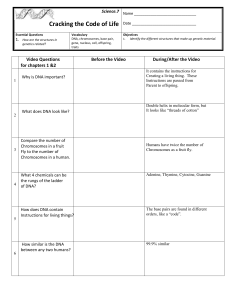
Science.7 Cracking the Code of Life Name Date Essential Questions
... DNA, chromosomes, base pair, gene, nucleus, cell, offspring, traits ...
... DNA, chromosomes, base pair, gene, nucleus, cell, offspring, traits ...
Ch 8-11 Review
... 1. Describe the structure of DNA. Be sure to include what forms the skeleton and how are the strands held together? 2. Compare and contrast chromosomes, chromatids, genes, and alleles. 3. Compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell division. 4. Describe the process of asexual reproduction i ...
... 1. Describe the structure of DNA. Be sure to include what forms the skeleton and how are the strands held together? 2. Compare and contrast chromosomes, chromatids, genes, and alleles. 3. Compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell division. 4. Describe the process of asexual reproduction i ...
Pamphlet from the Institute for Responsible Technology
... hard-to-detect side effects, including allergies, toxins, new diseases, and nutritional problems. They urged long-term safety studies, but were ignored. The FDA does not require any safety evaluations for GMOs. ...
... hard-to-detect side effects, including allergies, toxins, new diseases, and nutritional problems. They urged long-term safety studies, but were ignored. The FDA does not require any safety evaluations for GMOs. ...
Mutations - Lakeland Regional High School / Overview
... Types of Mutations • A. Chromosomal Mutations –Occurs during cell division ...
... Types of Mutations • A. Chromosomal Mutations –Occurs during cell division ...
epilepsy are reviewed from the Faculty of Medicine and Research
... is complex, with genetic heterogeneity and variable expression. The clinical genetic testing include medical management, diagnosis, prevention, and determination of risk to future children in family planning. Genetic research facilitates the recognition of new epilepsy syndromes and the development ...
... is complex, with genetic heterogeneity and variable expression. The clinical genetic testing include medical management, diagnosis, prevention, and determination of risk to future children in family planning. Genetic research facilitates the recognition of new epilepsy syndromes and the development ...
Genes and Natural Selection
... Who started this • Darwin proposed his theory of evolution, cell division, genes, and chromosomes had not yet been discovered ...
... Who started this • Darwin proposed his theory of evolution, cell division, genes, and chromosomes had not yet been discovered ...
Genetics in Agriculture
... and carefully monitored. b. Pollen can be gathered from male plants (or flowers) months or in some cases, years in advance and refrigerated for storage. c. Flowers on the female plant must be covered prior to opening, and if capable of self-pollination, must have the stamens removed. d. Once t ...
... and carefully monitored. b. Pollen can be gathered from male plants (or flowers) months or in some cases, years in advance and refrigerated for storage. c. Flowers on the female plant must be covered prior to opening, and if capable of self-pollination, must have the stamens removed. d. Once t ...
DNA—From Genes to Proteins
... nucleus of cells in order to identify an individual. double helix Two helixes wound around each other, as in the structure of DNA. enzyme A protein that functions to speed up a chemical reaction in an organism. eukaryotic Bearing a nuclear membrane. An animal cell is an example of a eukaryotic cell. ...
... nucleus of cells in order to identify an individual. double helix Two helixes wound around each other, as in the structure of DNA. enzyme A protein that functions to speed up a chemical reaction in an organism. eukaryotic Bearing a nuclear membrane. An animal cell is an example of a eukaryotic cell. ...
Did genetic links to modern maladies provide ancient
... may play similar—but likely more complex—roles in respond to a number of drugs, including growth health. hormone treatments. "Crohn's disease and psoriasis are damaging, but In the past, scientists have conducted similar our findings suggest that there may be something studies examining genetic vari ...
... may play similar—but likely more complex—roles in respond to a number of drugs, including growth health. hormone treatments. "Crohn's disease and psoriasis are damaging, but In the past, scientists have conducted similar our findings suggest that there may be something studies examining genetic vari ...
File
... migratory routes. » D The largest organisms in a species receive the only breeding opportunities ...
... migratory routes. » D The largest organisms in a species receive the only breeding opportunities ...
2D Barcode Quiz
... Thymine, Guanine, Adenine and Cytosine are the four bases or ‘nucleotides’ that make up DNA Adenine and Guanine are Pyrimidines (6-point ring), Cytosine and Thymine are Purines (fused 5- and 6-point rings) DNA has a triple helix structure Adenine pairs with Thymine through 2 Hydrogen bonds, Cytosine ...
... Thymine, Guanine, Adenine and Cytosine are the four bases or ‘nucleotides’ that make up DNA Adenine and Guanine are Pyrimidines (6-point ring), Cytosine and Thymine are Purines (fused 5- and 6-point rings) DNA has a triple helix structure Adenine pairs with Thymine through 2 Hydrogen bonds, Cytosine ...
BIO 10 Lecture 2
... Could destroy the function of a protein or subtly alter its function • Will get passed on and increase in frequency if it increases the reproductive fitness of its host ...
... Could destroy the function of a protein or subtly alter its function • Will get passed on and increase in frequency if it increases the reproductive fitness of its host ...
Document
... a. pulled toward that end by gravity. b. attracted to complementary DNA fragments at that end of the gel. c. attracted to the positively charged end of the gel. d. repelled by hydrophobic molecules at the other end of the gel. _____ 3. The accuracy of DNA fingerprinting can be increased by comparing ...
