Background on genetic diseases
... The distinction between gene therapy and eugenics rests on several different points. Gene therapy involves the informed participation of patients who suffer from a specific disease, while eugenics involves social programs, sometimes involuntary ones, focused on general human traits. Gene therapy is ...
... The distinction between gene therapy and eugenics rests on several different points. Gene therapy involves the informed participation of patients who suffer from a specific disease, while eugenics involves social programs, sometimes involuntary ones, focused on general human traits. Gene therapy is ...
BIOLOGY LAB: NATURAL SELECTION AND ALLELE FREQUENCY
... Evolution can be described as the change in the allele frequencies of a gene pool over time. Natural selection can place pressure upon specific phenotypes and cause a change in the frequency of the alleles that produce the phenotypes. For example, predators often select as prey individuals that are ...
... Evolution can be described as the change in the allele frequencies of a gene pool over time. Natural selection can place pressure upon specific phenotypes and cause a change in the frequency of the alleles that produce the phenotypes. For example, predators often select as prey individuals that are ...
Adaptive advantage of aggregation in a population with Allee effects
... Aggregation is often believed to be advantageous in populations with positive density dependence at small population size (i.e., Allee effects). Many species of nonsocial animals aggregate to acquire resources for survival and reproduction. By aggregating, organisms may create a more favorable envir ...
... Aggregation is often believed to be advantageous in populations with positive density dependence at small population size (i.e., Allee effects). Many species of nonsocial animals aggregate to acquire resources for survival and reproduction. By aggregating, organisms may create a more favorable envir ...
Experience On Preimplatation Genetic Diagnisis Combined With Hla
... “GENOMA”- Molecular Genetics Laboratory - Rome – Italy; ...
... “GENOMA”- Molecular Genetics Laboratory - Rome – Italy; ...
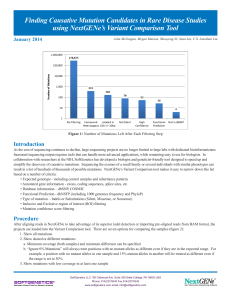
Finding Causative Mutation Candidates in Rare
... dozen (or even fewer) candidate mutations that can be confirmed with Sanger sequencing and assessed for their phenotypic impact. NextGENe is able to import 1000 genomes frequencies and several functional scores from the dbNSFP database including PolyPhen-2, SIFT, LRT, and MutationTaster. Hiding repo ...
... dozen (or even fewer) candidate mutations that can be confirmed with Sanger sequencing and assessed for their phenotypic impact. NextGENe is able to import 1000 genomes frequencies and several functional scores from the dbNSFP database including PolyPhen-2, SIFT, LRT, and MutationTaster. Hiding repo ...
Changing the Genetic Information Mutations
... will be passed onto the offspring. • If a mutation occurs in any other cell of the body (somatic cells) it will not be inherited, but it may affect the individual during their lifetime. ...
... will be passed onto the offspring. • If a mutation occurs in any other cell of the body (somatic cells) it will not be inherited, but it may affect the individual during their lifetime. ...
nov6_part1_Basics of molecular genetics
... replication errors (although DNA replication is almost error-free) • transitions (change of a purine-pyrimidine basepair against another ...
... replication errors (although DNA replication is almost error-free) • transitions (change of a purine-pyrimidine basepair against another ...
Vocab For Genetics - VCC Library
... As a verb, short for cross-breed: to mate two organisms with different traits, whether experimentally, or to create some advantageous result in the offspring. As a noun, an instance of cross-breeding. ...
... As a verb, short for cross-breed: to mate two organisms with different traits, whether experimentally, or to create some advantageous result in the offspring. As a noun, an instance of cross-breeding. ...
genetiC evidenCe for evolution - Origins
... that certain foods are sweet. It was recently discovered that in cats one of these sweet receptor genes is a pseudogene. Because cats have a pseudogene instead of a functioning gene, cats cannot taste sweet flavors. For most mammals the inability to taste sweets would be a bad thing because foods th ...
... that certain foods are sweet. It was recently discovered that in cats one of these sweet receptor genes is a pseudogene. Because cats have a pseudogene instead of a functioning gene, cats cannot taste sweet flavors. For most mammals the inability to taste sweets would be a bad thing because foods th ...
HUMAN GENETIC Variability
... Tongue Rolling: It used to be thought that a dominant allele (R) gave some people the ability to roll the tongue into a "U" shape when the tongue is extended from the mouth. Nonrollers (r) were thought to do no more than produce a slight downward curve of the tongue. There is current debate about th ...
