Chapter 20
... 1. Genetic variation must exist among individuals in a population 2. Differential fitness – variation among individuals must result in differences in the number of offspring surviving in the next ...
... 1. Genetic variation must exist among individuals in a population 2. Differential fitness – variation among individuals must result in differences in the number of offspring surviving in the next ...
Evolution
... – Homologous structures – Analagous structures • Vestigial structures • Embryology • Molecular biology (DNA differences) What Causes Evolution? 1. Mutations: changes in DNA 2. Nonrandom mating: choosing a mate because of proximity (being near by) or certain traits 3. Migration: Immigration = moving ...
... – Homologous structures – Analagous structures • Vestigial structures • Embryology • Molecular biology (DNA differences) What Causes Evolution? 1. Mutations: changes in DNA 2. Nonrandom mating: choosing a mate because of proximity (being near by) or certain traits 3. Migration: Immigration = moving ...
PPT - Artis
... Certain subsequences are found non-mutable: G{C*}T{C*}TG A long non-mutable sub-sequence injected to ancestor causes a relatively large lower bound of viable sizes upon its descendants, a reduced size-based selection pressure, and a highly biased mutational tendency to larger species Such “GMO” loop ...
... Certain subsequences are found non-mutable: G{C*}T{C*}TG A long non-mutable sub-sequence injected to ancestor causes a relatively large lower bound of viable sizes upon its descendants, a reduced size-based selection pressure, and a highly biased mutational tendency to larger species Such “GMO” loop ...
Mutations I
... three, four, or more alleles. One human gene is known with 59 alleles. – What counts as an “allele” depends on the method of analysis: two gene copies might have different DNA sequences but produce identical phenotypes. ...
... three, four, or more alleles. One human gene is known with 59 alleles. – What counts as an “allele” depends on the method of analysis: two gene copies might have different DNA sequences but produce identical phenotypes. ...
Unit 5 Notes
... limiting resource. Those that are best suited for a particular environment will survive, while those that don’t will perish. 3. Genetic variation is the unique combination of traits that results from sexual reproduction. Some variations may give one individual an advantage over another. These trait ...
... limiting resource. Those that are best suited for a particular environment will survive, while those that don’t will perish. 3. Genetic variation is the unique combination of traits that results from sexual reproduction. Some variations may give one individual an advantage over another. These trait ...
Lesson 19 - FineTunedUniverse.com
... First, he assumed that infinite changes in species had occurred even though only limited changes had ever been observed. For example, artificial selection of sugar beets for sugar content quickly reached a plateau and has remained stable ever since. For a breeder to establish a desirable new trait, ...
... First, he assumed that infinite changes in species had occurred even though only limited changes had ever been observed. For example, artificial selection of sugar beets for sugar content quickly reached a plateau and has remained stable ever since. For a breeder to establish a desirable new trait, ...
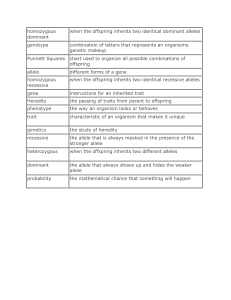
homozygous dominant when the offspring inherits two identical
... chart used to organize all possible combinations of offspring ...
... chart used to organize all possible combinations of offspring ...
Chapter 6 part 4 Maintaining allelic diversity
... Only individuals homozygous for the allele get sickle cell anemia. Individuals with only one copy of the allele (heterozygotes) get sickle cell trait (a mild form of the disease) Individuals with the sickle cell allele (one or two copies) don’t get malaria. ...
... Only individuals homozygous for the allele get sickle cell anemia. Individuals with only one copy of the allele (heterozygotes) get sickle cell trait (a mild form of the disease) Individuals with the sickle cell allele (one or two copies) don’t get malaria. ...
Genetics
... Genetic abnormalities can be inherited from one or both parents. A genetic counsellor is someone who understands a range of conditions that can be passed on in different genetic ways and can advice couples on how great the risk might be. If a couple feel that they may pass on a condition they can as ...
... Genetic abnormalities can be inherited from one or both parents. A genetic counsellor is someone who understands a range of conditions that can be passed on in different genetic ways and can advice couples on how great the risk might be. If a couple feel that they may pass on a condition they can as ...
Review Questions yeast lecture 18
... offspring due to the ability to switch mating type. These strains immediately convert form haplo to diplophase after spore growth. Heterothallic yeast strains are unable to switch mating type and cannot mate with their offspring. Therefore, they can be maintained in haploid form 5. Why does the exis ...
... offspring due to the ability to switch mating type. These strains immediately convert form haplo to diplophase after spore growth. Heterothallic yeast strains are unable to switch mating type and cannot mate with their offspring. Therefore, they can be maintained in haploid form 5. Why does the exis ...
Week 4 Evolution Ideas and Evidence
... Very generally, evolution means change through time Biological evolution (specifically) means the change in genetic frequency within a population of organisms (i.e. it is when a gene/allele/trait becomes more/less common in a population). Natural selection is the main (but not the only) mechan ...
