Tetrasomic inheritance in cultivated potato and implications in
... productive and stable in various environments. They can have high degree of intralocus interactions (dominance) due to the four alleles as well as interlocus (epistasis) interactions which can result in high yield. According to theory of heterosis in potatoes, these genic interactions are very impor ...
... productive and stable in various environments. They can have high degree of intralocus interactions (dominance) due to the four alleles as well as interlocus (epistasis) interactions which can result in high yield. According to theory of heterosis in potatoes, these genic interactions are very impor ...
The genetic basis of panic and phobic anxiety disorders
... loci for complex traits. identifying true association requires that the alleles studied include variants that are either directly related to the phenotype or strongly correlated with (i.e., in linkage disequilibrium with) such causal variants. Two approaches to association analysis are now feasible: ...
... loci for complex traits. identifying true association requires that the alleles studied include variants that are either directly related to the phenotype or strongly correlated with (i.e., in linkage disequilibrium with) such causal variants. Two approaches to association analysis are now feasible: ...
Symbiotic sympatric speciation through interaction
... 2000). In contrast, in our case, distinct phenotypes are formed in the same environment. Although some of the phenotypic plasticity studied to date may be related to developmental flexibility, we do not use the term ‘phenotypic plasticity’ here to avoid confusion. Following the above argument, it is ...
... 2000). In contrast, in our case, distinct phenotypes are formed in the same environment. Although some of the phenotypic plasticity studied to date may be related to developmental flexibility, we do not use the term ‘phenotypic plasticity’ here to avoid confusion. Following the above argument, it is ...
Slides Here
... Genome Comparison: Human - Mouse • Humans and mice have similar genomes, but their genes are in a different order. ...
... Genome Comparison: Human - Mouse • Humans and mice have similar genomes, but their genes are in a different order. ...
Supplementary Information (doc 132K)
... SNPs from 22 Candidate Genes for: (a) Case-Control samples and (b) Combined TrioCase-Control Samples. The 95% confidence interval of expected values is indicated in grey. Corresponding genomic control lambda values are indicated within each plot (lambda=1.085 for Case-Controls and lambda=1.168 for t ...
... SNPs from 22 Candidate Genes for: (a) Case-Control samples and (b) Combined TrioCase-Control Samples. The 95% confidence interval of expected values is indicated in grey. Corresponding genomic control lambda values are indicated within each plot (lambda=1.085 for Case-Controls and lambda=1.168 for t ...
VI. The relationship between genotype and phenotype is rarely simple
... • For example, the gene for flower color in pea plants exists in two alternative forms; one for purple color and one for white color. • Alternative forms for a gene are now called alleles. 2. For each character, an organism inherits two alleles, one from each parent. • Mendel deduced that each paren ...
... • For example, the gene for flower color in pea plants exists in two alternative forms; one for purple color and one for white color. • Alternative forms for a gene are now called alleles. 2. For each character, an organism inherits two alleles, one from each parent. • Mendel deduced that each paren ...
14. Development and Plasticity
... The fitness function of most EAs is a user-defined optimization criterion which evaluates the individuals in isolation from each other. Competitive fitness functions (Angeline and Pollack 1993) are a type of relative fitness function. They calculate the fitness of an individual through competition ...
... The fitness function of most EAs is a user-defined optimization criterion which evaluates the individuals in isolation from each other. Competitive fitness functions (Angeline and Pollack 1993) are a type of relative fitness function. They calculate the fitness of an individual through competition ...
Simplified Insertion of Transgenes Onto Balancer Chromosomes via
... RMCE was supported at appreciable levels using at least one representative target-bearing line for each of the three balancer chromosomes, namely FM7hFS5, CyOJ01, CyOJ08, and TM3FS18. In the presence of a genomic source of the phiC31 integrase (Bischof et al. 2007), we injected donor constructs carr ...
... RMCE was supported at appreciable levels using at least one representative target-bearing line for each of the three balancer chromosomes, namely FM7hFS5, CyOJ01, CyOJ08, and TM3FS18. In the presence of a genomic source of the phiC31 integrase (Bischof et al. 2007), we injected donor constructs carr ...
exploring genetics - Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory
... ALLELE one of the variant forms of a gene at a particular locus, or location, on a chromosome. Different alleles produce variation in inherited characteristics such as hair color or blood type. In an individual, one form of the allele (the dominant one) may be expressed more than another form (the r ...
... ALLELE one of the variant forms of a gene at a particular locus, or location, on a chromosome. Different alleles produce variation in inherited characteristics such as hair color or blood type. In an individual, one form of the allele (the dominant one) may be expressed more than another form (the r ...
Gene mapping of monogenic disorders and complex
... Mendelian inheritance pattern, and appear to be caused by an unknown number of genes. Only a small fraction of affected individuals in some complex diseases such as cardiovascular defects, diabetes and several cancers, have been found to result from a single mutant gene transmitted with Mendelian in ...
... Mendelian inheritance pattern, and appear to be caused by an unknown number of genes. Only a small fraction of affected individuals in some complex diseases such as cardiovascular defects, diabetes and several cancers, have been found to result from a single mutant gene transmitted with Mendelian in ...
