Slide 1 - Cloudfront.net
... will become a parent and not every set of parents will produce the same number of offspring. The effect, called random genetic drift, is particularly strong in small populations (e.g., 100 breeding pairs or fewer); when the gene is neutral; that is, is neither helpful nor deleterious. Eventually the ...
... will become a parent and not every set of parents will produce the same number of offspring. The effect, called random genetic drift, is particularly strong in small populations (e.g., 100 breeding pairs or fewer); when the gene is neutral; that is, is neither helpful nor deleterious. Eventually the ...
Abstract
... hominins and modern-day humans. There is evidence that ancient pastoralists may have had healthier genomes than hunter-gatherers or farmers, and genomes from the recent past appear to be healthier than genomes from the deep past. Evolutionary history also contributes to health disparities. We find t ...
... hominins and modern-day humans. There is evidence that ancient pastoralists may have had healthier genomes than hunter-gatherers or farmers, and genomes from the recent past appear to be healthier than genomes from the deep past. Evolutionary history also contributes to health disparities. We find t ...
Evolution Notes - C. Shirley Science EJCHS
... To explain Natural Selection, Darwin compared it to Artificial Selection ….. the selection by humans for breeding of desired traits from the natural variation among different organisms. Examples – Domestication of Animals, Crops, etc… ...
... To explain Natural Selection, Darwin compared it to Artificial Selection ….. the selection by humans for breeding of desired traits from the natural variation among different organisms. Examples – Domestication of Animals, Crops, etc… ...
Chapter 13
... cause, particularly among animals (choosing mates w/particular traits, ex: healthiest) - differential success in reproduction is probably always the case in natural populations (leads to adaptive elvolution) ...
... cause, particularly among animals (choosing mates w/particular traits, ex: healthiest) - differential success in reproduction is probably always the case in natural populations (leads to adaptive elvolution) ...
Genetic structure of a desynchronized population of Thaumetopoea
... monitored with funnel trap captures. Results indicate that this population belongs to T. pityocampa although there was a shift in the life cycle. Genetic distance between this and the normal populations suggests that the summer population is differentiated from the winter one, and there is little ge ...
... monitored with funnel trap captures. Results indicate that this population belongs to T. pityocampa although there was a shift in the life cycle. Genetic distance between this and the normal populations suggests that the summer population is differentiated from the winter one, and there is little ge ...
File - Mr. Shanks` Class
... decay… the half life is a _________________for any given isotope The time it takes for exactly ________of a parent isotope to decay into a daughter isotope The Modern Synthesis The knowledge and understanding of genetics and other fields of biology have been combined with Darwin’s theory of natural ...
... decay… the half life is a _________________for any given isotope The time it takes for exactly ________of a parent isotope to decay into a daughter isotope The Modern Synthesis The knowledge and understanding of genetics and other fields of biology have been combined with Darwin’s theory of natural ...
Mechanisms of Evolution
... a. Species: a group of organisms that can interbreed and produce fertile offspring b. Population: a group of interbreeding species occupying a particular area c. Evolution is simply a change in the frequency of genes in a population. Evolution occurs by Natural Selection. Natural selection states: 1 ...
... a. Species: a group of organisms that can interbreed and produce fertile offspring b. Population: a group of interbreeding species occupying a particular area c. Evolution is simply a change in the frequency of genes in a population. Evolution occurs by Natural Selection. Natural selection states: 1 ...
Chapter 10, 11, 12 Overview Evolution Define: Evolution, Species
... It is rare, therefore, for a peccary to move from one herd to another. Together, these socially and behaviorally egalitarian animals form a population. It is at the population level that the phenomenon of evolution is observed, studied and measured. Individual peccaries cannot evolve, but the little ...
... It is rare, therefore, for a peccary to move from one herd to another. Together, these socially and behaviorally egalitarian animals form a population. It is at the population level that the phenomenon of evolution is observed, studied and measured. Individual peccaries cannot evolve, but the little ...
b. geographic isolation
... sequence of DNA. May affect an organisms fitness (it’s ability to survive and reproduce in its environment) b. Gene shuffling- most caused during production of gametes. (sexual reproduction major source of variation within many populations) ...
... sequence of DNA. May affect an organisms fitness (it’s ability to survive and reproduce in its environment) b. Gene shuffling- most caused during production of gametes. (sexual reproduction major source of variation within many populations) ...
Introduction to Medical Genetics
... is concerned with variation and heredity in all living organisms Human genetics is the science of variation and heredity in humans Medical genetics deals with human genetic variation of significance in medical practice and research Cytogenetics: the study of chromosomes ...
... is concerned with variation and heredity in all living organisms Human genetics is the science of variation and heredity in humans Medical genetics deals with human genetic variation of significance in medical practice and research Cytogenetics: the study of chromosomes ...
Exam 3 Review material
... questions which draw from your knowledge, intelligence and creativity. Know the material below and you will be in great shape for the upcoming exam! ...
... questions which draw from your knowledge, intelligence and creativity. Know the material below and you will be in great shape for the upcoming exam! ...
