Genetic Optimization of Electric Machines, a State of the Art Study.
... Using a simple GA (SGA), users will experience optima being lost It is also hard to predict which optima is being chosen at each optimization run The losses are due to three effects: – selection pressure – selection noise – operator disruption ...
... Using a simple GA (SGA), users will experience optima being lost It is also hard to predict which optima is being chosen at each optimization run The losses are due to three effects: – selection pressure – selection noise – operator disruption ...
Gene affecting stature and body size in mammalian species
... infinite number of loci, each with infinitesimal effect, is not literally true but it ...
... infinite number of loci, each with infinitesimal effect, is not literally true but it ...
Chapter 23
... Immigration from the mainland introduces alleles that decrease fitness on the island Natural selection removes alleles that decrease fitness Birds born in the central region with high immigration have a lower fitness; birds born in the east with low immigration have a higher fitness © 2014 Pea ...
... Immigration from the mainland introduces alleles that decrease fitness on the island Natural selection removes alleles that decrease fitness Birds born in the central region with high immigration have a lower fitness; birds born in the east with low immigration have a higher fitness © 2014 Pea ...
Case-Parent Triads
... ingenious approach requires no controls in the usual sense but relies instead on allele frequencies among diseased persons and their biologic parents. The key observation, made by Rubinstein et al. (1) in 1981, is that alleles associated with a given disease will occur more often in diseased persons ...
... ingenious approach requires no controls in the usual sense but relies instead on allele frequencies among diseased persons and their biologic parents. The key observation, made by Rubinstein et al. (1) in 1981, is that alleles associated with a given disease will occur more often in diseased persons ...
ª2010 Elsevier Ltd All rights reserved DOI 10.1016/j.cub.2010.06.022
... conferring adaptation and reproductive isolation in experimental populations of yeast under strongly divergent selection. We studied experimental populations of S. cerevisiae that evolved from a single progenitor (P) in either a high-salt (S) or a low-glucose (M) environment [2]. These populations w ...
... conferring adaptation and reproductive isolation in experimental populations of yeast under strongly divergent selection. We studied experimental populations of S. cerevisiae that evolved from a single progenitor (P) in either a high-salt (S) or a low-glucose (M) environment [2]. These populations w ...
Coc - ARVO Journals
... 16. This map location eliminated the possibility that the Coc mutation may be allelic to the only autosomal dominant cataract mutation shown to be on chromosome 16 Opj, which is ~ 6 cM from the centromere. 26 In the region of the Coc locus, the Mouse Genome Database (MGD) l5 lists several genes. How ...
... 16. This map location eliminated the possibility that the Coc mutation may be allelic to the only autosomal dominant cataract mutation shown to be on chromosome 16 Opj, which is ~ 6 cM from the centromere. 26 In the region of the Coc locus, the Mouse Genome Database (MGD) l5 lists several genes. How ...
The influence of genomic imprinting on brain
... identical paternally derived allele will be found in multiple offspring of the same female is low ( < 0.5), compared to the probability for a maternally derived allele ( = 0.5) (Hurst & McVean, 1997). Thus, the male parent’s genetic interest in any future offspring of the female is decreased, as is ...
... identical paternally derived allele will be found in multiple offspring of the same female is low ( < 0.5), compared to the probability for a maternally derived allele ( = 0.5) (Hurst & McVean, 1997). Thus, the male parent’s genetic interest in any future offspring of the female is decreased, as is ...
Effects of linkage on response to directional selection from new
... No recombination. In this case, where L —* 0, no mutant site or recombination has to be considered, so mutant effects merely change the value of the chromosome and the chromosome is described solely by its value. In some runs, a model of several (k) chromosomes each with no recombination was simulat ...
... No recombination. In this case, where L —* 0, no mutant site or recombination has to be considered, so mutant effects merely change the value of the chromosome and the chromosome is described solely by its value. In some runs, a model of several (k) chromosomes each with no recombination was simulat ...
Building Better Beef The Building Blocks Behind Wagyu By: Tracy
... The tenderness, richly marbled, and unmatched flavor of Wayguy beef is a historic delicacy in Japan. More recently Americans have gotten a taste for the delicious beef with a buttery texture and documented health benefits. The foodie craze that has swept America has chefs featuring specialty Wagyu b ...
... The tenderness, richly marbled, and unmatched flavor of Wayguy beef is a historic delicacy in Japan. More recently Americans have gotten a taste for the delicious beef with a buttery texture and documented health benefits. The foodie craze that has swept America has chefs featuring specialty Wagyu b ...