... a. pulled toward that end by gravity. b. attracted to complementary DNA fragments at that end of the gel. c. attracted to the positively charged end of the gel. d. repelled by hydrophobic molecules at the other end of the gel. _____ 3. The accuracy of DNA fingerprinting can be increased by comparing ...
2016 Ag Biotechnology CDE
... 35. During transcription, the DNA code of a single gene is read and a copy is made called mRNA. Why is it not necessary for the entire DNA molecule (every one of hundreds of genes on the chromosome) to be copied during transcription? an mRNA strand the size of a chromosome would be too large to tra ...
... 35. During transcription, the DNA code of a single gene is read and a copy is made called mRNA. Why is it not necessary for the entire DNA molecule (every one of hundreds of genes on the chromosome) to be copied during transcription? an mRNA strand the size of a chromosome would be too large to tra ...
Heredity
... process of Mitosis (one parent) • Examples: – One-celled organisms (bacteria) – Regeneration: replacing lost body parts (lizard’s tail) – Budding: new organism grows out of the old one (hydra) – Cloning: make copies of an organism (grow new plant from part of another plant) ...
... process of Mitosis (one parent) • Examples: – One-celled organisms (bacteria) – Regeneration: replacing lost body parts (lizard’s tail) – Budding: new organism grows out of the old one (hydra) – Cloning: make copies of an organism (grow new plant from part of another plant) ...
Molecular and Genetic Dissection of Plant Defense Reactions
... Plant resistance against disease involves inducible defense mechanisms. One aspect of the plant defense response is the induction of programmed cell death known as hypersensitive response (HR). Our research focuses on understanding the signal transduction pathway by which a fungal protein elicitor i ...
... Plant resistance against disease involves inducible defense mechanisms. One aspect of the plant defense response is the induction of programmed cell death known as hypersensitive response (HR). Our research focuses on understanding the signal transduction pathway by which a fungal protein elicitor i ...
Using a Single-Nucleotide Polymorphism to Predict
... Verify GMO-negative result is not due to PCR reaction not working ...
... Verify GMO-negative result is not due to PCR reaction not working ...
Document
... Analogous are structurally different but have the same function. Homologous share structural similarities but may have different functions. Genetic Engineering 28) What are the steps used to engineer transgenic organisms? Isolate the desired gene and cut it out with restriction enzymes. Cut the plas ...
... Analogous are structurally different but have the same function. Homologous share structural similarities but may have different functions. Genetic Engineering 28) What are the steps used to engineer transgenic organisms? Isolate the desired gene and cut it out with restriction enzymes. Cut the plas ...
BUILDING THE LIFE MOLECULES: DNA AND RNA The
... The dissemination area of the Centro de Biotecnologia Molecular Estrutural (CBME) have been developing a program of new tools to help teaching and learning of structural molecular biology area at all levels, from elementary to graduate schools. In this way, we have developed a kit denoted Building t ...
... The dissemination area of the Centro de Biotecnologia Molecular Estrutural (CBME) have been developing a program of new tools to help teaching and learning of structural molecular biology area at all levels, from elementary to graduate schools. In this way, we have developed a kit denoted Building t ...
dna_notes - KScience
... Mutations are sometimes beneficial because they generate variability, which is the basis of natural selection. Mutations are more often deleterious because selection in a species has selected for the genome it now has and changes are therefore more likely to be less useful. Mutations can lead to sev ...
... Mutations are sometimes beneficial because they generate variability, which is the basis of natural selection. Mutations are more often deleterious because selection in a species has selected for the genome it now has and changes are therefore more likely to be less useful. Mutations can lead to sev ...
Katie-Arabidopsis
... with tiny, white, four-petalled flowers • Six week lifespan • No immediate agricultural importance and is not thought to cure any disease • Prolific seed production and easy cultivation in restricted space • A large number of mutant lines and genomic resources ...
... with tiny, white, four-petalled flowers • Six week lifespan • No immediate agricultural importance and is not thought to cure any disease • Prolific seed production and easy cultivation in restricted space • A large number of mutant lines and genomic resources ...
Genetic engineering
Genetic engineering, also called genetic modification, is the direct manipulation of an organism's genome using biotechnology. It is therefore a set of technologies used to change the genetic makeup of cells, including the transfer of genes within and across species boundaries to produce improved or novel organisms. New DNA may be inserted in the host genome by first isolating and copying the genetic material of interest using molecular cloning methods to generate a DNA sequence, or by synthesizing the DNA, and then inserting this construct into the host organism. Genes may be removed, or ""knocked out"", using a nuclease. Gene targeting is a different technique that uses homologous recombination to change an endogenous gene, and can be used to delete a gene, remove exons, add a gene, or introduce point mutations.An organism that is generated through genetic engineering is considered to be a genetically modified organism (GMO). The first GMOs were bacteria generated in 1973 and GM mice in 1974. Insulin-producing bacteria were commercialized in 1982 and genetically modified food has been sold since 1994. Glofish, the first GMO designed as a pet, was first sold in the United States December in 2003.Genetic engineering techniques have been applied in numerous fields including research, agriculture, industrial biotechnology, and medicine. Enzymes used in laundry detergent and medicines such as insulin and human growth hormone are now manufactured in GM cells, experimental GM cell lines and GM animals such as mice or zebrafish are being used for research purposes, and genetically modified crops have been commercialized.