DNA - VanityWolveriine
... molecules, or base pairs, called nucleotides: adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine (C) that are linked end to end. Each base on the opposite strand specifically pairs with, or is the complement of, the other: an A always pairs with a T, and a C always pairs with a G. A DNA molecule wi ...
... molecules, or base pairs, called nucleotides: adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine (C) that are linked end to end. Each base on the opposite strand specifically pairs with, or is the complement of, the other: an A always pairs with a T, and a C always pairs with a G. A DNA molecule wi ...
Section 5.1
... 15. cancer – (pg 158) a group of disorders characterized by the uncontrolled division of cells. Known as “selfish cells” that divide indefinitely and are considered immortal. ...
... 15. cancer – (pg 158) a group of disorders characterized by the uncontrolled division of cells. Known as “selfish cells” that divide indefinitely and are considered immortal. ...
Human genome study reveals certain genes are less essential than
... entirely in some people,” said Jan Korbel of the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, who led one of the genome project’s studies. The finding has astonished researchers because it was thought that all the 20,000 or so genes that make up the human genome must be essen ...
... entirely in some people,” said Jan Korbel of the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, who led one of the genome project’s studies. The finding has astonished researchers because it was thought that all the 20,000 or so genes that make up the human genome must be essen ...
File - Dixie Middle School Science
... • Virus -made of DNA and protein • The experiments • a virus with either radioactive DNA or radioactive protein were used to infect bacteria • Either the radioactive proteins or radioactive DNA would be transferred to the bacteria • Identifying which one is transferred would identify the genetic mat ...
... • Virus -made of DNA and protein • The experiments • a virus with either radioactive DNA or radioactive protein were used to infect bacteria • Either the radioactive proteins or radioactive DNA would be transferred to the bacteria • Identifying which one is transferred would identify the genetic mat ...
Genetics and Evolution
... Alleles-different forms of trait (eye color) Allele frequency-measure of how common an allele is in a population ...
... Alleles-different forms of trait (eye color) Allele frequency-measure of how common an allele is in a population ...
NOVA – Cracking the Code of Life
... 5. It was long thought that humans had around 100,000 genes. The initial survey of the human genome indicated that there were only about __________ genes in humans. What interesting fact about human genes allows humans to be so much more complex than something like a fruit fly? ...
... 5. It was long thought that humans had around 100,000 genes. The initial survey of the human genome indicated that there were only about __________ genes in humans. What interesting fact about human genes allows humans to be so much more complex than something like a fruit fly? ...
Gene and Gene Regulation
... A section of DNA that synthesizes a protein that is needed for traits ...
... A section of DNA that synthesizes a protein that is needed for traits ...
What do I need to know for the test?
... How is the number of phenotypes related to the number of genes that control the trait? What type of distribution curve can be seen with polygenic inheritance? Tell the 3 ways natural selection can affect the distributions of phenotypes in a bell-shaped curve? Be able to identify examples of each of ...
... How is the number of phenotypes related to the number of genes that control the trait? What type of distribution curve can be seen with polygenic inheritance? Tell the 3 ways natural selection can affect the distributions of phenotypes in a bell-shaped curve? Be able to identify examples of each of ...
Non-Mendelian Genetics Test Review
... 3. What is the anomaly in the karyotype below? Is the human a female or male? Trisomy 21 (extra chromosome on the 21st pair. This is a male with Downs syndrome (XY) ...
... 3. What is the anomaly in the karyotype below? Is the human a female or male? Trisomy 21 (extra chromosome on the 21st pair. This is a male with Downs syndrome (XY) ...
Study Guide
... c. Microinjection: by using a small needle to inject DNA directly into plant cells d. Agrobacterium tumefaciens: a bacteria that acts as a natural gene transfer vector to deliver DNA into plants e. osmotic or electric shock treatments ...
... c. Microinjection: by using a small needle to inject DNA directly into plant cells d. Agrobacterium tumefaciens: a bacteria that acts as a natural gene transfer vector to deliver DNA into plants e. osmotic or electric shock treatments ...
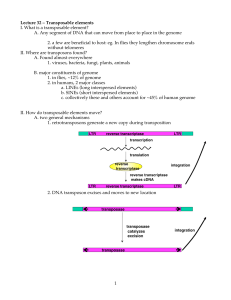
Transposable elements I. What is a transposable element?
... II. Where are transposons found? A. Found almost everywhere 1. viruses, bacteria, fungi, plants, animals B. major constituents of genome 1. in flies, ~12% of genome 2. in humans, 2 major classes a. LINEs (long interspersed elements) b. SINEs (short interspersed elements) c. collectively these and ot ...
... II. Where are transposons found? A. Found almost everywhere 1. viruses, bacteria, fungi, plants, animals B. major constituents of genome 1. in flies, ~12% of genome 2. in humans, 2 major classes a. LINEs (long interspersed elements) b. SINEs (short interspersed elements) c. collectively these and ot ...
