The Evolutionary Reduction Principle for Linear Variation in Genetic
... includes gene conversion, methylation, deletions, duplications, insertions, transpositions, and other chromosomal alterations. These two processes, augmented by a third — the randomness of sampling in finite populations — provide the basis for our causal explanations of the characteristics of organ ...
... includes gene conversion, methylation, deletions, duplications, insertions, transpositions, and other chromosomal alterations. These two processes, augmented by a third — the randomness of sampling in finite populations — provide the basis for our causal explanations of the characteristics of organ ...
The genetic basis of adaptive melanism in
... are found on lava flows. The mice from these lava sites are typically melanic, with dark-colored dorsal hairs and white underbellies. Most of the lava flows are surrounded by lightcolored substrate and are isolated from one another by hundreds of kilometers, raising the possibility that melanic mice ...
... are found on lava flows. The mice from these lava sites are typically melanic, with dark-colored dorsal hairs and white underbellies. Most of the lava flows are surrounded by lightcolored substrate and are isolated from one another by hundreds of kilometers, raising the possibility that melanic mice ...
Sex-linked traits
... Law of Independent AssortmentSeparate genes for separate traits are passed independently of one another from parents to offspring. These allele pairs are then randomly united at fertilization. ...
... Law of Independent AssortmentSeparate genes for separate traits are passed independently of one another from parents to offspring. These allele pairs are then randomly united at fertilization. ...
Revealing the demographic histories of species
... can be traced back to the work of Ronald Fisherc and Sewall Wrightd but it was the development of the theory of neutral evolution of nucleotide sequencese that led to fuller development of coalescent theory. The descent of any set of individuals (DNA sequences) can be traced back, with common ancest ...
... can be traced back to the work of Ronald Fisherc and Sewall Wrightd but it was the development of the theory of neutral evolution of nucleotide sequencese that led to fuller development of coalescent theory. The descent of any set of individuals (DNA sequences) can be traced back, with common ancest ...
ppt
... 3) Offspring survival high in same environment Costs 1) “Muller’s ratchet” 2) Mutation (rare) only source of variation 3) Offspring survival is “all or none” in a changing environment ...
... 3) Offspring survival high in same environment Costs 1) “Muller’s ratchet” 2) Mutation (rare) only source of variation 3) Offspring survival is “all or none” in a changing environment ...
Mendelian inheritance - Center of Statistical Genetics
... organisms, show inheritance patterns both of the type discovered by Mendel (autosomal inheritance) and of sex linkage. In general, what in the hand of an experimental geneticist is simply a “mutant phenotype”, in the hand of a human geneticists becomes a disease or a condition of disability (often a ...
... organisms, show inheritance patterns both of the type discovered by Mendel (autosomal inheritance) and of sex linkage. In general, what in the hand of an experimental geneticist is simply a “mutant phenotype”, in the hand of a human geneticists becomes a disease or a condition of disability (often a ...
Scientist finds the gene that determines major sensitivity to bitter taste
... world. Those millions of Europeans, Asians, and individuals from other populations around the world who are non-tasters descended from a common ancestor who emerged from Africa far back in prehistory. Human DNA sequences are overwhelmingly similar, with some small, but sometimes important difference ...
... world. Those millions of Europeans, Asians, and individuals from other populations around the world who are non-tasters descended from a common ancestor who emerged from Africa far back in prehistory. Human DNA sequences are overwhelmingly similar, with some small, but sometimes important difference ...
Effective Gene Selection Method Using Bayesian Discriminant
... genes originally given in a microarray dataset are irrelevant to certain tasks, a widely used prefiltering-gene strategy is used to eliminate the irrelevant or insignificantly relevant genes before the commencement of gene selection. This is an effective way to relieve the computational burden. In d ...
... genes originally given in a microarray dataset are irrelevant to certain tasks, a widely used prefiltering-gene strategy is used to eliminate the irrelevant or insignificantly relevant genes before the commencement of gene selection. This is an effective way to relieve the computational burden. In d ...
Genetics of allergic disease
... which is preferable; but, in most cases, the parameters are not known. No specification of a genetic model is needed in non-parametric approaches such as the sibling pair analysis and affected relative pair analysis. These methods test whether the inheritance of a chromosomal region is not consisten ...
... which is preferable; but, in most cases, the parameters are not known. No specification of a genetic model is needed in non-parametric approaches such as the sibling pair analysis and affected relative pair analysis. These methods test whether the inheritance of a chromosomal region is not consisten ...
NAME: 07/23 SSA Science NATURAL SELECTION VIRTUAL LAB
... 2. This simulation is investigating the effect of ___ on certain phenotypes. 3. By placing pressure on these specific phenotypes, what will change? 4. What can natural selection alter in a population’s gene pool over time? 5. So how can evolution be described when referring to changes in gene pools? ...
