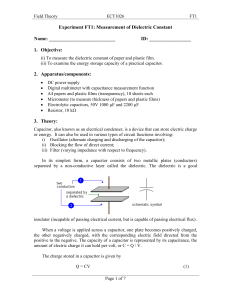
Experiment FT1
... plates (up to 10 sheets). Using a micrometer, measure the thickness for 10 sheets of papers. Assuming the thickness for every sheet is the same, calculate the thickness for 1 sheet of paper. Plot the graph of C versus 1/d and determine the relative dielectric constant (εr) of the paper. Repeat steps ...
... plates (up to 10 sheets). Using a micrometer, measure the thickness for 10 sheets of papers. Assuming the thickness for every sheet is the same, calculate the thickness for 1 sheet of paper. Plot the graph of C versus 1/d and determine the relative dielectric constant (εr) of the paper. Repeat steps ...
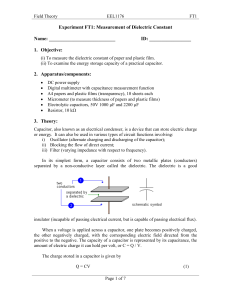
Experiment FT1
... plates (up to 10 sheets). Using a micrometer, measure the thickness for 10 sheets of papers. Assuming the thickness for every sheet is the same, calculate the thickness for 1 sheet of paper. Plot the graph of C versus 1/d and determine the relative dielectric constant (εr) of the paper. Repeat steps ...
... plates (up to 10 sheets). Using a micrometer, measure the thickness for 10 sheets of papers. Assuming the thickness for every sheet is the same, calculate the thickness for 1 sheet of paper. Plot the graph of C versus 1/d and determine the relative dielectric constant (εr) of the paper. Repeat steps ...
EC notes - Emanthra.com
... Mica capacitors are constructed from plates of aluminum foil separated by sheets of mica. The plates are connected to two electrodes. Mica capacitors have excellent characteristics under stress of temperature variations and high voltage applications. Electrolytic Capacitors ...
... Mica capacitors are constructed from plates of aluminum foil separated by sheets of mica. The plates are connected to two electrodes. Mica capacitors have excellent characteristics under stress of temperature variations and high voltage applications. Electrolytic Capacitors ...
Experiment FT1
... to 10 sheets). Using a micrometer, measure the thickness for 10 sheets of papers. Assuming the thickness for every sheet is the same, calculate the thickness for 1 sheet of paper. Plot the graph of C versus 1/d and determine the relative dielectric constant (εr) of the ...
... to 10 sheets). Using a micrometer, measure the thickness for 10 sheets of papers. Assuming the thickness for every sheet is the same, calculate the thickness for 1 sheet of paper. Plot the graph of C versus 1/d and determine the relative dielectric constant (εr) of the ...
IPDiA Ultra Thin Low ESR/ESL Silicon Decoupling Capacitors
... In order to anticipate the demand for more miniaturization and signal integrity over a wide range of frequencies in the decoupling applications, IPDiA adds to its silicon passive component library some ultra low ESR/ESL structures, in low profile form factor. These new silicon capacitors enable to d ...
... In order to anticipate the demand for more miniaturization and signal integrity over a wide range of frequencies in the decoupling applications, IPDiA adds to its silicon passive component library some ultra low ESR/ESL structures, in low profile form factor. These new silicon capacitors enable to d ...
Chapter 26
... In general, capacitors act as energy reservoirs that can be slowly charged and then discharged quickly to provide large amounts of energy in a short pulse ...
... In general, capacitors act as energy reservoirs that can be slowly charged and then discharged quickly to provide large amounts of energy in a short pulse ...
Capacitor
.jpg?width=300)
A capacitor (originally known as a condenser) is a passive two-terminal electrical component used to store electrical energy temporarily in an electric field. The forms of practical capacitors vary widely, but all contain at least two electrical conductors (plates) separated by a dielectric (i.e. an insulator that can store energy by becoming polarized). The conductors can be thin films, foils or sintered beads of metal or conductive electrolyte, etc. The nonconducting dielectric acts to increase the capacitor's charge capacity. A dielectric can be glass, ceramic, plastic film, air, vacuum, paper, mica, oxide layer etc. Capacitors are widely used as parts of electrical circuits in many common electrical devices. Unlike a resistor, an ideal capacitor does not dissipate energy. Instead, a capacitor stores energy in the form of an electrostatic field between its plates.When there is a potential difference across the conductors (e.g., when a capacitor is attached across a battery), an electric field develops across the dielectric, causing positive charge +Q to collect on one plate and negative charge −Q to collect on the other plate. If a battery has been attached to a capacitor for a sufficient amount of time, no current can flow through the capacitor. However, if a time-varying voltage is applied across the leads of the capacitor, a displacement current can flow.An ideal capacitor is characterized by a single constant value, its capacitance. Capacitance is defined as the ratio of the electric charge Q on each conductor to the potential difference V between them. The SI unit of capacitance is the farad (F), which is equal to one coulomb per volt (1 C/V). Typical capacitance values range from about 1 pF (10−12 F) to about 1 mF (10−3 F).The larger the surface area of the ""plates"" (conductors) and the narrower the gap between them, the greater the capacitance is. In practice, the dielectric between the plates passes a small amount of leakage current and also has an electric field strength limit, known as the breakdown voltage. The conductors and leads introduce an undesired inductance and resistance.Capacitors are widely used in electronic circuits for blocking direct current while allowing alternating current to pass. In analog filter networks, they smooth the output of power supplies. In resonant circuits they tune radios to particular frequencies. In electric power transmission systems, they stabilize voltage and power flow.