The Significance of Genetics Across Disciplines: Genetic
... Mutation: A change in the genetic code of a gene/chromosome, can be positive or negative Nucleotide: basic building block of an amino acid, made up of a nitrogenous base (adenine, guanine, thymine, uracil, cytosine), sugar (deoxyribose in DNA) and a phosphate group Amin0 Acid: structural pieces of a ...
... Mutation: A change in the genetic code of a gene/chromosome, can be positive or negative Nucleotide: basic building block of an amino acid, made up of a nitrogenous base (adenine, guanine, thymine, uracil, cytosine), sugar (deoxyribose in DNA) and a phosphate group Amin0 Acid: structural pieces of a ...
Unit 6 Heredity Objective Questions
... Chapters 14 and 15 At the conclusion of this unit, you should be able to: List several features of Mendel’s methods that contributed to his success. State four components of Mendel’s hypothesis of inheritance. Describe Mendel’s law of segregation. Use a Punnett square to predict the results of monoh ...
... Chapters 14 and 15 At the conclusion of this unit, you should be able to: List several features of Mendel’s methods that contributed to his success. State four components of Mendel’s hypothesis of inheritance. Describe Mendel’s law of segregation. Use a Punnett square to predict the results of monoh ...
Read these reviews and answer the questions
... I. Evolution Practice Worksheet Directions: Circle the correct answer in questions 1 – 17. 1. The process in which the environment puts pressure on a species to change: (evolution or natural selection) 2. Slow change in a species over time describes Darwin’s theory of (evolution or natural selection ...
... I. Evolution Practice Worksheet Directions: Circle the correct answer in questions 1 – 17. 1. The process in which the environment puts pressure on a species to change: (evolution or natural selection) 2. Slow change in a species over time describes Darwin’s theory of (evolution or natural selection ...
Founder Effect Exercise
... Founder Effect Occurs when a small sample of a population settles in a location separated f from the th restt off the th population l ti Alleles that were uncommon in the original g population might be common in the new population. ...
... Founder Effect Occurs when a small sample of a population settles in a location separated f from the th restt off the th population l ti Alleles that were uncommon in the original g population might be common in the new population. ...
In Silico Mapping of Complex Disease
... on the carrier chromosomes. Depending on how close the two loci are, this will occur more or less frequently, and if the two loci are very close together, the haplotype a1 m1 may remain in the population a very long time. During this time the frequency of could increase well beyond its original 1/n, ...
... on the carrier chromosomes. Depending on how close the two loci are, this will occur more or less frequently, and if the two loci are very close together, the haplotype a1 m1 may remain in the population a very long time. During this time the frequency of could increase well beyond its original 1/n, ...
lesson#2 Probability and Punnett squares 11.2
... Objective: Students will be able to explain how geneticists use the principles of probability State standard: 2c 2d, 3a, Students know how to predict possible combinations of alleles in a zygote from th ...
... Objective: Students will be able to explain how geneticists use the principles of probability State standard: 2c 2d, 3a, Students know how to predict possible combinations of alleles in a zygote from th ...
Quantitative Genetics - Northern Illinois University
... • This measure, the broad-sense heritability, is fairly easy to measure, especially in human populations where identical twins are available. However, different studies show wide variations in H values for the same traits, and plant breeders have found that it doesn’t accurately reflect the results ...
... • This measure, the broad-sense heritability, is fairly easy to measure, especially in human populations where identical twins are available. However, different studies show wide variations in H values for the same traits, and plant breeders have found that it doesn’t accurately reflect the results ...
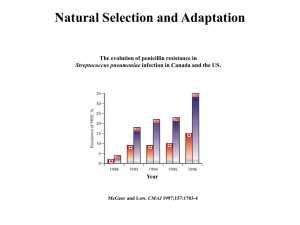
Natural Selection and Adaptation
... predators. The same team was also interested in predicting whether increased shell thickness would evolve as a result. To this end, the scientists measured the average shell thickness of all crabs in the population at the beginning of the year and found it to be xT 10mm . At the end of the year, b ...
