Comprehension Question - We can offer most test bank and solution
... 5. Identify a false statement from the descriptions of genetics below. a. Humans first applied genetics to the domestication of plants and animals between approximately 10,000 and 12,000 years ago. b. Some viruses use RNA to carry their genetic information. c. Albinism results from a mutation in the ...
... 5. Identify a false statement from the descriptions of genetics below. a. Humans first applied genetics to the domestication of plants and animals between approximately 10,000 and 12,000 years ago. b. Some viruses use RNA to carry their genetic information. c. Albinism results from a mutation in the ...
Unit 5 Lesson 1 Theory of Evolution by Natural Selection
... • Darwin was influenced by the ideas of many scientists. These helped him develop his theory about how populations change over time. • Farmers and breeders select plants or animals for breeding based on desired traits. This is called artificial selection. • A trait is a form of an inherited characte ...
... • Darwin was influenced by the ideas of many scientists. These helped him develop his theory about how populations change over time. • Farmers and breeders select plants or animals for breeding based on desired traits. This is called artificial selection. • A trait is a form of an inherited characte ...
30 Fungal Genetics Newsletter ras-1
... The 5' and 3' split marker products were co-transformed by electroporation into the wild type Mauriceville-1-c mat A + strain (FGSC 2225) (Colot et al., 2006). We restricted this work to the mat A + strain since the mat a + Mauriceville-1d strain (FGSC 2226) cannot be used as a crossing partner with ...
... The 5' and 3' split marker products were co-transformed by electroporation into the wild type Mauriceville-1-c mat A + strain (FGSC 2225) (Colot et al., 2006). We restricted this work to the mat A + strain since the mat a + Mauriceville-1d strain (FGSC 2226) cannot be used as a crossing partner with ...
Perspectives
... different proteins and different sites within specific proteins evolve at different rates; and (4) uniform rates of evolutionary change within a protein were thought to lend credence to the proposition of neutrality. Like King and Jukes, Wilson and Sarich (1969) also noted that the immunological clo ...
... different proteins and different sites within specific proteins evolve at different rates; and (4) uniform rates of evolutionary change within a protein were thought to lend credence to the proposition of neutrality. Like King and Jukes, Wilson and Sarich (1969) also noted that the immunological clo ...
Section 7.4 Human Pedigrees and Genetics Examine patterns of
... their sex chromosomes, must have two recessive alleles to show a recessive phenotype, such as for a recessive sex-linked disorder. Males, on the other hand, have an XY genotype. They will show all of the phenotypes from the genes on their X chromosome, even the recessive alleles, because they cannot ...
... their sex chromosomes, must have two recessive alleles to show a recessive phenotype, such as for a recessive sex-linked disorder. Males, on the other hand, have an XY genotype. They will show all of the phenotypes from the genes on their X chromosome, even the recessive alleles, because they cannot ...
ACCOMMODATION OF GENE-CHROMOSOME CONFIGURATION
... [Manuscript received January 16, 1961J Summary Gene-chromosome configuration effects may be generated in at least two different ways. The first results from the position.effect phenomenon, and the second, which is manifest if the individual is evaluated on the basis of its inbred progeny, is due to ...
... [Manuscript received January 16, 1961J Summary Gene-chromosome configuration effects may be generated in at least two different ways. The first results from the position.effect phenomenon, and the second, which is manifest if the individual is evaluated on the basis of its inbred progeny, is due to ...
Using whole genome sequence data to develop
... transmission and outbreaks arising from imported cases, and there is a need to establish molecular barcodes for implementation in the field. The genetic diversity and nonrecombining properties of mitochondrial and apicoplast sequence can be powerfully exploited for geographic genetic profiling of P. ...
... transmission and outbreaks arising from imported cases, and there is a need to establish molecular barcodes for implementation in the field. The genetic diversity and nonrecombining properties of mitochondrial and apicoplast sequence can be powerfully exploited for geographic genetic profiling of P. ...
Mutation Accumulation in Populations of Varying Size
... broad array of selection coefficients. The dynamics of mutations with effects Ⰶ1/(2Ne) are expected to be governed exclusively by random genetic drift, causing them to accumulate at close to the neutral rate (Kimura 1983, Chap. 3). Under complete selfing, Ne ⫽ 1, so populations of the above sizes wo ...
... broad array of selection coefficients. The dynamics of mutations with effects Ⰶ1/(2Ne) are expected to be governed exclusively by random genetic drift, causing them to accumulate at close to the neutral rate (Kimura 1983, Chap. 3). Under complete selfing, Ne ⫽ 1, so populations of the above sizes wo ...
Notes
... or egg cell, the altered gene would become part of the genetic makeup of the offspring ● the result could be: a new trait (beneficial or harmful); a protein that does not work correctly; miscarriage ...
... or egg cell, the altered gene would become part of the genetic makeup of the offspring ● the result could be: a new trait (beneficial or harmful); a protein that does not work correctly; miscarriage ...
NOTES: 13.3
... or egg cell, the altered gene would become part of the genetic makeup of the offspring ● the result could be: a new trait (beneficial or harmful); a protein that does not work correctly; miscarriage ...
... or egg cell, the altered gene would become part of the genetic makeup of the offspring ● the result could be: a new trait (beneficial or harmful); a protein that does not work correctly; miscarriage ...
Genetics - Osteogenesis Imperfecta Foundation
... 1. A Dominant Mutation Inherited from an Affected Parent. A person with dominant OI has a mutation in one copy of a gene for type I collagen, and a normal sequence in the second copy of that gene. The presence of the altered copy of the gene is enough to result in OI. Each time the affected person ...