... Tongue Rolling: It used to be thought that a dominant allele (R) gave some people the ability to roll the tongue into a "U" shape when the tongue is extended from the mouth. Nonrollers (r) were thought to do no more than produce a slight downward curve of the tongue. There is current debate about th ...
013368718X_CH11_159-178.indd
... Mendel prevented self-pollination in the peas. He controlled fertilization so he could study how traits passed from one generation to the next. He created hybrids, which are crosses between true-breeding parents (the P generation) with different traits. These hybrids were the F1 (first filial) gen ...
... Mendel prevented self-pollination in the peas. He controlled fertilization so he could study how traits passed from one generation to the next. He created hybrids, which are crosses between true-breeding parents (the P generation) with different traits. These hybrids were the F1 (first filial) gen ...
Experimental Evolution and the Krogh Principle
... capacity. Evidently, modification of these key aspects of oxygen transport capacity was not involved in achieving this increased performance. The physiological traits that were modified were a decrease in body mass, an increased insulin-stimulated glucose uptake in some hind-limb muscles, an enhance ...
... capacity. Evidently, modification of these key aspects of oxygen transport capacity was not involved in achieving this increased performance. The physiological traits that were modified were a decrease in body mass, an increased insulin-stimulated glucose uptake in some hind-limb muscles, an enhance ...
7-2.6 Standard Notes
... It is essential for students to know that offspring inherit the genes for particular traits from their parents. Genes for a particular trait normally come in pairs. Since each parent normally has two alleles for a single trait, we use a Punnett square to determine the possibilities of the combin ...
... It is essential for students to know that offspring inherit the genes for particular traits from their parents. Genes for a particular trait normally come in pairs. Since each parent normally has two alleles for a single trait, we use a Punnett square to determine the possibilities of the combin ...
Positive Darwinian Selection
... based on the ratio of fixed to polymorphic differences We note that the McDonald-Kreitman test requires data from many individuals from two populations or species. Let’s assume we only have one sequence from each species. ...
... based on the ratio of fixed to polymorphic differences We note that the McDonald-Kreitman test requires data from many individuals from two populations or species. Let’s assume we only have one sequence from each species. ...
Patterns of Autosomal Inheritance
... humans. Such traits are inherited from parents who carry the recessive condition. Other organisms, too, carry recessive traits that may be passed on to offspring. In this investigation, your class will model the inheritance of alleles in a population of randomly mating American coots. The American c ...
... humans. Such traits are inherited from parents who carry the recessive condition. Other organisms, too, carry recessive traits that may be passed on to offspring. In this investigation, your class will model the inheritance of alleles in a population of randomly mating American coots. The American c ...
Pedigree Analysis
... In a pedigree, squares represent males and circles represent females. Horizontal lines connecting a male and female represent mating. Vertical lines extending downward from a couple represent their children. Subsequent generations are therefore written underneath the parental generations and the old ...
... In a pedigree, squares represent males and circles represent females. Horizontal lines connecting a male and female represent mating. Vertical lines extending downward from a couple represent their children. Subsequent generations are therefore written underneath the parental generations and the old ...
Clocks
... Molecular clocks? • Zuckerkandl and Pauling, therefore, proposed that for any given protein, the rate of molecular evolution is approximately constant over time in all lineages. ...
... Molecular clocks? • Zuckerkandl and Pauling, therefore, proposed that for any given protein, the rate of molecular evolution is approximately constant over time in all lineages. ...
Genetic mapping and manipulation: Chapter 8
... (dom-1/Df). If the homozygous mutants show a more severe phenotype than the mutant allele over the deficiency, then it is likely that the mutation is at least partially dominant, although one can have both dominance and haploinsufficient effects for the same allele. In addition, a hypermorphic mutat ...
... (dom-1/Df). If the homozygous mutants show a more severe phenotype than the mutant allele over the deficiency, then it is likely that the mutation is at least partially dominant, although one can have both dominance and haploinsufficient effects for the same allele. In addition, a hypermorphic mutat ...
MENDEL`S MAIZE MAZE Objectives: Perform a dihybrid cross on
... E. Write down the total number of each ratio counted in the entire class from the board. Convert these numbers to ratios out of 16 (they should add up to 16, when rounding remember about significant digits). Data: Show work for part A here. ...
