Genetics (to generate- the coming into being)
... Schwarzenegger-like mice" by genetically engineering animals with a missing growth regulator called myostatin. Myostatin is a gene that is a member of the Transforming Growth Factor-b (TGF-b) Superfamily.1 These genes encode factors that are essential to proper biological development during the embr ...
... Schwarzenegger-like mice" by genetically engineering animals with a missing growth regulator called myostatin. Myostatin is a gene that is a member of the Transforming Growth Factor-b (TGF-b) Superfamily.1 These genes encode factors that are essential to proper biological development during the embr ...
APOC1 gene rs4420638 SNP
... and as a result the effect of the gene depends on the presence of one or more modifier genes. There is that one gene or allele masking the phenotypic expression of the other genes or alleles in the interaction. That gene or allele masking the effect is referred to as epistatic. In contrast, the othe ...
... and as a result the effect of the gene depends on the presence of one or more modifier genes. There is that one gene or allele masking the phenotypic expression of the other genes or alleles in the interaction. That gene or allele masking the effect is referred to as epistatic. In contrast, the othe ...
Darwin`s Theory of Evolution
... Genetic drift, gene flow, and mutations could each result in microevolution, but only by chance could these events improve a population’s fit to its environment Natural selection is a blend of o Chance o And sorting Because of this sorting, only natural selection consistently leads to adaptive evolu ...
... Genetic drift, gene flow, and mutations could each result in microevolution, but only by chance could these events improve a population’s fit to its environment Natural selection is a blend of o Chance o And sorting Because of this sorting, only natural selection consistently leads to adaptive evolu ...
Genetic
... Zygote. The cell formed by the fusion of an egg and a sperm; the unique diploid cell that will divide mitotically to create a differentiated ...
... Zygote. The cell formed by the fusion of an egg and a sperm; the unique diploid cell that will divide mitotically to create a differentiated ...
Grandmothering
... children a woman can have. • IBI - The period of time between births is longer for humans than some species- perhaps due to the extended childhood - which is unique to humans.. • IBI - longer in larger species and shorter for smaller primates. • Grandmothers are able to help facilitate shorter IBIs ...
... children a woman can have. • IBI - The period of time between births is longer for humans than some species- perhaps due to the extended childhood - which is unique to humans.. • IBI - longer in larger species and shorter for smaller primates. • Grandmothers are able to help facilitate shorter IBIs ...
PPT
... genes, less than 30,000, but they have a complex architecture that we are only beginning to understand and appreciate. ...
... genes, less than 30,000, but they have a complex architecture that we are only beginning to understand and appreciate. ...
File
... There is a large amount of technical vocabulary associated with genetic engineering – present this in context and recap at regular points in the teaching sequence. Understanding genetic engineering requires a basic understanding of DNA, enzyme action, cell structure and gene regulation – relate back ...
... There is a large amount of technical vocabulary associated with genetic engineering – present this in context and recap at regular points in the teaching sequence. Understanding genetic engineering requires a basic understanding of DNA, enzyme action, cell structure and gene regulation – relate back ...
Evolution Exam practice - AP-Science-Experience-JMHS
... A) often only a fraction of offspring survive because there is a struggle for limited resources. B) subsequent generations of a population should have greater proportions of individuals that possess favorable traits. C) an individual organism undergoes evolution over the course of its lifetime. D) u ...
... A) often only a fraction of offspring survive because there is a struggle for limited resources. B) subsequent generations of a population should have greater proportions of individuals that possess favorable traits. C) an individual organism undergoes evolution over the course of its lifetime. D) u ...
Genetics - Is there a role in clinical practice?
... • Liver biopsy - provides additional information about the liver status • Genetic testing maybe offered in inconclusive report ...
... • Liver biopsy - provides additional information about the liver status • Genetic testing maybe offered in inconclusive report ...
Document
... 1. Did the variation in the west side of the forest increase or decrease after the Skittlebugs were able to move between populations? (Think about how many alleles existed in the population before versus after) ...
... 1. Did the variation in the west side of the forest increase or decrease after the Skittlebugs were able to move between populations? (Think about how many alleles existed in the population before versus after) ...
There has been a lot of excitement lately over the new gene
... proven to improve the specificity and efficacy of CRISPR gene editing, some of which were developed in my lab. The Chinese group must have known that their work was going to get a lot of attention, so it was disappointing that they chose not to use these techniques. They may have felt that if they w ...