Insulin gene polymorphism and premature male pattern baldness in
... resistance appears to be the main cause of the hyperinsulinaemia, and PCOS patients have a 7-fold increased risk of Type II (non-insulin-dependent) diabetes [7]. In males from families with PCOS, an increase in the prevalence of premature MPB (significant balding before 30 years of age) in an autoso ...
... resistance appears to be the main cause of the hyperinsulinaemia, and PCOS patients have a 7-fold increased risk of Type II (non-insulin-dependent) diabetes [7]. In males from families with PCOS, an increase in the prevalence of premature MPB (significant balding before 30 years of age) in an autoso ...
Genetics of behavioural isolation
... between two sympatric races of this moth is caused by differences in the ratio of two pheromones produced by the females35. By using gas chromatography of pheromone glands and single sensillum recordings of reciprocal crosses, it was found that the behaviour is controlled by three different genetic ...
... between two sympatric races of this moth is caused by differences in the ratio of two pheromones produced by the females35. By using gas chromatography of pheromone glands and single sensillum recordings of reciprocal crosses, it was found that the behaviour is controlled by three different genetic ...
Virtual Fly Lab (7-10th grade)
... Drosophila melanogaster, the fruit fly, is an excellent organism for genetics studies because it has simple food requirements, occupies little space, is hardy and completes its life cycle in about 12 days at room temperature. While you will be using a computer program that simulates Drosophila genet ...
... Drosophila melanogaster, the fruit fly, is an excellent organism for genetics studies because it has simple food requirements, occupies little space, is hardy and completes its life cycle in about 12 days at room temperature. While you will be using a computer program that simulates Drosophila genet ...
A locus for posterior polymorphous corneal dystrophy (PPCD3
... membrane and transformation of corneal endothelial cells into cells with an epithelial-like appearance [Krachamer, 1985]. The clinical phenotype of PPCD can vary from relatively benign Descemet’s thickening to severe progression towards vision loss from corneal edema [Cibis et al., 1977; Threlkeld e ...
... membrane and transformation of corneal endothelial cells into cells with an epithelial-like appearance [Krachamer, 1985]. The clinical phenotype of PPCD can vary from relatively benign Descemet’s thickening to severe progression towards vision loss from corneal edema [Cibis et al., 1977; Threlkeld e ...
Chapter 3 Mendelism: The Basic Principles of Inheritance
... genes segregate,(assort) independently of each other (The traits in the offspring of this crosses did not always match the combinations of traits in the parental organisms). In humans, diploid cells contain 46 chromosomes, 23 female chromosomes 23 male chromosomes During meiosis, the pairs of simila ...
... genes segregate,(assort) independently of each other (The traits in the offspring of this crosses did not always match the combinations of traits in the parental organisms). In humans, diploid cells contain 46 chromosomes, 23 female chromosomes 23 male chromosomes During meiosis, the pairs of simila ...
Computational Biology
... Last lecture (mouse:man) we saw that many more genomic elements are conserved between related species than only the genes. Therefore, genome rearrangement studies that are based on genome-wide analysis of gene orders rather than individual genes, may provide a more general picture on evolution. In f ...
... Last lecture (mouse:man) we saw that many more genomic elements are conserved between related species than only the genes. Therefore, genome rearrangement studies that are based on genome-wide analysis of gene orders rather than individual genes, may provide a more general picture on evolution. In f ...
software development and application in bioinformatics: single
... Polyphred tends to be more accurate in its analysis than for sequences prepared with dye-labeled terminators [23]. Therefore, it is important to know how the DNA to be analyzed was obtained. It reports a heterozygous allele only when the site shows a decrease of about 50% in peak height compared to ...
... Polyphred tends to be more accurate in its analysis than for sequences prepared with dye-labeled terminators [23]. Therefore, it is important to know how the DNA to be analyzed was obtained. It reports a heterozygous allele only when the site shows a decrease of about 50% in peak height compared to ...
Abstract/Session Information for Program Number 1264
... ossification. Until now, transcriptional repressors of Runx2 in vivo have yet to be identified. By combining SNP analysis of control and CCD subjects and cross species sequence analysis, we have identified conserved GATA domain binding sites in the RUNX2 promoter. Because TRPS1 is the only GATA doma ...
... ossification. Until now, transcriptional repressors of Runx2 in vivo have yet to be identified. By combining SNP analysis of control and CCD subjects and cross species sequence analysis, we have identified conserved GATA domain binding sites in the RUNX2 promoter. Because TRPS1 is the only GATA doma ...