Genetics and Evolution
... Alleles-different forms of trait (eye color) Allele frequency-measure of how common an allele is in a population ...
... Alleles-different forms of trait (eye color) Allele frequency-measure of how common an allele is in a population ...
Genetic engineering
... DNA ligase is an enzyme that is used to get the foreign DNA to join with the DNA of the cloning vector. Genetic ‘glue’. The altered DNA is called recombinant DNA because it recombines after the small section of DNA is inserted into it. Transgenic organisms are organisms that have been altered using ...
... DNA ligase is an enzyme that is used to get the foreign DNA to join with the DNA of the cloning vector. Genetic ‘glue’. The altered DNA is called recombinant DNA because it recombines after the small section of DNA is inserted into it. Transgenic organisms are organisms that have been altered using ...
Document
... genes; and introns do not interrupt the cloned sequence. Disadvantages: contain only sequences that are presence in mature mRNA; and sequences expressed in the tissue from which RNA was isolated. ...
... genes; and introns do not interrupt the cloned sequence. Disadvantages: contain only sequences that are presence in mature mRNA; and sequences expressed in the tissue from which RNA was isolated. ...
Study Questions – Chapter 1
... 15. In the late 1980s when the Huntington disease gene was mapped, it took years afterwards to find the gene. After the turn of the century, when the progeria gene was mapped, it took less than a year to find the gene. What had changed that made such a big difference in the timelines of these two p ...
... 15. In the late 1980s when the Huntington disease gene was mapped, it took years afterwards to find the gene. After the turn of the century, when the progeria gene was mapped, it took less than a year to find the gene. What had changed that made such a big difference in the timelines of these two p ...
Vocab table - Genetics and variation teacher
... Formed by crossing two pure-bedding parents differing with respect to one pair of contrasting traits ...
... Formed by crossing two pure-bedding parents differing with respect to one pair of contrasting traits ...
OUR GENES, OUR SELVES VOCABULARY
... HOMOZYGOUS / PURBRED: (AKA Purebred) An organism with identical alleles for a characteristic is homozygous. HETEROZYGOUS / HYBRID: (AKA Hybrid) An organism with different pairs of alleles for a characteristic is heterozygous. ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION: Reproduction of offspring in which it is not necessa ...
... HOMOZYGOUS / PURBRED: (AKA Purebred) An organism with identical alleles for a characteristic is homozygous. HETEROZYGOUS / HYBRID: (AKA Hybrid) An organism with different pairs of alleles for a characteristic is heterozygous. ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION: Reproduction of offspring in which it is not necessa ...
4 - On Cells, DNA, Proteins, and Populations
... • Each side of the original is a template for making a new copy of its complement ...
... • Each side of the original is a template for making a new copy of its complement ...
Sex Cells (gametes)
... • Each side of the original is a template for making a new copy of its complement ...
... • Each side of the original is a template for making a new copy of its complement ...
Regulatory genes
... • Bacteria have three mechanisms for exchanging genetic information between themselves: – 1. Transformation – 2. Transduction – 3. Conjugation ...
... • Bacteria have three mechanisms for exchanging genetic information between themselves: – 1. Transformation – 2. Transduction – 3. Conjugation ...
biology-final-exam-jeopardy-game
... The long, slow process of change in a species over time is called what? Evolution ...
... The long, slow process of change in a species over time is called what? Evolution ...
Genetic engineering
Genetic engineering, also called genetic modification, is the direct manipulation of an organism's genome using biotechnology. It is therefore a set of technologies used to change the genetic makeup of cells, including the transfer of genes within and across species boundaries to produce improved or novel organisms. New DNA may be inserted in the host genome by first isolating and copying the genetic material of interest using molecular cloning methods to generate a DNA sequence, or by synthesizing the DNA, and then inserting this construct into the host organism. Genes may be removed, or ""knocked out"", using a nuclease. Gene targeting is a different technique that uses homologous recombination to change an endogenous gene, and can be used to delete a gene, remove exons, add a gene, or introduce point mutations.An organism that is generated through genetic engineering is considered to be a genetically modified organism (GMO). The first GMOs were bacteria generated in 1973 and GM mice in 1974. Insulin-producing bacteria were commercialized in 1982 and genetically modified food has been sold since 1994. Glofish, the first GMO designed as a pet, was first sold in the United States December in 2003.Genetic engineering techniques have been applied in numerous fields including research, agriculture, industrial biotechnology, and medicine. Enzymes used in laundry detergent and medicines such as insulin and human growth hormone are now manufactured in GM cells, experimental GM cell lines and GM animals such as mice or zebrafish are being used for research purposes, and genetically modified crops have been commercialized.