... predators. The same team was also interested in predicting whether increased shell thickness would evolve as a result. To this end, the scientists measured the average shell thickness of all crabs in the population at the beginning of the year and found it to be xT 10mm . At the end of the year, b ...
Final Exam 4a - Buffalo State College Faculty and Staff Web Server
... A. If they can both asexually reproduce and their offspring can also successfully asexually reproduce, then they are all the same species. B. If they mate successfully and their offspring can also mate successfully, all are the same species. C. If they mate when they are put together then they are t ...
... A. If they can both asexually reproduce and their offspring can also successfully asexually reproduce, then they are all the same species. B. If they mate successfully and their offspring can also mate successfully, all are the same species. C. If they mate when they are put together then they are t ...
quantitative genetics
... • This measure, the broad-sense heritability, is fairly easy to measure, especially in human populations where identical twins are available. However, different studies show wide variations in H values for the same traits, and plant breeders have found that it doesn’t accurately reflect the results ...
... • This measure, the broad-sense heritability, is fairly easy to measure, especially in human populations where identical twins are available. However, different studies show wide variations in H values for the same traits, and plant breeders have found that it doesn’t accurately reflect the results ...
What Is Genetics?
... parental chromosome pair and exchange genetic material with each other. The result is that no transmitted chromosome is identical to a parental chromosome. If recombination did not occur, no new combinations of genes on a chromosome would result except through mutation. ...
... parental chromosome pair and exchange genetic material with each other. The result is that no transmitted chromosome is identical to a parental chromosome. If recombination did not occur, no new combinations of genes on a chromosome would result except through mutation. ...
Lecture 22
... iv. If plasmid is integrated into whole genome or chromosome of F+. can become Ff. Bacterial sex i. Transposition 1. If sequence is repeated and inverted, it will be copied and copy will excise and insert somewhere else at random 2. Diagram ...
... iv. If plasmid is integrated into whole genome or chromosome of F+. can become Ff. Bacterial sex i. Transposition 1. If sequence is repeated and inverted, it will be copied and copy will excise and insert somewhere else at random 2. Diagram ...
Document
... 3. A __________________ cross is one where you only deal with one trait. (MM x mm) 4. A dihybrid cross examines the inheritance of _______ different traits.( MMYy x mmYy) 5.Mendel’s 2nd law is the law of ___________________ __________________. It states that ____________ pairs __________________ ind ...
... 3. A __________________ cross is one where you only deal with one trait. (MM x mm) 4. A dihybrid cross examines the inheritance of _______ different traits.( MMYy x mmYy) 5.Mendel’s 2nd law is the law of ___________________ __________________. It states that ____________ pairs __________________ ind ...
b2 6 mark question challenge
... will inherit a recessive disorder whether both parents are carriers. •Draw another punnet square to predict whether future offspring will inherit a dominant genetic disorder where the father is heterozygous for the condition and the mother homozygous with the ‘normal’ allele. ...
... will inherit a recessive disorder whether both parents are carriers. •Draw another punnet square to predict whether future offspring will inherit a dominant genetic disorder where the father is heterozygous for the condition and the mother homozygous with the ‘normal’ allele. ...
File
... In this Lab you will be controlling the mutations and environment of a population of rabbits. Your will create three hypotheses and design an experiment to test each one. Your hypothesis will follow the format where you fill in the (...) with your own ideas and reasons. I hypothesize that brown rabb ...
... In this Lab you will be controlling the mutations and environment of a population of rabbits. Your will create three hypotheses and design an experiment to test each one. Your hypothesis will follow the format where you fill in the (...) with your own ideas and reasons. I hypothesize that brown rabb ...
DNA and Mutations Webquest
... 4. What are some of the positive effects of sickle cell? Mutations are Random 1. Mutations can be _________________, neutral, or _________________ to the organism. 2. What are two possible explanations for “resistant” lice? 3. What is directed mutation? 4. In 1952, Esther and Joshua Lederberg perfor ...
