Online resources for genetic variation study-Part One
... Deletions, inversions, or translocation of large DNA fragments Rare but often causing serious genetic diseases ...
... Deletions, inversions, or translocation of large DNA fragments Rare but often causing serious genetic diseases ...
Lab 7: Mutation, Selection and Drift
... rate of backward mutations is ν = 0, and if: a. A1 is completely dominant to A2. b. There is additivity. c. If the equilibrium frequencies of A2 in a) and b) are different, explain ...
... rate of backward mutations is ν = 0, and if: a. A1 is completely dominant to A2. b. There is additivity. c. If the equilibrium frequencies of A2 in a) and b) are different, explain ...
The distribution of substitutions reflects features of homologous
... There are four well-defined phylogroups A, B1, B2 and E in E. coli [17]. Phylogroups A and B1 are close and DND for pairs of genomes from these phylogroups with the same distance have the same shape, whereas B2 separated from them much earlier and demonstrates the different behaviour. Phylogroup E c ...
... There are four well-defined phylogroups A, B1, B2 and E in E. coli [17]. Phylogroups A and B1 are close and DND for pairs of genomes from these phylogroups with the same distance have the same shape, whereas B2 separated from them much earlier and demonstrates the different behaviour. Phylogroup E c ...
The Ins and Outs of Pedigree Analysis, Genetic
... that established breeds are separate entities among themselves, they all are genetically the same species. While a mating within a breed may be considered outbred, it still must be viewed as part of the whole genetic picture: a mating within an isolated, closely related, interbred population. Each b ...
... that established breeds are separate entities among themselves, they all are genetically the same species. While a mating within a breed may be considered outbred, it still must be viewed as part of the whole genetic picture: a mating within an isolated, closely related, interbred population. Each b ...
A criticism of the value of midparent in
... control theory which aims to predict phenotype from biochemistry, increased metabolic flux is expected to be monotonically related to performance (Kacser and Burns, 1981). Of course, the value of a given trait cannot increase indefinitely, but most traits do not appear to be limited by physical cons ...
... control theory which aims to predict phenotype from biochemistry, increased metabolic flux is expected to be monotonically related to performance (Kacser and Burns, 1981). Of course, the value of a given trait cannot increase indefinitely, but most traits do not appear to be limited by physical cons ...
An Unusual Missense Mutation in the GJB3 Gene Resulting in
... it causes an amino acid exchange from phenylalanine to leucine at position 137 in the third transmembrane domain of connexin 31 (p.Phe137Leu, F137L) (2). This amino acid exchange occasionally leads to a phenotype of pronounced hyperkeratoses, as in our patient. Furthermore, it can cause erythema gyr ...
... it causes an amino acid exchange from phenylalanine to leucine at position 137 in the third transmembrane domain of connexin 31 (p.Phe137Leu, F137L) (2). This amino acid exchange occasionally leads to a phenotype of pronounced hyperkeratoses, as in our patient. Furthermore, it can cause erythema gyr ...
Chapter 3: Forming a New Life: coneeption, Heredity and Environment
... or absence of dimples, are called alleles. Alleles are the different version of a particular gene. Every person receives one maternal and one paternal allele for any given trait. When both alleles are the same, the person is homozygous for the characteristic; when they are different, the perso ...
... or absence of dimples, are called alleles. Alleles are the different version of a particular gene. Every person receives one maternal and one paternal allele for any given trait. When both alleles are the same, the person is homozygous for the characteristic; when they are different, the perso ...
FREE Sample Here - We can offer most test bank and
... or absence of dimples, are called alleles. Alleles are the different version of a particular gene. Every person receives one maternal and one paternal allele for any given trait. When both alleles are the same, the person is homozygous for the characteristic; when they are different, the perso ...
... or absence of dimples, are called alleles. Alleles are the different version of a particular gene. Every person receives one maternal and one paternal allele for any given trait. When both alleles are the same, the person is homozygous for the characteristic; when they are different, the perso ...
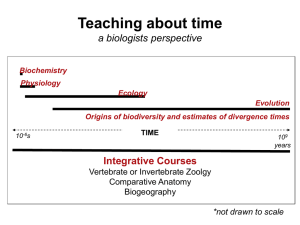
Teaching deep time through macroevolution and
... rRNA gene you made earlier in the week. Which gave a more robust hypothesis (and why), and what are the reasons why the two genes resolved different hypotheses?” ….but that’s it. ...
