Gen.1303 Genome: The total genetic content contained in a haploid
... A hereditary unit consisting of a sequence of DNA that occupies a specific location on a chromosome and determines a particular characteristic in an organism. Genes undergo mutation when their DNA sequence changes. Chromatin: A complex of nucleic acids and proteins, primary histones, in the cell nuc ...
... A hereditary unit consisting of a sequence of DNA that occupies a specific location on a chromosome and determines a particular characteristic in an organism. Genes undergo mutation when their DNA sequence changes. Chromatin: A complex of nucleic acids and proteins, primary histones, in the cell nuc ...
Chapter 3 Section 4
... Chapter 3 Section 4 THE GENETIC CODE The main function of genes is to control the production of proteins. Proteins help determine the size, shape and other traits of organisms. Nitrogen bases form “rungs” of DNA ladder. The order of the nitrogen bases along a gene form a genetic code that spec ...
... Chapter 3 Section 4 THE GENETIC CODE The main function of genes is to control the production of proteins. Proteins help determine the size, shape and other traits of organisms. Nitrogen bases form “rungs” of DNA ladder. The order of the nitrogen bases along a gene form a genetic code that spec ...
Aim: How do scientists use biotechnology to manipulate genomes?
... Bacteria, help us make yogurt & cheese. ...
... Bacteria, help us make yogurt & cheese. ...
Genetic Engineering & Gene Therapy
... Potential benefits of transgenic organisms (GMOs - Genetically-modified organisms) • Genetic engineering can produce organisms that are: – able to synthesize oils, starches, hormones (e.g., bacteria that produce human insulin for use by diabetics) and plastics – edible vaccines from vegetables and ...
... Potential benefits of transgenic organisms (GMOs - Genetically-modified organisms) • Genetic engineering can produce organisms that are: – able to synthesize oils, starches, hormones (e.g., bacteria that produce human insulin for use by diabetics) and plastics – edible vaccines from vegetables and ...
Genes
... new medicines, vaccines and disease diagnostic tools; and higher yielding and more nutrient-rich crop plants. ...
... new medicines, vaccines and disease diagnostic tools; and higher yielding and more nutrient-rich crop plants. ...
Genetic Engineering
... a. mechanical vectors = Carry DNA into a cell, micropipette or metal bullet b. biological vectors = virus or bacterial plasmid (____small rings of DNA_____) 3. If host and foreign DNA have been cleaved by the same restriction enzyme, the ends can ___join the ends ____ together. 4. Gene cloning occur ...
... a. mechanical vectors = Carry DNA into a cell, micropipette or metal bullet b. biological vectors = virus or bacterial plasmid (____small rings of DNA_____) 3. If host and foreign DNA have been cleaved by the same restriction enzyme, the ends can ___join the ends ____ together. 4. Gene cloning occur ...
Creating Transgenic Mice
... Goals of this tutorial -To learn a few term related to genetically modified organisms -To understand the value of using genetically engineered organisms to study developmental biology -To learn the basic approaches about how transgenic mice are produced Genetically Modified Organisms Genetically mod ...
... Goals of this tutorial -To learn a few term related to genetically modified organisms -To understand the value of using genetically engineered organisms to study developmental biology -To learn the basic approaches about how transgenic mice are produced Genetically Modified Organisms Genetically mod ...
Applied Genetics
... organism with the DNA of another organism. • Recombinant DNA technology was first used in the 1970’s with bacteria. ...
... organism with the DNA of another organism. • Recombinant DNA technology was first used in the 1970’s with bacteria. ...
Genetic Engineering
... – Plants with double or triple the normal number of chromosomes – Produced by using drugs that prevent chromosomes from separating during meiosis ...
... – Plants with double or triple the normal number of chromosomes – Produced by using drugs that prevent chromosomes from separating during meiosis ...
No patents on Life - Diakonia Council Of Churches
... Invading the cell There are a few ways in which genetic engineers force the foreign gene cassette into the host plant cell: 1. Certain bacteria (Agrobacterium tumefaciens) normally infect plants by inserting a portion of its own DNA into a plant, which causes the plant to grow tumours. Gene scientis ...
... Invading the cell There are a few ways in which genetic engineers force the foreign gene cassette into the host plant cell: 1. Certain bacteria (Agrobacterium tumefaciens) normally infect plants by inserting a portion of its own DNA into a plant, which causes the plant to grow tumours. Gene scientis ...
Genetic Engineering
... Genetic Engineering As a base, man should realize that genetic engineering has already been done, by nature, during evolution. Some of the things man struggles with, some of his diseases, are in fact protections from other problems, genetically selected to be passed forward only becaue they were ben ...
... Genetic Engineering As a base, man should realize that genetic engineering has already been done, by nature, during evolution. Some of the things man struggles with, some of his diseases, are in fact protections from other problems, genetically selected to be passed forward only becaue they were ben ...