Quantitative Genetics: II
... additive genetic variance, we fitted a regression line that minimizes the squared differences between the observed genotypic values and those predicted by the regression line. This procedure is deliberately geared to maximize additive genetic variance (the variance associated with the regression lin ...
... additive genetic variance, we fitted a regression line that minimizes the squared differences between the observed genotypic values and those predicted by the regression line. This procedure is deliberately geared to maximize additive genetic variance (the variance associated with the regression lin ...
Figure Captions - Blackwell Publishing
... frequency of a alleles is 10/24. Any given A has a frequency of 14/24 and will encounter another A with probability of 14/24 or an a with the probability of 10/24. This makes the frequency of an A–A collision (14/24)2 and an A–a collision (14/24)(10/24), just as the probability of two independent ev ...
... frequency of a alleles is 10/24. Any given A has a frequency of 14/24 and will encounter another A with probability of 14/24 or an a with the probability of 10/24. This makes the frequency of an A–A collision (14/24)2 and an A–a collision (14/24)(10/24), just as the probability of two independent ev ...
Teaching scheme - Pearson Schools and FE Colleges
... which a nucleotide sequence codes for the amino acid sequence in a polypeptide. OCR Scheme of Work topic outlines • Describe, with the aid of diagrams, how the sequence of nucleotides within a gene is used F215 Control, genomes and environment to construct a polypeptide – include the roles 5.1.1 Cel ...
... which a nucleotide sequence codes for the amino acid sequence in a polypeptide. OCR Scheme of Work topic outlines • Describe, with the aid of diagrams, how the sequence of nucleotides within a gene is used F215 Control, genomes and environment to construct a polypeptide – include the roles 5.1.1 Cel ...
Genetic variation in the transforming growth susceptibility to IgA nephropathy
... respectively. A relatively high degree of linkage disequilibrium (LD) was detected in this locus, which resulted in 5 observed out of 32 expected haplotypes, which made it relatively easy to reveal genetic variability with the selected number of SNPs. Two out of five marker haplotypes, TGGCG and CTG ...
... respectively. A relatively high degree of linkage disequilibrium (LD) was detected in this locus, which resulted in 5 observed out of 32 expected haplotypes, which made it relatively easy to reveal genetic variability with the selected number of SNPs. Two out of five marker haplotypes, TGGCG and CTG ...
The human Y chromosome: a sole survivor Noordam, MJ - UvA-DARE
... and thus reproductive fitness. This effect of DAZ on spermatogenesis was noticed previously in DAZL-knockout mice and in studies where human DAZ rescued spermatogenesis in the mouse DAZL-knockout and the degree of rescue was determined by the number of human DAZ copies that integrated into the mouse ...
... and thus reproductive fitness. This effect of DAZ on spermatogenesis was noticed previously in DAZL-knockout mice and in studies where human DAZ rescued spermatogenesis in the mouse DAZL-knockout and the degree of rescue was determined by the number of human DAZ copies that integrated into the mouse ...
Goings on in Mendel`s Garden
... multiple genes, multiple alleles, and multiple environmental effects. Mendel’s traits can be produced by other mutations in the same genes or in other genes. For example, the spontaneous mutation rate for the p gene is 0.05– 0.2%, and mutations at another, v, are similar. At least eight known genes ...
... multiple genes, multiple alleles, and multiple environmental effects. Mendel’s traits can be produced by other mutations in the same genes or in other genes. For example, the spontaneous mutation rate for the p gene is 0.05– 0.2%, and mutations at another, v, are similar. At least eight known genes ...
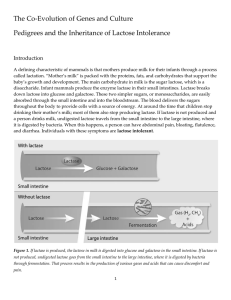
The Co-Evolution of Genes and Culture Pedigrees and the
... lactose tolerant. They can also be referred to as being lactase persistent, meaning that lactase production persists beyond childhood. (People who no longer produce lactase as adults are called lactase nonpersistent.) Genetic studies suggest that lactose tolerance arose among human populations in th ...
... lactose tolerant. They can also be referred to as being lactase persistent, meaning that lactase production persists beyond childhood. (People who no longer produce lactase as adults are called lactase nonpersistent.) Genetic studies suggest that lactose tolerance arose among human populations in th ...
Chapter 1 Introduction to Evolutionary Computation and Genetic
... Evolutionary computation is the study of non-deterministic search algorithms that are based on aspects of Darwin’s theory of evolution by natural selection [10]. The principal originators of evolutionary algorithms were John Holland, Ingo Rechenberg, Hans-Paul Schwefel and Lawrence Fogel. Holland pr ...
... Evolutionary computation is the study of non-deterministic search algorithms that are based on aspects of Darwin’s theory of evolution by natural selection [10]. The principal originators of evolutionary algorithms were John Holland, Ingo Rechenberg, Hans-Paul Schwefel and Lawrence Fogel. Holland pr ...