... E. Write down the total number of each ratio counted in the entire class from the board. Convert these numbers to ratios out of 16 (they should add up to 16, when rounding remember about significant digits). Data: Show work for part A here. ...
Complications to Mendel: Gene Interactions Lecture starts on next
... Dwarfism in plants and deafness in humans are examples of genetic heterogeneity Genetic (or locus) heterogeneity: Mutations in any one of several genes may result in identical phenotypes (such as when the genes are required for a common biochemical pathway or cellular structure) ...
... Dwarfism in plants and deafness in humans are examples of genetic heterogeneity Genetic (or locus) heterogeneity: Mutations in any one of several genes may result in identical phenotypes (such as when the genes are required for a common biochemical pathway or cellular structure) ...
HARNETT COUNTY HIGH SCHOOLS Course: Biology Title of Unit
... Mutations can be random and spontaneous or caused by radiation and/or chemical exposure. • Develop a cause and effect model in order to describe how mutations: changing amino acid sequence, protein function, phenotype. Only mutations in sex cells (egg and sperm) or in the gamete produced from the pr ...
... Mutations can be random and spontaneous or caused by radiation and/or chemical exposure. • Develop a cause and effect model in order to describe how mutations: changing amino acid sequence, protein function, phenotype. Only mutations in sex cells (egg and sperm) or in the gamete produced from the pr ...
Chapter 5-1 Genetics
... • One trait is not completely dominant over the another. When a plant which is homozygous for red flowers (AA) is crossed with a plant which is homozygous for white flowers (aa), the plants of the F1 generation produce pink flowers which is a blend of red and white condition. This result clearly ind ...
... • One trait is not completely dominant over the another. When a plant which is homozygous for red flowers (AA) is crossed with a plant which is homozygous for white flowers (aa), the plants of the F1 generation produce pink flowers which is a blend of red and white condition. This result clearly ind ...
Mader/Biology, 11/e – Chapter Outline
... H. Testing for Genetic Disorders (Nature of Science reading) 1. Two genetic disorders resulting from faulty genes are Huntington disease and cystic fibrosis. 2. Researchers are tests that can detect particular DNA base sequencing that may be able to identify individuals who may either have a genetic ...
... H. Testing for Genetic Disorders (Nature of Science reading) 1. Two genetic disorders resulting from faulty genes are Huntington disease and cystic fibrosis. 2. Researchers are tests that can detect particular DNA base sequencing that may be able to identify individuals who may either have a genetic ...
AP Bio Steps Wednesday February 25 SWBAT - APICA
... EU 3.A: Heritable information provides for continuity of life. EK 3.A.2: In eukaryotes, heritable information is passed to the next generation via processes that include the cell cycle and mitosis or meiosis plus fertilization. EK 3.A.3: The chromosomal basis of inheritance provides an understanding ...
... EU 3.A: Heritable information provides for continuity of life. EK 3.A.2: In eukaryotes, heritable information is passed to the next generation via processes that include the cell cycle and mitosis or meiosis plus fertilization. EK 3.A.3: The chromosomal basis of inheritance provides an understanding ...
unit 7 overview: genetics
... 7. How many chromosomes do human body cells have? Are they 2n or n? How many pairs of homologous chromosomes do they have? What about sex cells? 8. Differentiate between mitosis and meiosis. How many cell divisions? Which cells are involved? 9. Compare and contrast zygote with gametes. Haploid or di ...
... 7. How many chromosomes do human body cells have? Are they 2n or n? How many pairs of homologous chromosomes do they have? What about sex cells? 8. Differentiate between mitosis and meiosis. How many cell divisions? Which cells are involved? 9. Compare and contrast zygote with gametes. Haploid or di ...
Population genetics

Population genetics is the study of the distribution and change in frequency of alleles within populations, and as such it sits firmly within the field of evolutionary biology. The main processes of evolution (natural selection, genetic drift, gene flow, mutation, and genetic recombination) form an integral part of the theory that underpins population genetics. Studies in this branch of biology examine such phenomena as adaptation, speciation, population subdivision, and population structure.Population genetics was a vital ingredient in the emergence of the modern evolutionary synthesis. Its primary founders were Sewall Wright, J. B. S. Haldane and Ronald Fisher, who also laid the foundations for the related discipline of quantitative genetics.Traditionally a highly mathematical discipline, modern population genetics encompasses theoretical, lab and field work. Computational approaches, often utilising coalescent theory, have played a central role since the 1980s.