DNA Technology
... DNA Technology This involves Restriction enzymes: Enzymes that recognize a DNA sequence (usually a palindrome) and cut DNA at that sequence. ( p. 398 in textbook) Two major types of DNA Technology A. Gene Splicing: DNA from one organism is spliced into another organism (bacteria) (see p. 397-399) (R ...
... DNA Technology This involves Restriction enzymes: Enzymes that recognize a DNA sequence (usually a palindrome) and cut DNA at that sequence. ( p. 398 in textbook) Two major types of DNA Technology A. Gene Splicing: DNA from one organism is spliced into another organism (bacteria) (see p. 397-399) (R ...
Study guide - MabryOnline.org
... 3: What controls variations in skin color among humans? 4:How does geneticist use pedigrees? 5:What must occur for a girl to be colorblind? 6: Which trait is controlled by a gene with multiple alleles? 7:Genetic disorders are caused by? 8:Cloning results in two organisms that are _________ 9:What is ...
... 3: What controls variations in skin color among humans? 4:How does geneticist use pedigrees? 5:What must occur for a girl to be colorblind? 6: Which trait is controlled by a gene with multiple alleles? 7:Genetic disorders are caused by? 8:Cloning results in two organisms that are _________ 9:What is ...
Exp 4 Lecture - Seattle Central College
... In addition to one large chromosome, bacteria often contain one or more small circular pieces of DNA called plasmids. • Plasmid DNA usually contains genes for more than one trait. Genetic engineering involves inserting genes coding for new traits into a plasmid. • In this experiment, the pGLO plasmi ...
... In addition to one large chromosome, bacteria often contain one or more small circular pieces of DNA called plasmids. • Plasmid DNA usually contains genes for more than one trait. Genetic engineering involves inserting genes coding for new traits into a plasmid. • In this experiment, the pGLO plasmi ...
Cracking the code of life
... 10. Would you be willing to take a test to tell you if your children would be at risk for certain disorders and diseases? Why or why not? ...
... 10. Would you be willing to take a test to tell you if your children would be at risk for certain disorders and diseases? Why or why not? ...
CPS - General Biology Review.cps
... Messenger RNA is made from DNA Transfer RNA is made from messenger RNA The cell uses information from messenger RNA to produce proteins. Copies of DNA molecules are made ...
... Messenger RNA is made from DNA Transfer RNA is made from messenger RNA The cell uses information from messenger RNA to produce proteins. Copies of DNA molecules are made ...
Genes Trends - Pearland ISD
... sheets very quickly, certainly a lot faster than when covering a wound during natural healing. ...
... sheets very quickly, certainly a lot faster than when covering a wound during natural healing. ...
Study Guide-Exam II Chapter 10 Know which recombinant proteins
... 2 Exam questions (Bring your typewritten answers to class; limit each answer to 1 single sided page) 1. Explain how you would go about creating a traditional vaccine for the H1N1 virus, and then explain how you could produce an effective recombinant subunit vaccine for this H1N1 virus in yeast. What ...
... 2 Exam questions (Bring your typewritten answers to class; limit each answer to 1 single sided page) 1. Explain how you would go about creating a traditional vaccine for the H1N1 virus, and then explain how you could produce an effective recombinant subunit vaccine for this H1N1 virus in yeast. What ...
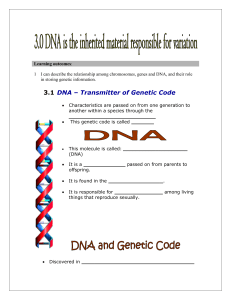
Sc9 - a 3.1(student notes)
... Learning outcomes: 1 I can describe the relationship among chromosomes, genes and DNA, and their role in storing genetic information. ...
... Learning outcomes: 1 I can describe the relationship among chromosomes, genes and DNA, and their role in storing genetic information. ...
Bill Nye: Genes - stephaniemcoggins
... 4. How long is the DNA string model of science? 5. How many times longer is DNA than it is wide? 6. How does Bill define a Gene? 7. Why is the white blood cell dark on the computer screen? 8. What does the nucleus of the cell contain? 9. What can you do with DNA after you take it out of an organism? ...
... 4. How long is the DNA string model of science? 5. How many times longer is DNA than it is wide? 6. How does Bill define a Gene? 7. Why is the white blood cell dark on the computer screen? 8. What does the nucleus of the cell contain? 9. What can you do with DNA after you take it out of an organism? ...
Chapter 13 Genetic Engineering - Mrs. Moyer
... and connect it to a circular DNA molecule known as a plasmid… which can be found naturally in bacteria. This bacteria can then be injected into a plant, and will insert its DNA into the plant. ► If transformation is successful, the recombinant DNA is integrated into one of the chromosomes of the cel ...
... and connect it to a circular DNA molecule known as a plasmid… which can be found naturally in bacteria. This bacteria can then be injected into a plant, and will insert its DNA into the plant. ► If transformation is successful, the recombinant DNA is integrated into one of the chromosomes of the cel ...