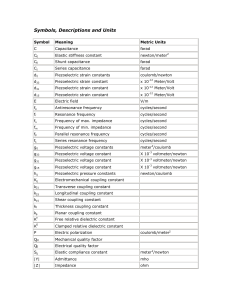
Symbols used at this site - Boston Piezo
... Coupling Coefficient (k): A dimensionless number related to the ratio of the energy stored in the mechanical and electrical portions of the material. The first subscript indicates the direction of the electric field and the second indicates the direction of the mechanical strain, expressed in percen ...
... Coupling Coefficient (k): A dimensionless number related to the ratio of the energy stored in the mechanical and electrical portions of the material. The first subscript indicates the direction of the electric field and the second indicates the direction of the mechanical strain, expressed in percen ...
schematic-symbols-page-1
... circuit, and the third contact, attached to the output of the circuit, is usually a movable terminal that slides across the resistance element, effectively dividing it into two resistors. An electrical device consisting of two conducting plates separated by an electrical insulator (the dielectric), ...
... circuit, and the third contact, attached to the output of the circuit, is usually a movable terminal that slides across the resistance element, effectively dividing it into two resistors. An electrical device consisting of two conducting plates separated by an electrical insulator (the dielectric), ...
MAX3250 ±50V Isolated, 3.0V to 5.5V, 250kbps, 2 Tx/2 Rx, RS-232 Transceiver
... The MAX3250 is powered by a single 3V to 5.5V supply on the logic side. Power is transferred from the logic side to the isolated side by ±100V external capacitors. The MAX3250 has two receivers (Rx) and two drivers (Tx) and is guaranteed to run at data rates of 250kbps while maintaining RS-232 outpu ...
... The MAX3250 is powered by a single 3V to 5.5V supply on the logic side. Power is transferred from the logic side to the isolated side by ±100V external capacitors. The MAX3250 has two receivers (Rx) and two drivers (Tx) and is guaranteed to run at data rates of 250kbps while maintaining RS-232 outpu ...
Lab 1
... coil due to Faraday's Law of Induction: N (where is the magnitude of the dt electromotive force (in volts), N is the number of turns of wire and B is the magnetic flux (in webers) through a single loop). It is assumed that coil is a short circuit for DC and has purely imaginary frequency-dep ...
... coil due to Faraday's Law of Induction: N (where is the magnitude of the dt electromotive force (in volts), N is the number of turns of wire and B is the magnetic flux (in webers) through a single loop). It is assumed that coil is a short circuit for DC and has purely imaginary frequency-dep ...
Input Filter Design of a Mains Connected Matrix
... close as possible to the converter input, in order to allow the decoupling between the line inductances and the converter switching circuits. The introduction of these capacitors, together with the mains inductors, results in a second order filter [4]. To guarantee that the resultant filter has the ...
... close as possible to the converter input, in order to allow the decoupling between the line inductances and the converter switching circuits. The introduction of these capacitors, together with the mains inductors, results in a second order filter [4]. To guarantee that the resultant filter has the ...
OPTIMIZACIN EN EL DISEO DE DISPOSITIVOS RF APLICADOS EN
... In practice, if the frequency response is measured as function of the control voltage at a constant bias voltage VDC, the curve shown in Fig. 7 results. The response corresponds to the nine-stage VCO reported in [7]. This result shows that the VCO operate correctly at low bias voltages. A common fig ...
... In practice, if the frequency response is measured as function of the control voltage at a constant bias voltage VDC, the curve shown in Fig. 7 results. The response corresponds to the nine-stage VCO reported in [7]. This result shows that the VCO operate correctly at low bias voltages. A common fig ...
APER
... A DEG is, in essence, a mechano-capacitive device creating comprise relatively few moving parts and because large elaselectrical energy by transferring charge from a low to high tomer sheets can be mass produced. Demonstrations of harvoltage. Since the capacitance of a dielectric elastomer (DE) vest ...
... A DEG is, in essence, a mechano-capacitive device creating comprise relatively few moving parts and because large elaselectrical energy by transferring charge from a low to high tomer sheets can be mass produced. Demonstrations of harvoltage. Since the capacitance of a dielectric elastomer (DE) vest ...
Evaluates: MAX2620 MAX2620 Evaluation Kit ________________General Description ____________________________Features
... The resonator tank circuit is critical in determining VCO performance. It typically contains a varactor (voltagevariable capacitance) for voltage-tuning the center frequency. For best performance, use high-Q components and choose values carefully. The external resonant circuit on the MAX2620 EV kit ...
... The resonator tank circuit is critical in determining VCO performance. It typically contains a varactor (voltagevariable capacitance) for voltage-tuning the center frequency. For best performance, use high-Q components and choose values carefully. The external resonant circuit on the MAX2620 EV kit ...
Component7 - Glow Blogs
... Capacitors are electronic components that store electricity for short periods of time within electronic circuits or networks. They are made from two metal plates or films separated by an insulator. In many capacitors, film is used so that the layers of metal film and insulator can be wound into a cy ...
... Capacitors are electronic components that store electricity for short periods of time within electronic circuits or networks. They are made from two metal plates or films separated by an insulator. In many capacitors, film is used so that the layers of metal film and insulator can be wound into a cy ...
EUP3651 4-Channel, 1X/1.5X Charge Pump White LED Driver
... TDFN exposed pad (TAB) must be connected to the ground plane underneath. The use of multiple via improves the package heat dissipation. ...
... TDFN exposed pad (TAB) must be connected to the ground plane underneath. The use of multiple via improves the package heat dissipation. ...