... proven to improve the specificity and efficacy of CRISPR gene editing, some of which were developed in my lab. The Chinese group must have known that their work was going to get a lot of attention, so it was disappointing that they chose not to use these techniques. They may have felt that if they w ...
What is bioinformatics? - The British Association of Sport and
... gene where you do not know the genomic location. In these cases, you will have to use a search engine and type the name of the gene or protein in. To do so, open the Ensembl website (www.ensembl.org) and click the species, normally human. On the top of the page it states “Search for anything with” a ...
... gene where you do not know the genomic location. In these cases, you will have to use a search engine and type the name of the gene or protein in. To do so, open the Ensembl website (www.ensembl.org) and click the species, normally human. On the top of the page it states “Search for anything with” a ...
Identifying the genetic and environmental
... An exciting opportunity to work on a translational genomic project embedded within a phase III multi-centre clinical trial in Africa (Dr Jarvis Principal Investigator). The project is part of an H3Africa 1000 cryptococcal meningitis African genomes project led by the University of Cape Town for whic ...
... An exciting opportunity to work on a translational genomic project embedded within a phase III multi-centre clinical trial in Africa (Dr Jarvis Principal Investigator). The project is part of an H3Africa 1000 cryptococcal meningitis African genomes project led by the University of Cape Town for whic ...
Methods of studying wild
... Significant loss of allelic richness/genetic diversity at MHC I after 1958 but subsequent recovery Relative stability at neutral loci ...
... Significant loss of allelic richness/genetic diversity at MHC I after 1958 but subsequent recovery Relative stability at neutral loci ...
Ancient DNA (aDNA): What is it? Why is it important?
... is comprised not only of biological and genetic connections, but also sociocultural and geographic factors, family histories and lived experiences. What problems arise when one’s identity and ancestry is reduced to a molecular origin, such as when genetic markers are used for tribal enrollment? • Re ...
... is comprised not only of biological and genetic connections, but also sociocultural and geographic factors, family histories and lived experiences. What problems arise when one’s identity and ancestry is reduced to a molecular origin, such as when genetic markers are used for tribal enrollment? • Re ...
Natural selection
... migratory (in three generations) or 100 per cent residents (in six generations) (Fig. 1.2). Not only does this experiment confirm a genetic basis to differences in migratory behaviour, but it also shows how an ecologically important trait such as migration may respond rapidly to selection. These var ...
... migratory (in three generations) or 100 per cent residents (in six generations) (Fig. 1.2). Not only does this experiment confirm a genetic basis to differences in migratory behaviour, but it also shows how an ecologically important trait such as migration may respond rapidly to selection. These var ...
Needles in a DNA-stack - ESRC Genomics Network
... • Women have 1 in 10 lifetime risk of developing breast cancer • There are many factors that influence risk, including: - mammographic density - lifestyle and reproductive history - genetic factors • Nowgen Forum on 5 December 2008; pilot to explore views of potential ‘personalised’ screening • Iden ...
... • Women have 1 in 10 lifetime risk of developing breast cancer • There are many factors that influence risk, including: - mammographic density - lifestyle and reproductive history - genetic factors • Nowgen Forum on 5 December 2008; pilot to explore views of potential ‘personalised’ screening • Iden ...
BioFlix Study Sheet for Mechanisms of Evolution
... C. natural selection. D. genetic variation. E. has more effect in large populations than in small populations. ____2. If color is an inherited trait in beetles, and birds are more likely to eat brown beetles than green beetles, A. the frequency of the green allele will increase. B. the frequency of ...
... C. natural selection. D. genetic variation. E. has more effect in large populations than in small populations. ____2. If color is an inherited trait in beetles, and birds are more likely to eat brown beetles than green beetles, A. the frequency of the green allele will increase. B. the frequency of ...
The purple loosestrife (Lythrum salicaria) is a flowering plant native t
... 18. Which of the following is a human adaptation to survive in cold temperatures? A. You turn the thermostat up B. You grow hair to insulate your head C. You cozy up under a blanket with a warm cup of hot chocolate D. You put on your coat 19. All domestic dogs are descended from the A. Grey Fox B. B ...
... 18. Which of the following is a human adaptation to survive in cold temperatures? A. You turn the thermostat up B. You grow hair to insulate your head C. You cozy up under a blanket with a warm cup of hot chocolate D. You put on your coat 19. All domestic dogs are descended from the A. Grey Fox B. B ...
