ECE 3041 - ECE Users Pages
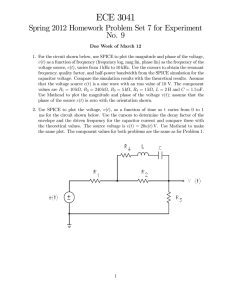
... that the voltage source () is a sine wave with an rms value of 10 V. The component values are 1 = 10 kΩ, 2 = 240 kΩ, 3 = 5 kΩ, 4 = 1 kΩ, = 2 H and = 15 nF. Use Mathcad to plot the magnitude and phase of the voltage (); assume that the phase of the source () is zero with the orientatio ...
... that the voltage source () is a sine wave with an rms value of 10 V. The component values are 1 = 10 kΩ, 2 = 240 kΩ, 3 = 5 kΩ, 4 = 1 kΩ, = 2 H and = 15 nF. Use Mathcad to plot the magnitude and phase of the voltage (); assume that the phase of the source () is zero with the orientatio ...
PDN Planning and Capacitor Selection Part 1
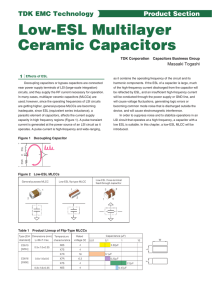
... noise generated at the initial di/dt energy transfers. Large capacitance value ceramics provide effective decoupling at about 25% of the nominal capacitance value compared to standard tantalums. This is because the capacitance of the ceramic is more stable with increasing frequency, while that of th ...
... noise generated at the initial di/dt energy transfers. Large capacitance value ceramics provide effective decoupling at about 25% of the nominal capacitance value compared to standard tantalums. This is because the capacitance of the ceramic is more stable with increasing frequency, while that of th ...
Zinger - Ceramic Ind. Coatings
... world’s leading suppliers of electrical ceramic capacitors with about 12% of the market. In 1995, KEMET began a program using the Microfluidizer processor that sharply reduced the amount of dangerous chemical waste that needed to be dispose of, and in the process saved itself over $1 million a year ...
... world’s leading suppliers of electrical ceramic capacitors with about 12% of the market. In 1995, KEMET began a program using the Microfluidizer processor that sharply reduced the amount of dangerous chemical waste that needed to be dispose of, and in the process saved itself over $1 million a year ...
Considerations for Polymer Capacitors in Extreme Environments
... offer a number of advantages over other capacitor types when used in extreme environments. KEMET continues to investigate the behaviors of polymer-tantalum capacitors in extreme environments. If you have questions about using these capacitors in a specific environment or specific application, we sug ...
... offer a number of advantages over other capacitor types when used in extreme environments. KEMET continues to investigate the behaviors of polymer-tantalum capacitors in extreme environments. If you have questions about using these capacitors in a specific environment or specific application, we sug ...
Ganpat University - UV Patel College of Engineering
... Learn to predict the behavior of any electrical and magnetic circuits. Distinguish between DC, AC, single phase and three-phase AC supply systems, highlighting the advantages and disadvantages of the different systems. Apply basic electric laws in solving circuit problems and able to perform power c ...
... Learn to predict the behavior of any electrical and magnetic circuits. Distinguish between DC, AC, single phase and three-phase AC supply systems, highlighting the advantages and disadvantages of the different systems. Apply basic electric laws in solving circuit problems and able to perform power c ...
How the Desulfator Really Works Hi all! Let me introduce myself. I
... I was prepared to refute the “resonant frequency” theory; however I think everyone will agree it is now debunked. In July of 2005 Don Denhardt is quoted as saying, "The sulfate crystals do not vibrate or resonate. That was a theory proposed initially but has since been debunked…In the end, it's the ...
... I was prepared to refute the “resonant frequency” theory; however I think everyone will agree it is now debunked. In July of 2005 Don Denhardt is quoted as saying, "The sulfate crystals do not vibrate or resonate. That was a theory proposed initially but has since been debunked…In the end, it's the ...
RC Circuits tutorial
... 3. At the instant the switch is closed – you have the initial conditions for the circuit. Use the loop equation and knowledge of circuits to determine the initial value for: I= Vc = Vr = Qc = 4. Describe the changes in each of the initial values as current flows in the circuit – Qc Vc Vr ...
... 3. At the instant the switch is closed – you have the initial conditions for the circuit. Use the loop equation and knowledge of circuits to determine the initial value for: I= Vc = Vr = Qc = 4. Describe the changes in each of the initial values as current flows in the circuit – Qc Vc Vr ...
BSMJ series self-healing LV Shunt capacitors
... a、Usage environment:surrounding temperaturt is -25℃~+50℃the humidity is less than 85% the altitude is below 2000m. b、Rated voltage:0.23~1.2kV,AC. c、Rated capacity:1~60kvar. d、Capacity deviation:0~+10%. e 、 Tangent of the dielectric loss angle:In the power frequency rated voltage,20℃is less than 0.2% ...