RF Filtering for Audio Amplifier Circuits
... important than ever. Audio amplifiers are used in everything from car and home stereos to portable CD devices and MP3 players. Any device that outputs sound to a speaker requires an audio amplifier and their use has increased dramatically along with the growing numbers of consumer electronic devices ...
... important than ever. Audio amplifiers are used in everything from car and home stereos to portable CD devices and MP3 players. Any device that outputs sound to a speaker requires an audio amplifier and their use has increased dramatically along with the growing numbers of consumer electronic devices ...
Characterization of atomic layer deposition HfO2, Al2O3
... deposition (LPCVD), plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PECVD), and atomic layer deposition (ALD).16–24 One of the most common methods to deposit MIM capacitor dielectric in the semiconductor industry is the PECVD method. The films deposited using this method typically result in relatively go ...
... deposition (LPCVD), plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PECVD), and atomic layer deposition (ALD).16–24 One of the most common methods to deposit MIM capacitor dielectric in the semiconductor industry is the PECVD method. The films deposited using this method typically result in relatively go ...
1MHz, 6A Integrated Switch Synchronous Buck Regulator
... switch, synchronous buck (step-down) regulator. The MIC22600 is optimized for highest efficiency and achieves more than 90% efficiency, while still switching at 1MHz over a broad load range with only 1µH inductor and down to 47µF output capacitor. The ultra-high-speed control loop keeps the output v ...
... switch, synchronous buck (step-down) regulator. The MIC22600 is optimized for highest efficiency and achieves more than 90% efficiency, while still switching at 1MHz over a broad load range with only 1µH inductor and down to 47µF output capacitor. The ultra-high-speed control loop keeps the output v ...
Applications of Semiconductor devices.
... positive and negative. The transistor will only work with one polarity npn – positive and pnp – negative inputs. We therefore need to ensure that as the input swings positive and negative that the input to the transistor remains positive (npn). This is done by raising the starting point on the base ...
... positive and negative. The transistor will only work with one polarity npn – positive and pnp – negative inputs. We therefore need to ensure that as the input swings positive and negative that the input to the transistor remains positive (npn). This is done by raising the starting point on the base ...
Summary
... The power and ground planes of a PCB have some amount of inductance associated with them. The geometry of these planes determines their inductance. Since power and ground planes are by definition a planar structure, current does not just flow through them in one direction. It tends to spread out as ...
... The power and ground planes of a PCB have some amount of inductance associated with them. The geometry of these planes determines their inductance. Since power and ground planes are by definition a planar structure, current does not just flow through them in one direction. It tends to spread out as ...
the oscilloscope
... f) Measure the period of the signal. Recall that the period is the time required for one cycle as illustrated in Fig. 1. Using this value of T, calculate the frequency f of the signal. Is this value close to 100 Hz? It may not agree exactly since the frequency knob of the SSG may not be ...
... f) Measure the period of the signal. Recall that the period is the time required for one cycle as illustrated in Fig. 1. Using this value of T, calculate the frequency f of the signal. Is this value close to 100 Hz? It may not agree exactly since the frequency knob of the SSG may not be ...
THE OSCILLOSCOPE OBJECTIVE: To become familiar with the
... f) Measure the period of the signal. Recall that the period is the time required for one cycle as illustrated in Fig. 1. Using this value of T, calculate the frequency f of the signal. Is this value close to 100 Hz? It may not agree exactly since the frequency knob of the SSG may not be ...
... f) Measure the period of the signal. Recall that the period is the time required for one cycle as illustrated in Fig. 1. Using this value of T, calculate the frequency f of the signal. Is this value close to 100 Hz? It may not agree exactly since the frequency knob of the SSG may not be ...
Capacitor
.jpg?width=300)
A capacitor (originally known as a condenser) is a passive two-terminal electrical component used to store electrical energy temporarily in an electric field. The forms of practical capacitors vary widely, but all contain at least two electrical conductors (plates) separated by a dielectric (i.e. an insulator that can store energy by becoming polarized). The conductors can be thin films, foils or sintered beads of metal or conductive electrolyte, etc. The nonconducting dielectric acts to increase the capacitor's charge capacity. A dielectric can be glass, ceramic, plastic film, air, vacuum, paper, mica, oxide layer etc. Capacitors are widely used as parts of electrical circuits in many common electrical devices. Unlike a resistor, an ideal capacitor does not dissipate energy. Instead, a capacitor stores energy in the form of an electrostatic field between its plates.When there is a potential difference across the conductors (e.g., when a capacitor is attached across a battery), an electric field develops across the dielectric, causing positive charge +Q to collect on one plate and negative charge −Q to collect on the other plate. If a battery has been attached to a capacitor for a sufficient amount of time, no current can flow through the capacitor. However, if a time-varying voltage is applied across the leads of the capacitor, a displacement current can flow.An ideal capacitor is characterized by a single constant value, its capacitance. Capacitance is defined as the ratio of the electric charge Q on each conductor to the potential difference V between them. The SI unit of capacitance is the farad (F), which is equal to one coulomb per volt (1 C/V). Typical capacitance values range from about 1 pF (10−12 F) to about 1 mF (10−3 F).The larger the surface area of the ""plates"" (conductors) and the narrower the gap between them, the greater the capacitance is. In practice, the dielectric between the plates passes a small amount of leakage current and also has an electric field strength limit, known as the breakdown voltage. The conductors and leads introduce an undesired inductance and resistance.Capacitors are widely used in electronic circuits for blocking direct current while allowing alternating current to pass. In analog filter networks, they smooth the output of power supplies. In resonant circuits they tune radios to particular frequencies. In electric power transmission systems, they stabilize voltage and power flow.