Report Broad and Narrow Heritabilities of Quantitative Traits in a
... high additive variance does not necessarily indicate that there are any QTLs that follow a strictly additive model. It is, in fact, possible to have a high additive variance even when all loci follow a dominant model. Most important, when the influence of genetics on a trait is considered, the addit ...
... high additive variance does not necessarily indicate that there are any QTLs that follow a strictly additive model. It is, in fact, possible to have a high additive variance even when all loci follow a dominant model. Most important, when the influence of genetics on a trait is considered, the addit ...
lecture4-eQTLmapping
... For each marker: Split mice into groups according to their genotypes at each marker. Do a t-test/F-statistic Repeat for each typed marker ...
... For each marker: Split mice into groups according to their genotypes at each marker. Do a t-test/F-statistic Repeat for each typed marker ...
Genome-wide search for signatures of selection in three
... The haplotypes of each individual were separately reconstructed for each chromosome within each breed, using fastPHASE software (Scheet and Stephens, 2006). Population recombination rates (ρ=4×Ne ×r ) were estimated separately for each chromosome within each breed, using LDhat (McVean et al., 2004). ...
... The haplotypes of each individual were separately reconstructed for each chromosome within each breed, using fastPHASE software (Scheet and Stephens, 2006). Population recombination rates (ρ=4×Ne ×r ) were estimated separately for each chromosome within each breed, using LDhat (McVean et al., 2004). ...
Genetic control of broad-spectrum resistance to turnip mosaic virus
... and tobacco etch virus (TEV), corresponds to the eukaryotic initiation factor 4E gene (eIF4E) (Ruffel et al., 2002). Similarly, in Arabidopsis thaliana, disrupting the function of eIF(iso)4E produces plants that are resistant to TEV (Lellis et al., 2002), TuMV (Duprat et al., 2002; Lellis et al., 20 ...
... and tobacco etch virus (TEV), corresponds to the eukaryotic initiation factor 4E gene (eIF4E) (Ruffel et al., 2002). Similarly, in Arabidopsis thaliana, disrupting the function of eIF(iso)4E produces plants that are resistant to TEV (Lellis et al., 2002), TuMV (Duprat et al., 2002; Lellis et al., 20 ...
The stationary distribution of a continuously varying strategy in a
... inclusive fitness effect. The exploration of the phenotypic space varies exponentially with the cumulative inclusive fitness effect over state space, which determines an adaptive landscape. The peaks of the landscapes are those phenotypes that are candidate evolutionary stable strategies and can be ...
... inclusive fitness effect. The exploration of the phenotypic space varies exponentially with the cumulative inclusive fitness effect over state space, which determines an adaptive landscape. The peaks of the landscapes are those phenotypes that are candidate evolutionary stable strategies and can be ...
Alleles of a reelin CGG repeat do not convey
... Our findings agree with those recently published by Krebs et al. [2002], who analyzed a sample of 117 simplex and 50 multiplex families. The estimated allele distribution from our families is quite similar to that estimated by both the Persico and Krebs studies, showing two common alleles with 8 and ...
... Our findings agree with those recently published by Krebs et al. [2002], who analyzed a sample of 117 simplex and 50 multiplex families. The estimated allele distribution from our families is quite similar to that estimated by both the Persico and Krebs studies, showing two common alleles with 8 and ...
Human genetic variation

Human genetic variation is the genetic differences both within and among populations. There may be multiple variants of any given gene in the human population (genes), leading to polymorphism. Many genes are not polymorphic, meaning that only a single allele is present in the population: the gene is then said to be fixed. On average, in terms of DNA sequence all humans are 99.9% similar to any other humans.No two humans are genetically identical. Even monozygotic twins, who develop from one zygote, have infrequent genetic differences due to mutations occurring during development and gene copy-number variation. Differences between individuals, even closely related individuals, are the key to techniques such as genetic fingerprinting. Alleles occur at different frequencies in different human populations, with populations that are more geographically and ancestrally remote tending to differ more.Causes of differences between individuals include the exchange of genes during meiosis and various mutational events. There are at least two reasons why genetic variation exists between populations. Natural selection may confer an adaptive advantage to individuals in a specific environment if an allele provides a competitive advantage. Alleles under selection are likely to occur only in those geographic regions where they confer an advantage. The second main cause of genetic variation is due to the high degree of neutrality of most mutations. Most mutations do not appear to have any selective effect one way or the other on the organism. The main cause is genetic drift, this is the effect of random changes in the gene pool. In humans, founder effect and past small population size (increasing the likelihood of genetic drift) may have had an important influence in neutral differences between populations. The theory that humans recently migrated out of Africa supports this.The study of human genetic variation has both evolutionary significance and medical applications. It can help scientists understand ancient human population migrations as well as how different human groups are biologically related to one another. For medicine, study of human genetic variation may be important because some disease-causing alleles occur more often in people from specific geographic regions. New findings show that each human has on average 60 new mutations compared to their parents.Apart from mutations, many genes that may have aided humans in ancient times plague humans today. For example, it is suspected that genes that allow humans to more efficiently process food are those that make people susceptible to obesity and diabetes today.