... a、Usage environment:surrounding temperaturt is -25℃~+50℃the humidity is less than 85% the altitude is below 2000m. b、Rated voltage:0.23~1.2kV,AC. c、Rated capacity:1~60kvar. d、Capacity deviation:0~+10%. e 、 Tangent of the dielectric loss angle:In the power frequency rated voltage,20℃is less than 0.2% ...
Here are the second exam and solutions for 2015.
... immediately when the switch is closed compare to when it has been closed for a very long time? When the switch is closed, there is no charge yet in the capacitor and current flow through it as if it were a wire. After a certain amount of time, the capacitor is fully charged and no current flows thro ...
... immediately when the switch is closed compare to when it has been closed for a very long time? When the switch is closed, there is no charge yet in the capacitor and current flow through it as if it were a wire. After a certain amount of time, the capacitor is fully charged and no current flows thro ...
Capacitance graphs support
... Introduction Capacitors are electronic components that store charge and so can be used in time delay circuits. For example, as you open your front door there is a delay (giving you a chance to enter the correct code) before the burglar alarm goes off. Time delay circuits work with a combination of a ...
... Introduction Capacitors are electronic components that store charge and so can be used in time delay circuits. For example, as you open your front door there is a delay (giving you a chance to enter the correct code) before the burglar alarm goes off. Time delay circuits work with a combination of a ...
Chapter_4_Lecture_PowerPoint
... phasor notation, and vice versa, and represent circuits using impedances. ...
... phasor notation, and vice versa, and represent circuits using impedances. ...
difference between run and start capacitors
... DIFFERENCE BETWEEN RUN AND START CAPACITORS The simplest way to explain the mechanics of a capacitor would be to compare it to a battery; both store and release electricity. Capacitors are charged with electricity then release its stored energy at a rate of sixty times per second in a 60 cycle alter ...
... DIFFERENCE BETWEEN RUN AND START CAPACITORS The simplest way to explain the mechanics of a capacitor would be to compare it to a battery; both store and release electricity. Capacitors are charged with electricity then release its stored energy at a rate of sixty times per second in a 60 cycle alter ...
Combinations of Capacitors
... Capacitors store charge and energy. A battery must do work to move electrons from one plate to the other. The work done to move a small charge q across a voltage V is W = V·q. As the charge increases, V increases so the work to bring q increases. The energy (U) stored on a capacitor is given by ...
... Capacitors store charge and energy. A battery must do work to move electrons from one plate to the other. The work done to move a small charge q across a voltage V is W = V·q. As the charge increases, V increases so the work to bring q increases. The energy (U) stored on a capacitor is given by ...
Capacitor
.jpg?width=300)
A capacitor (originally known as a condenser) is a passive two-terminal electrical component used to store electrical energy temporarily in an electric field. The forms of practical capacitors vary widely, but all contain at least two electrical conductors (plates) separated by a dielectric (i.e. an insulator that can store energy by becoming polarized). The conductors can be thin films, foils or sintered beads of metal or conductive electrolyte, etc. The nonconducting dielectric acts to increase the capacitor's charge capacity. A dielectric can be glass, ceramic, plastic film, air, vacuum, paper, mica, oxide layer etc. Capacitors are widely used as parts of electrical circuits in many common electrical devices. Unlike a resistor, an ideal capacitor does not dissipate energy. Instead, a capacitor stores energy in the form of an electrostatic field between its plates.When there is a potential difference across the conductors (e.g., when a capacitor is attached across a battery), an electric field develops across the dielectric, causing positive charge +Q to collect on one plate and negative charge −Q to collect on the other plate. If a battery has been attached to a capacitor for a sufficient amount of time, no current can flow through the capacitor. However, if a time-varying voltage is applied across the leads of the capacitor, a displacement current can flow.An ideal capacitor is characterized by a single constant value, its capacitance. Capacitance is defined as the ratio of the electric charge Q on each conductor to the potential difference V between them. The SI unit of capacitance is the farad (F), which is equal to one coulomb per volt (1 C/V). Typical capacitance values range from about 1 pF (10−12 F) to about 1 mF (10−3 F).The larger the surface area of the ""plates"" (conductors) and the narrower the gap between them, the greater the capacitance is. In practice, the dielectric between the plates passes a small amount of leakage current and also has an electric field strength limit, known as the breakdown voltage. The conductors and leads introduce an undesired inductance and resistance.Capacitors are widely used in electronic circuits for blocking direct current while allowing alternating current to pass. In analog filter networks, they smooth the output of power supplies. In resonant circuits they tune radios to particular frequencies. In electric power transmission systems, they stabilize voltage and power flow.