Unit 6
... Summary of the Text: As the most extensive survey to date on how humans vary at the level of their genes, the book The History and Geography of Human Genes made two remarkable contributions to science: There is no scientific basis for the genetic superiority of one race over any other one; and it c ...
... Summary of the Text: As the most extensive survey to date on how humans vary at the level of their genes, the book The History and Geography of Human Genes made two remarkable contributions to science: There is no scientific basis for the genetic superiority of one race over any other one; and it c ...
genetic disorder
... Human Genetic Disorders Autosome - Any chromosome other than a sex chromosome. – When a genetic disorder is autosomal dominant, an individual with AA or Aa has the disorder. – When a genetic disorder is autosomal recessive, only aa individuals have the disorder. Carriers - Individuals unaffected by ...
... Human Genetic Disorders Autosome - Any chromosome other than a sex chromosome. – When a genetic disorder is autosomal dominant, an individual with AA or Aa has the disorder. – When a genetic disorder is autosomal recessive, only aa individuals have the disorder. Carriers - Individuals unaffected by ...
NOTES: CH 14 part 2 - Spokane Public Schools
... ● recessive alleles that cause human disorders are usually defective versions of normal alleles ● defective alleles code for either a malfunctioning protein or no protein at all ...
... ● recessive alleles that cause human disorders are usually defective versions of normal alleles ● defective alleles code for either a malfunctioning protein or no protein at all ...
Phenotype Genotype and the Environment
... Gene Flow - The loss or gain of alleles in a population due to the migration of fertile individuals or between gamete populations. When an organism moves from one area to another, it takes its alleles with it. ...
... Gene Flow - The loss or gain of alleles in a population due to the migration of fertile individuals or between gamete populations. When an organism moves from one area to another, it takes its alleles with it. ...
102KB - NZQA
... Genetic diversity is variations in genetic make-up / genotypes / total number of genetic characteristics in a species / population / genome / gene pool OR Having many different combinations of alleles may offer a survival advantage to a species if conditions change. In small island populations, ther ...
... Genetic diversity is variations in genetic make-up / genotypes / total number of genetic characteristics in a species / population / genome / gene pool OR Having many different combinations of alleles may offer a survival advantage to a species if conditions change. In small island populations, ther ...
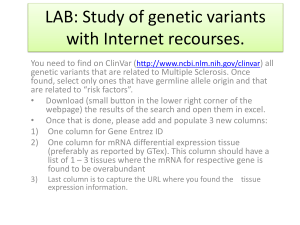
Human genetic variation

Human genetic variation is the genetic differences both within and among populations. There may be multiple variants of any given gene in the human population (genes), leading to polymorphism. Many genes are not polymorphic, meaning that only a single allele is present in the population: the gene is then said to be fixed. On average, in terms of DNA sequence all humans are 99.9% similar to any other humans.No two humans are genetically identical. Even monozygotic twins, who develop from one zygote, have infrequent genetic differences due to mutations occurring during development and gene copy-number variation. Differences between individuals, even closely related individuals, are the key to techniques such as genetic fingerprinting. Alleles occur at different frequencies in different human populations, with populations that are more geographically and ancestrally remote tending to differ more.Causes of differences between individuals include the exchange of genes during meiosis and various mutational events. There are at least two reasons why genetic variation exists between populations. Natural selection may confer an adaptive advantage to individuals in a specific environment if an allele provides a competitive advantage. Alleles under selection are likely to occur only in those geographic regions where they confer an advantage. The second main cause of genetic variation is due to the high degree of neutrality of most mutations. Most mutations do not appear to have any selective effect one way or the other on the organism. The main cause is genetic drift, this is the effect of random changes in the gene pool. In humans, founder effect and past small population size (increasing the likelihood of genetic drift) may have had an important influence in neutral differences between populations. The theory that humans recently migrated out of Africa supports this.The study of human genetic variation has both evolutionary significance and medical applications. It can help scientists understand ancient human population migrations as well as how different human groups are biologically related to one another. For medicine, study of human genetic variation may be important because some disease-causing alleles occur more often in people from specific geographic regions. New findings show that each human has on average 60 new mutations compared to their parents.Apart from mutations, many genes that may have aided humans in ancient times plague humans today. For example, it is suspected that genes that allow humans to more efficiently process food are those that make people susceptible to obesity and diabetes today.