... rRNA gene you made earlier in the week. Which gave a more robust hypothesis (and why), and what are the reasons why the two genes resolved different hypotheses?” ….but that’s it. ...
Activity 1: Breeding Bunnies In this activity, you will examine natural
... Activity 1: Breeding Bunnies In this activity, you will examine natural selection in a small population of wild rabbits. Evolution, on a genetic level, is a change in the frequency of alleles in a population over a period of time. Breeders of rabbits have long been familiar with a variety of genetic ...
... Activity 1: Breeding Bunnies In this activity, you will examine natural selection in a small population of wild rabbits. Evolution, on a genetic level, is a change in the frequency of alleles in a population over a period of time. Breeders of rabbits have long been familiar with a variety of genetic ...
ppt
... realm of population genetics Human genome took 10 years to sequence originally, and hundreds of millions of dollars Now we can do it in a week for <$2,000 ...
... realm of population genetics Human genome took 10 years to sequence originally, and hundreds of millions of dollars Now we can do it in a week for <$2,000 ...
Causal Democracy And Causal Contributions In Developmental
... ways, including simple persistence in the niche. Phenotypic traits, on the other hand, are not transmitted but must be constructed in development. The usual flow of disembodied genetic "information" between the generations, with or without a second channel for culture, is replaced by more or less fa ...
... ways, including simple persistence in the niche. Phenotypic traits, on the other hand, are not transmitted but must be constructed in development. The usual flow of disembodied genetic "information" between the generations, with or without a second channel for culture, is replaced by more or less fa ...
NTP Activities for the National Children’s Study Funding Redirect
... – Demonstrate performance by measuring gene expression levels in extracts from different sample types, each treated with developmental toxicants identified by NICEATM at multiple doses, in triplicate ...
... – Demonstrate performance by measuring gene expression levels in extracts from different sample types, each treated with developmental toxicants identified by NICEATM at multiple doses, in triplicate ...
Deriving Trading Rules Using Gene Expression Programming
... data about exchange rates, and the fact that quotations are real numbers, further analysis has to be made to divide the problem into smaller problems that can be easily solved. The mapping between the concepts and the genetic structures is given in Table 1. ...
... data about exchange rates, and the fact that quotations are real numbers, further analysis has to be made to divide the problem into smaller problems that can be easily solved. The mapping between the concepts and the genetic structures is given in Table 1. ...
3.C.1 - The Bio Edge
... inherited and passed generation after generation • Somatic (body cells) mutations can not be inherited and thus die with the individual. ...
... inherited and passed generation after generation • Somatic (body cells) mutations can not be inherited and thus die with the individual. ...
THE MID YEAR EXAM GRADE WILL BE DIVIDED 90 % FROM
... Describe how Mendel was able to control how his pea plants were pollinated. Describe the steps in Mendel’s experiments on true-breeding garden peas. Distinguish between dominant and recessive traits. State two laws of heredity that were developed from Mendel’s work. Describe how Mendel’s results can ...
... Describe how Mendel was able to control how his pea plants were pollinated. Describe the steps in Mendel’s experiments on true-breeding garden peas. Distinguish between dominant and recessive traits. State two laws of heredity that were developed from Mendel’s work. Describe how Mendel’s results can ...
Theoretical Approaches to the Evolution of Development and
... trajectories simply compared the shapes of different trajectories, making no attempt to map the shape of these curves to underlying genetic processes. This approach can provide some limited insight into developmental evolution. Specifically, we can test whether or not a particular evolutionary trans ...
... trajectories simply compared the shapes of different trajectories, making no attempt to map the shape of these curves to underlying genetic processes. This approach can provide some limited insight into developmental evolution. Specifically, we can test whether or not a particular evolutionary trans ...
positionalCloning15
... • Look in genome for potential candidates What’s nearby in genome? . . . a [very good] MODEL of reality No luck in genome sequence? (rare) misassembly or gaps • conserved synteny with other fish • Physical map: BAC clones • genetic or RH maps ...
... • Look in genome for potential candidates What’s nearby in genome? . . . a [very good] MODEL of reality No luck in genome sequence? (rare) misassembly or gaps • conserved synteny with other fish • Physical map: BAC clones • genetic or RH maps ...