Evolutionary Genetics - The Institute for Environmental Modeling
... sometimes alter the structure or number of genes or entire chromosomes. Most mutations are harmful, but some are advantageous. Mutations occur naturally at low rates (10−5 −10−6 per gene per generation). Mutation is considered to be the major factor limiting the speed of evolution. Isolated populati ...
... sometimes alter the structure or number of genes or entire chromosomes. Most mutations are harmful, but some are advantageous. Mutations occur naturally at low rates (10−5 −10−6 per gene per generation). Mutation is considered to be the major factor limiting the speed of evolution. Isolated populati ...
Genetic Variation in Natural Selection
... gene pool is important for the survival of a species in a changing environment. 1A.1d: Environments can be more or less stable or fluctuating, and this affects evolutionary rate and direction; different genetic variations can be selected in each generation. 1A.1e: An adaptation is a genetic variatio ...
... gene pool is important for the survival of a species in a changing environment. 1A.1d: Environments can be more or less stable or fluctuating, and this affects evolutionary rate and direction; different genetic variations can be selected in each generation. 1A.1e: An adaptation is a genetic variatio ...
Bottlenecks and Founder Effects
... reduced their population size to as few as 20 individuals. There population has since rebounded to 30,000 but there traits still reflect the effects of the bottleneck event ...
... reduced their population size to as few as 20 individuals. There population has since rebounded to 30,000 but there traits still reflect the effects of the bottleneck event ...
Evolution Study Guide KEY Evolution Study Guide
... What is Lamarck’s theory of evolution? Parents pass on acquired traits to offspring. How does Darwin’s theory of evolution explain extinction? If an organism is not suited to its environment it will usually go extinct. Occasionally a helpful mutation can occur that will become an adaptation in the s ...
... What is Lamarck’s theory of evolution? Parents pass on acquired traits to offspring. How does Darwin’s theory of evolution explain extinction? If an organism is not suited to its environment it will usually go extinct. Occasionally a helpful mutation can occur that will become an adaptation in the s ...
Population genetics
... in this population may have several alternate forms, which account for variations between the phenotypes of the organisms. An example might be a gene for coloration in moths that has two alleles: black and white. The allele frequency for an allele is the fraction of the genes in the pool that is com ...
... in this population may have several alternate forms, which account for variations between the phenotypes of the organisms. An example might be a gene for coloration in moths that has two alleles: black and white. The allele frequency for an allele is the fraction of the genes in the pool that is com ...
NAME_______________________________ EXAM
... ifference in frequency of an allele between two populations at generation n (dn) equals the difference in frequency at generation 1 (do) times 1 minus 2m to the nth power, where m is the portion of each population that migrates to the other one each generation. The expression assumes that m is symme ...
... ifference in frequency of an allele between two populations at generation n (dn) equals the difference in frequency at generation 1 (do) times 1 minus 2m to the nth power, where m is the portion of each population that migrates to the other one each generation. The expression assumes that m is symme ...
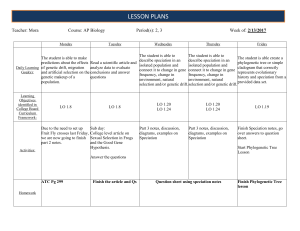
lesson Plans - Lemon Bay High School
... The student is able to The student is able to The student is able create a describe speciation in an describe speciation in an phylogenetic tree or simple isolated population and isolated population and cladogram that correctly connect it to change in gene connect it to change in gene represents evo ...
... The student is able to The student is able to The student is able create a describe speciation in an describe speciation in an phylogenetic tree or simple isolated population and isolated population and cladogram that correctly connect it to change in gene connect it to change in gene represents evo ...
CH 23 Population Evolution Smallest Unit of Evolution One
... One misconception is that organisms evolve during their lifetimes. Natural selection acts on individuals, but only populations evolve. Consider, for example, a population of medium ground finches on Daphne Major Island; During a drought, large-beaked birds were more likely to crack large seeds and s ...
... One misconception is that organisms evolve during their lifetimes. Natural selection acts on individuals, but only populations evolve. Consider, for example, a population of medium ground finches on Daphne Major Island; During a drought, large-beaked birds were more likely to crack large seeds and s ...
Chpt. 5 Review Questions
... • Genetic Engineering the process of transferring genes from one organism to another • Gene Therapy involves inserting copies of a gene directly into a person’s cells. ...
... • Genetic Engineering the process of transferring genes from one organism to another • Gene Therapy involves inserting copies of a gene directly into a person’s cells. ...
Population genetics

Population genetics is the study of the distribution and change in frequency of alleles within populations, and as such it sits firmly within the field of evolutionary biology. The main processes of evolution (natural selection, genetic drift, gene flow, mutation, and genetic recombination) form an integral part of the theory that underpins population genetics. Studies in this branch of biology examine such phenomena as adaptation, speciation, population subdivision, and population structure.Population genetics was a vital ingredient in the emergence of the modern evolutionary synthesis. Its primary founders were Sewall Wright, J. B. S. Haldane and Ronald Fisher, who also laid the foundations for the related discipline of quantitative genetics.Traditionally a highly mathematical discipline, modern population genetics encompasses theoretical, lab and field work. Computational approaches, often utilising coalescent theory, have played a central role since the 1980s.