... 2. This simulation is investigating the effect of ___ on certain phenotypes. 3. By placing pressure on these specific phenotypes, what will change? 4. What can natural selection alter in a population’s gene pool over time? 5. So how can evolution be described when referring to changes in gene pools? ...
The Genetic Theory of Natural Selection
... Selection-Drift equilibrium We have seen that directional selection will always increase the frequency of a beneficial allele. This property, however, only holds if we assume infinitely large population size. In finite populations, we need to factor in the effects of random sampling from one generat ...
... Selection-Drift equilibrium We have seen that directional selection will always increase the frequency of a beneficial allele. This property, however, only holds if we assume infinitely large population size. In finite populations, we need to factor in the effects of random sampling from one generat ...
Mendel`s Theory
... There are alternative versions of genes. Today these are called alleles. In the case with flower color, the alleles would be purple or yellow. One allele comes from each parent. ...
... There are alternative versions of genes. Today these are called alleles. In the case with flower color, the alleles would be purple or yellow. One allele comes from each parent. ...
Association of MMP-3 (-1612 5A/6A) polymorphism with knee
... affected joint with OA characterized by progressive destruction of articular cartilage, which leads to pain and loss of joint function. Although the multifactorial nature of OA is well recognized, genetic factors have been shown to be strong determinants of this disorder. Previous studies have shown ...
... affected joint with OA characterized by progressive destruction of articular cartilage, which leads to pain and loss of joint function. Although the multifactorial nature of OA is well recognized, genetic factors have been shown to be strong determinants of this disorder. Previous studies have shown ...
VCS: Tool for Visualizing Copy Number Variation and Single Nucleotide Polymorphism
... but VCS can provide the criteria which is the useradjustable log2 ratio. So a user can create the view of CNV filtrated by adjusting the criteria with different log2 ratio values for different research purposes. In addition, user can draw a Manhattan plot which easily can define appropriate signific ...
... but VCS can provide the criteria which is the useradjustable log2 ratio. So a user can create the view of CNV filtrated by adjusting the criteria with different log2 ratio values for different research purposes. In addition, user can draw a Manhattan plot which easily can define appropriate signific ...
Genetics of ankylosing spondylitis
... complex segregation analysis has demonstrated a high degree of genetic control of disease severity assessed by the Bath AS Disease Activity index (BASDAI) and functional impairment assessed by the Bath AS Functional Index (BASFI) (4). Heritability of these measures was estimated at 51% and 68% respe ...
... complex segregation analysis has demonstrated a high degree of genetic control of disease severity assessed by the Bath AS Disease Activity index (BASDAI) and functional impairment assessed by the Bath AS Functional Index (BASFI) (4). Heritability of these measures was estimated at 51% and 68% respe ...
Genetic Counseling and Testing for FMR1 Gene Mutations: Practice
... Testing is 99 % sensitive, missing only rare individuals who have FXS due to point mutations or deletions located outside the CGG repeat region. ACMG’s Standards and Guidelines for Clinical Genetics Laboratories (Spector and Kronquist 2006) details testing methodology and defines the normal and muta ...
... Testing is 99 % sensitive, missing only rare individuals who have FXS due to point mutations or deletions located outside the CGG repeat region. ACMG’s Standards and Guidelines for Clinical Genetics Laboratories (Spector and Kronquist 2006) details testing methodology and defines the normal and muta ...
14_DetailLectOut
... o Peas have a short generation time; each mating produces many offspring. o Mendel was able to strictly control the matings of his pea plants. o Each pea plant has male (stamens) and female (carpal) sexual organs. o In nature, pea plants typically self-fertilize, fertilizing ova with the sperm nucle ...
... o Peas have a short generation time; each mating produces many offspring. o Mendel was able to strictly control the matings of his pea plants. o Each pea plant has male (stamens) and female (carpal) sexual organs. o In nature, pea plants typically self-fertilize, fertilizing ova with the sperm nucle ...
Mendel - Spring Branch ISD
... features, or characters (such as flower color); character variants (such as purple or white flowers) are called traits – Mating can be controlled – Each flower has sperm-producing organs (stamens) and an egg-producing organ (carpel) – Cross-pollination (fertilization between different plants) involv ...
... features, or characters (such as flower color); character variants (such as purple or white flowers) are called traits – Mating can be controlled – Each flower has sperm-producing organs (stamens) and an egg-producing organ (carpel) – Cross-pollination (fertilization between different plants) involv ...
Chapter 2: Mendelian Inheritance
... c. The phenotypic ratio of the F2 generation was determined. 4. Mendel’s experimental data (page 26) indicated the following: a. The F2 generation of seeds possessed a 9:3:3:1 phenotypic ratio, not the 1:2:1 ratio expected by a linked model. b. Some seeds of the F2 generation were nonparentals, thus ...
... c. The phenotypic ratio of the F2 generation was determined. 4. Mendel’s experimental data (page 26) indicated the following: a. The F2 generation of seeds possessed a 9:3:3:1 phenotypic ratio, not the 1:2:1 ratio expected by a linked model. b. Some seeds of the F2 generation were nonparentals, thus ...