Mutation, Transposition, and Recombination
... 4) also show an extremely important feature of recombination, that is, the homogenizing effect of all kinds of recombination, from the most conservative to the most disruptive. For obvious reasons, these recombination-specific dynamics are called Homogenizing dynamics. Note that, in all cases, after ...
... 4) also show an extremely important feature of recombination, that is, the homogenizing effect of all kinds of recombination, from the most conservative to the most disruptive. For obvious reasons, these recombination-specific dynamics are called Homogenizing dynamics. Note that, in all cases, after ...
Molecular tools for breeding basidiomycetes
... and for positional gene cloning. The number of linkage maps available is low in filamentous fungi [7, 22, 29, 36]. Only one linkage map of edible fungi is currently available: the map for the button mushroom, Agaricus bisporus [15]. We have developed a map for P. ostreatus based on 196 markers (RAPD ...
... and for positional gene cloning. The number of linkage maps available is low in filamentous fungi [7, 22, 29, 36]. Only one linkage map of edible fungi is currently available: the map for the button mushroom, Agaricus bisporus [15]. We have developed a map for P. ostreatus based on 196 markers (RAPD ...
Preimplantation genetic diagnosis today
... shown that this phenomenon is partly explained by incomplete denaturation of the genomic template DNA during the initial cycles of PCR (Ray and Handyside, 1996). Raising the temperature in the initial cycles improves the efficiency of denaturation and minimizes but does not eliminate allelic dropout ...
... shown that this phenomenon is partly explained by incomplete denaturation of the genomic template DNA during the initial cycles of PCR (Ray and Handyside, 1996). Raising the temperature in the initial cycles improves the efficiency of denaturation and minimizes but does not eliminate allelic dropout ...
Lab: Breeding Bunnies
... 4. Label one dish FF for the homozygous dominant genotype. Label a second dish Ff for the heterozygous condition. Label the third dish ff for those rabbits with the homozygous recessive genotype. 5. Place the 50 purple and 50 black beads (alleles) in the container and shake up (mate) the rabbits. (P ...
... 4. Label one dish FF for the homozygous dominant genotype. Label a second dish Ff for the heterozygous condition. Label the third dish ff for those rabbits with the homozygous recessive genotype. 5. Place the 50 purple and 50 black beads (alleles) in the container and shake up (mate) the rabbits. (P ...
Human genetic variation

Human genetic variation is the genetic differences both within and among populations. There may be multiple variants of any given gene in the human population (genes), leading to polymorphism. Many genes are not polymorphic, meaning that only a single allele is present in the population: the gene is then said to be fixed. On average, in terms of DNA sequence all humans are 99.9% similar to any other humans.No two humans are genetically identical. Even monozygotic twins, who develop from one zygote, have infrequent genetic differences due to mutations occurring during development and gene copy-number variation. Differences between individuals, even closely related individuals, are the key to techniques such as genetic fingerprinting. Alleles occur at different frequencies in different human populations, with populations that are more geographically and ancestrally remote tending to differ more.Causes of differences between individuals include the exchange of genes during meiosis and various mutational events. There are at least two reasons why genetic variation exists between populations. Natural selection may confer an adaptive advantage to individuals in a specific environment if an allele provides a competitive advantage. Alleles under selection are likely to occur only in those geographic regions where they confer an advantage. The second main cause of genetic variation is due to the high degree of neutrality of most mutations. Most mutations do not appear to have any selective effect one way or the other on the organism. The main cause is genetic drift, this is the effect of random changes in the gene pool. In humans, founder effect and past small population size (increasing the likelihood of genetic drift) may have had an important influence in neutral differences between populations. The theory that humans recently migrated out of Africa supports this.The study of human genetic variation has both evolutionary significance and medical applications. It can help scientists understand ancient human population migrations as well as how different human groups are biologically related to one another. For medicine, study of human genetic variation may be important because some disease-causing alleles occur more often in people from specific geographic regions. New findings show that each human has on average 60 new mutations compared to their parents.Apart from mutations, many genes that may have aided humans in ancient times plague humans today. For example, it is suspected that genes that allow humans to more efficiently process food are those that make people susceptible to obesity and diabetes today.