... 4. What are some of the positive effects of sickle cell? Mutations are Random 1. Mutations can be _________________, neutral, or _________________ to the organism. 2. What are two possible explanations for “resistant” lice? 3. What is directed mutation? 4. In 1952, Esther and Joshua Lederberg perfor ...
Study Guide: Lecture 1 1. What does “GMO” stand for and what does
... c. What ploidy level is a plant with this formula? 3. Explain the meaning of “genome size”, and the units sizes used to describe genome sizes. 4. Is a 758 Mb genome size a huge, average, or small genome size for a diploid plant? 5. What is “gene flow” and does it only occur with transgenic plants? 6 ...
... c. What ploidy level is a plant with this formula? 3. Explain the meaning of “genome size”, and the units sizes used to describe genome sizes. 4. Is a 758 Mb genome size a huge, average, or small genome size for a diploid plant? 5. What is “gene flow” and does it only occur with transgenic plants? 6 ...
Genetics Guided Notes: ANSWER KEY Name
... Homozygous Dominant – when an individual has two dominant alleles for a gene Ex : AA Homozygous Recessive – when an individual has two recessive alleles for a gene Ex: aa Heterozygous – when an individual has both a dominant and a recessive allele for a gene ...
... Homozygous Dominant – when an individual has two dominant alleles for a gene Ex : AA Homozygous Recessive – when an individual has two recessive alleles for a gene Ex: aa Heterozygous – when an individual has both a dominant and a recessive allele for a gene ...
Lab 7-POPULATION GENETICS
... Population genetics is the study of allele frequency distribution and change under the influence of four main evolutionary processes: 1) natural selection; 2) genetic drift; 3) mutation and 4) gene flow. In other words, population genetics focuses on the genetic composition of a population and how i ...
... Population genetics is the study of allele frequency distribution and change under the influence of four main evolutionary processes: 1) natural selection; 2) genetic drift; 3) mutation and 4) gene flow. In other words, population genetics focuses on the genetic composition of a population and how i ...
Word
... Population genetics is the study of allele frequency distribution and change under the influence of four main evolutionary processes: 1) natural selection; 2) genetic drift; 3) mutation and 4) gene flow. In other words, population genetics focuses on the genetic composition of a population and how i ...
... Population genetics is the study of allele frequency distribution and change under the influence of four main evolutionary processes: 1) natural selection; 2) genetic drift; 3) mutation and 4) gene flow. In other words, population genetics focuses on the genetic composition of a population and how i ...
BIO 1109 PRACTICE Midterm II November 3, 2008 Professor Dr
... 8. Which statement is NOT true about natural selection? A. Directional selection occurs when one extreme phenotype is favored over another different extreme phenotype. B. Stabilizing selection favors an intermediate phenotype over either of the extreme phenotypes. C. Disruptive selection favors both ...
... 8. Which statement is NOT true about natural selection? A. Directional selection occurs when one extreme phenotype is favored over another different extreme phenotype. B. Stabilizing selection favors an intermediate phenotype over either of the extreme phenotypes. C. Disruptive selection favors both ...
Population genetics

Population genetics is the study of the distribution and change in frequency of alleles within populations, and as such it sits firmly within the field of evolutionary biology. The main processes of evolution (natural selection, genetic drift, gene flow, mutation, and genetic recombination) form an integral part of the theory that underpins population genetics. Studies in this branch of biology examine such phenomena as adaptation, speciation, population subdivision, and population structure.Population genetics was a vital ingredient in the emergence of the modern evolutionary synthesis. Its primary founders were Sewall Wright, J. B. S. Haldane and Ronald Fisher, who also laid the foundations for the related discipline of quantitative genetics.Traditionally a highly mathematical discipline, modern population genetics encompasses theoretical, lab and field work. Computational approaches, often utilising coalescent theory, have played a central role since the 1980s.