Complete Genome Sequence of Bacillus thuringiensis Strain 407 Cry-
... activities of the cry toxins, B. thuringiensis has been used widely as a biopesticide, and there is a great deal of interest to understand further its pathogenic properties and how host resistance may evolve. Strains of B. thuringiensis vary in their amenability to genetic manipulation, and acrystal ...
... activities of the cry toxins, B. thuringiensis has been used widely as a biopesticide, and there is a great deal of interest to understand further its pathogenic properties and how host resistance may evolve. Strains of B. thuringiensis vary in their amenability to genetic manipulation, and acrystal ...
Modern Genetics
... *Inbreeding—the crossing of closely related organisms. Self-pollination in plants is an example. Purebred animals are an example. It is a way of keeping desirable traits in a breed. ...
... *Inbreeding—the crossing of closely related organisms. Self-pollination in plants is an example. Purebred animals are an example. It is a way of keeping desirable traits in a breed. ...
Modern Genetics
... *Inbreeding—the crossing of closely related organisms. Self-pollination in plants is an example. Purebred animals are an example. It is a way of keeping desirable traits in a breed. ...
... *Inbreeding—the crossing of closely related organisms. Self-pollination in plants is an example. Purebred animals are an example. It is a way of keeping desirable traits in a breed. ...
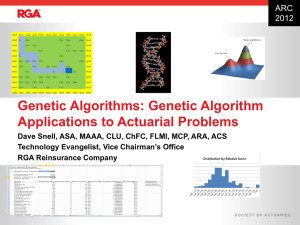
Genetic Algorithms: Genetic Algorithm Applications to Actuarial Problems ARC 2012
... Very basic genetics § Humans have about 25,000 genes made from A-T and C-G pairs § DNA strand – double helix of two strands – each about 1.8 meters § In meiosis, the strand separates into 46 chromosomes (in 23 pairs) § Alleles (forms of a gene) help determine physical or behavioral traits ...
... Very basic genetics § Humans have about 25,000 genes made from A-T and C-G pairs § DNA strand – double helix of two strands – each about 1.8 meters § In meiosis, the strand separates into 46 chromosomes (in 23 pairs) § Alleles (forms of a gene) help determine physical or behavioral traits ...
BMC Genomics - LCBB
... Background: Genome evolution is shaped not only by nucleotide substitutions, but also by structural changes including gene and genome duplications, insertions, deletions and gene order rearrangements. The most popular methods for reconstructing phylogeny from genome rearrangements include GRAPPA and ...
... Background: Genome evolution is shaped not only by nucleotide substitutions, but also by structural changes including gene and genome duplications, insertions, deletions and gene order rearrangements. The most popular methods for reconstructing phylogeny from genome rearrangements include GRAPPA and ...
chapter 13 meiosis and sexual life cycles
... Lecture Outline for Campbell/Reece Biology, 7th Edition, © Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... Lecture Outline for Campbell/Reece Biology, 7th Edition, © Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Human genetic variation

Human genetic variation is the genetic differences both within and among populations. There may be multiple variants of any given gene in the human population (genes), leading to polymorphism. Many genes are not polymorphic, meaning that only a single allele is present in the population: the gene is then said to be fixed. On average, in terms of DNA sequence all humans are 99.9% similar to any other humans.No two humans are genetically identical. Even monozygotic twins, who develop from one zygote, have infrequent genetic differences due to mutations occurring during development and gene copy-number variation. Differences between individuals, even closely related individuals, are the key to techniques such as genetic fingerprinting. Alleles occur at different frequencies in different human populations, with populations that are more geographically and ancestrally remote tending to differ more.Causes of differences between individuals include the exchange of genes during meiosis and various mutational events. There are at least two reasons why genetic variation exists between populations. Natural selection may confer an adaptive advantage to individuals in a specific environment if an allele provides a competitive advantage. Alleles under selection are likely to occur only in those geographic regions where they confer an advantage. The second main cause of genetic variation is due to the high degree of neutrality of most mutations. Most mutations do not appear to have any selective effect one way or the other on the organism. The main cause is genetic drift, this is the effect of random changes in the gene pool. In humans, founder effect and past small population size (increasing the likelihood of genetic drift) may have had an important influence in neutral differences between populations. The theory that humans recently migrated out of Africa supports this.The study of human genetic variation has both evolutionary significance and medical applications. It can help scientists understand ancient human population migrations as well as how different human groups are biologically related to one another. For medicine, study of human genetic variation may be important because some disease-causing alleles occur more often in people from specific geographic regions. New findings show that each human has on average 60 new mutations compared to their parents.Apart from mutations, many genes that may have aided humans in ancient times plague humans today. For example, it is suspected that genes that allow humans to more efficiently process food are those that make people susceptible to obesity and diabetes today.