Chapter 11 Complex Inheritance and Human
... affected, each child has a onein-two chance of having achondroplasia, and a one-intwo chance of being average height. Those born with achondroplasia may pass the condition on to their own children, while those of average height will not. ...
... affected, each child has a onein-two chance of having achondroplasia, and a one-intwo chance of being average height. Those born with achondroplasia may pass the condition on to their own children, while those of average height will not. ...
Association of CLU and TLR2 gene - Tubitak Journals
... been clearly identified as a susceptibility gene in the more common form of AD, data from recent genome-wide * Correspondence: [email protected] ...
... been clearly identified as a susceptibility gene in the more common form of AD, data from recent genome-wide * Correspondence: [email protected] ...
Chapter 2: Mendelian Inheritance
... c. The phenotypic ratio of the F2 generation was determined. 4. Mendel’s experimental data (page 26) indicated the following: a. The F2 generation of seeds possessed a 9:3:3:1 phenotypic ratio, not the 1:2:1 ratio expected by a linked model. b. Some seeds of the F2 generation were nonparentals, thus ...
... c. The phenotypic ratio of the F2 generation was determined. 4. Mendel’s experimental data (page 26) indicated the following: a. The F2 generation of seeds possessed a 9:3:3:1 phenotypic ratio, not the 1:2:1 ratio expected by a linked model. b. Some seeds of the F2 generation were nonparentals, thus ...
Mitochondrial DNA disease - Human Molecular Genetics
... spindle transfer is performed at an earlier stage and the karyoplast is smaller than with pronuclear transfer, with the potential for less carryover of mtDNA. However, recent studies in human embryos show equivalent levels of carryover (unpublished data), providing further evidence that the risks of ...
... spindle transfer is performed at an earlier stage and the karyoplast is smaller than with pronuclear transfer, with the potential for less carryover of mtDNA. However, recent studies in human embryos show equivalent levels of carryover (unpublished data), providing further evidence that the risks of ...
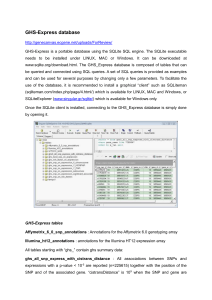
GHS-Express database http://genecanvas.ecgene.net/uploads/Fo
... expressions with a p-value < 10-5 are reported (n=225615) together with the position of the SNP and of the associated gene. “cistransDistance” is 109 when the SNP and gene are ...
... expressions with a p-value < 10-5 are reported (n=225615) together with the position of the SNP and of the associated gene. “cistransDistance” is 109 when the SNP and gene are ...
8th grade Chapter 8
... can result from the random fusion of parent gametes. B. The alleles within the gametes of one parent are written across the top of the square. C. The alleles within the gametes of the other parent are written down the side of the square. D. The products of the different possible fusion of gametes ar ...
... can result from the random fusion of parent gametes. B. The alleles within the gametes of one parent are written across the top of the square. C. The alleles within the gametes of the other parent are written down the side of the square. D. The products of the different possible fusion of gametes ar ...
Human genetic variation

Human genetic variation is the genetic differences both within and among populations. There may be multiple variants of any given gene in the human population (genes), leading to polymorphism. Many genes are not polymorphic, meaning that only a single allele is present in the population: the gene is then said to be fixed. On average, in terms of DNA sequence all humans are 99.9% similar to any other humans.No two humans are genetically identical. Even monozygotic twins, who develop from one zygote, have infrequent genetic differences due to mutations occurring during development and gene copy-number variation. Differences between individuals, even closely related individuals, are the key to techniques such as genetic fingerprinting. Alleles occur at different frequencies in different human populations, with populations that are more geographically and ancestrally remote tending to differ more.Causes of differences between individuals include the exchange of genes during meiosis and various mutational events. There are at least two reasons why genetic variation exists between populations. Natural selection may confer an adaptive advantage to individuals in a specific environment if an allele provides a competitive advantage. Alleles under selection are likely to occur only in those geographic regions where they confer an advantage. The second main cause of genetic variation is due to the high degree of neutrality of most mutations. Most mutations do not appear to have any selective effect one way or the other on the organism. The main cause is genetic drift, this is the effect of random changes in the gene pool. In humans, founder effect and past small population size (increasing the likelihood of genetic drift) may have had an important influence in neutral differences between populations. The theory that humans recently migrated out of Africa supports this.The study of human genetic variation has both evolutionary significance and medical applications. It can help scientists understand ancient human population migrations as well as how different human groups are biologically related to one another. For medicine, study of human genetic variation may be important because some disease-causing alleles occur more often in people from specific geographic regions. New findings show that each human has on average 60 new mutations compared to their parents.Apart from mutations, many genes that may have aided humans in ancient times plague humans today. For example, it is suspected that genes that allow humans to more efficiently process food are those that make people susceptible to obesity and diabetes today.