... Very generally, evolution means change through time Biological evolution (specifically) means the change in genetic frequency within a population of organisms (i.e. it is when a gene/allele/trait becomes more/less common in a population). Natural selection is the main (but not the only) mechan ...
chapter 3: biological beginnings
... Natural Selection and Adaptive Behavior Natural Selection – The evolutionary process that favors individuals of a species that are best adapted to survive and reproduce – Darwin’s On the Origin of Species. Adaptive Behavior – That which promotes an organism’s survival in its habitat (e.g, eagle’s c ...
... Natural Selection and Adaptive Behavior Natural Selection – The evolutionary process that favors individuals of a species that are best adapted to survive and reproduce – Darwin’s On the Origin of Species. Adaptive Behavior – That which promotes an organism’s survival in its habitat (e.g, eagle’s c ...
Chapter 23 - Trimble County Schools
... • Gene flow can increase the fitness of a population • Consider, for example, the spread of alleles for resistance to insecticides – Insecticides have been used to target mosquitoes that carry West Nile virus and malaria – Alleles have evolved in some populations that confer insecticide resistance ...
... • Gene flow can increase the fitness of a population • Consider, for example, the spread of alleles for resistance to insecticides – Insecticides have been used to target mosquitoes that carry West Nile virus and malaria – Alleles have evolved in some populations that confer insecticide resistance ...
13 Genetics - One Cue Systems
... the mutation will drift to fixation. As mutation is a recurring event, a gene will accumulate differences over time by chance alone. In this way the genes of two related lineages can be compared and used to estimate the date since they last shared a common ...
... the mutation will drift to fixation. As mutation is a recurring event, a gene will accumulate differences over time by chance alone. In this way the genes of two related lineages can be compared and used to estimate the date since they last shared a common ...
Variation Lecture
... Objective: Explain how biological evolution is the consequence of the interactions of genetic variation, reproduction and inheritance, and natural selection and time. ...
... Objective: Explain how biological evolution is the consequence of the interactions of genetic variation, reproduction and inheritance, and natural selection and time. ...
Variation and Selection
... The process by which organisms well adapted to their environments have a greater chance to breed and pass on their genes to the next generation than those that are less well adapted. ...
... The process by which organisms well adapted to their environments have a greater chance to breed and pass on their genes to the next generation than those that are less well adapted. ...
EVOLUTION NOTEScomplete2010 - Fredericksburg City Public
... 1. Directional selection-Individuals @ one end of curve have higher fitness than those @ middle or other end-Example-birds w/ large,wide beaks can crack large seeds….If the supply of small seeds ...
... 1. Directional selection-Individuals @ one end of curve have higher fitness than those @ middle or other end-Example-birds w/ large,wide beaks can crack large seeds….If the supply of small seeds ...
Salmonella typhimurium
... • The phenotype of an organism is its observable properties • The genotype is the set of alleles it has for all of its genes (5,000 in bacteria; 40,000 in humans) • The relationship between genotype and phenotype is what genetics is all about • New alleles are created by mutation and their effect th ...
... • The phenotype of an organism is its observable properties • The genotype is the set of alleles it has for all of its genes (5,000 in bacteria; 40,000 in humans) • The relationship between genotype and phenotype is what genetics is all about • New alleles are created by mutation and their effect th ...
Evolution
... are not similar in structure (bird wings are made up of a set of bones while insect wings are mainly made of chitin). ...
... are not similar in structure (bird wings are made up of a set of bones while insect wings are mainly made of chitin). ...
Document
... form a new offspring (children). If no crossover was performed, offspring is an exact copy of parents. 3. [Mutation] With a mutation probability mutate new offspring at each locus (position in chromosome). 4. [Accepting] Place new offspring in a new population [Replace] Use new generated population ...
... form a new offspring (children). If no crossover was performed, offspring is an exact copy of parents. 3. [Mutation] With a mutation probability mutate new offspring at each locus (position in chromosome). 4. [Accepting] Place new offspring in a new population [Replace] Use new generated population ...
EVOLUTION study guide File
... o Define and give an example of a Vestigal Structure o Define and give an example of a Homologous Structure o Explain how DNA evidence support Darwin’s ideas about evolution o Similarities in Embryology o Artificial Selection Process of Speciation o Identify an important factor that is necessary f ...
... o Define and give an example of a Vestigal Structure o Define and give an example of a Homologous Structure o Explain how DNA evidence support Darwin’s ideas about evolution o Similarities in Embryology o Artificial Selection Process of Speciation o Identify an important factor that is necessary f ...
Population genetics

Population genetics is the study of the distribution and change in frequency of alleles within populations, and as such it sits firmly within the field of evolutionary biology. The main processes of evolution (natural selection, genetic drift, gene flow, mutation, and genetic recombination) form an integral part of the theory that underpins population genetics. Studies in this branch of biology examine such phenomena as adaptation, speciation, population subdivision, and population structure.Population genetics was a vital ingredient in the emergence of the modern evolutionary synthesis. Its primary founders were Sewall Wright, J. B. S. Haldane and Ronald Fisher, who also laid the foundations for the related discipline of quantitative genetics.Traditionally a highly mathematical discipline, modern population genetics encompasses theoretical, lab and field work. Computational approaches, often utilising coalescent theory, have played a central role since the 1980s.