... 1. A Dominant Mutation Inherited from an Affected Parent. A person with dominant OI has a mutation in one copy of a gene for type I collagen, and a normal sequence in the second copy of that gene. The presence of the altered copy of the gene is enough to result in OI. Each time the affected person ...
Section 8.1 Power point
... 8.1 Identifying DNA as the Genetic Material Historical timeline of discovering DNA 1875 - 1953 • Although Gregor Mendel’s experiments with pea plants in the 1870’s led to the the new science of genetics, he was never able to answer an important question – “What are the “factors” that control heredi ...
... 8.1 Identifying DNA as the Genetic Material Historical timeline of discovering DNA 1875 - 1953 • Although Gregor Mendel’s experiments with pea plants in the 1870’s led to the the new science of genetics, he was never able to answer an important question – “What are the “factors” that control heredi ...
I. Comparing genome sequences
... • Orthologous sequences = homologous sequences separated by a speciation event (e.g., human HOXA and mouse Hoxa) • Paralogous sequences = homologous sequences separated by gene duplication (e.g., human HOXA and human HOXB) ...
... • Orthologous sequences = homologous sequences separated by a speciation event (e.g., human HOXA and mouse Hoxa) • Paralogous sequences = homologous sequences separated by gene duplication (e.g., human HOXA and human HOXB) ...
Population Genetics and a Study of Speciation Using Next
... the genome at which all G. firmus individuals have one nucleotide and all G. pennsylvanicus individuals have another. The authors began by identifying all sites that showed differences in the frequency of alternative alleles between species. To avoid interpreting sequencing errors as polymorphisms, t ...
... the genome at which all G. firmus individuals have one nucleotide and all G. pennsylvanicus individuals have another. The authors began by identifying all sites that showed differences in the frequency of alternative alleles between species. To avoid interpreting sequencing errors as polymorphisms, t ...
Math 5652: Introduction to Stochastic Processes Homework 3: due
... and Carol – walk into the bank at almost the same time, but in that order. Alice and Bob go directly into service, while Carol waits for the first available teller. Suppose that the service time of each of the three customers is independent, exponentially distributed, with a mean of 4 minutes. (Care ...
... and Carol – walk into the bank at almost the same time, but in that order. Alice and Bob go directly into service, while Carol waits for the first available teller. Suppose that the service time of each of the three customers is independent, exponentially distributed, with a mean of 4 minutes. (Care ...
Open questions: What has genetics told us about autism spectrum disorders?
... drive for sameness and predictability (which is an important part of the restricted interests and obsessive behaviors phenotype), and this leads to a secondary social withdrawal; after all, people are the least predictable objects in a developing child’s environment. Another possibility is that the ...
... drive for sameness and predictability (which is an important part of the restricted interests and obsessive behaviors phenotype), and this leads to a secondary social withdrawal; after all, people are the least predictable objects in a developing child’s environment. Another possibility is that the ...
Horizontal and Vertical Gene Transfer
... functions can be introduced into eukaryocytes by transfection or conjugation. Retrovirus infection or hepatitis B virus infection transfers the viral genes to the chromosome of the host. These are examples of horizontal gene transfer in humans. Bacterial and viral DNA are thought to be constantly be ...
... functions can be introduced into eukaryocytes by transfection or conjugation. Retrovirus infection or hepatitis B virus infection transfers the viral genes to the chromosome of the host. These are examples of horizontal gene transfer in humans. Bacterial and viral DNA are thought to be constantly be ...
Inheriting Your Future - American Federation of New Zealand Rabbit
... Understanding the basic units of inheritance and the associated principles is so very important to each of us as rabbit breeders. Chromosomes are the largest units of inheritance. In rabbit cells there are a total of 44 chromosomes; 22 from the buck and 22 from the doe. So many times, I hear breeder ...
... Understanding the basic units of inheritance and the associated principles is so very important to each of us as rabbit breeders. Chromosomes are the largest units of inheritance. In rabbit cells there are a total of 44 chromosomes; 22 from the buck and 22 from the doe. So many times, I hear breeder ...
I. Misconceptions about evolutionary theory and processes
... genetic drift may cause populations to evolve in ways that are actually harmful overall or make them less suitable for their environments. For example, the Afrikaner population of South Africa has an unusually high frequency of the gene responsible for Huntington’s disease because the gene version d ...
... genetic drift may cause populations to evolve in ways that are actually harmful overall or make them less suitable for their environments. For example, the Afrikaner population of South Africa has an unusually high frequency of the gene responsible for Huntington’s disease because the gene version d ...
D. 100% dominant
... all of the affected males could trace their ancestry to Queen Victoria of England. Because none of the queen's ancestor or relatives were affected, it seems that the RECESSIVE allele she carried arose by mutation either in Queen Victoria or one of her parents. Her daughters Alice and Beatrice were c ...
... all of the affected males could trace their ancestry to Queen Victoria of England. Because none of the queen's ancestor or relatives were affected, it seems that the RECESSIVE allele she carried arose by mutation either in Queen Victoria or one of her parents. Her daughters Alice and Beatrice were c ...
Chapter 5 Power Point Slides
... Heritability is estimated by observing the amount of variation among relatives who have a known fraction of genes in common (known as genetic relatedness) Heritability can be estimated only for the population under study and the environmental condition in effect at the time of the study ...
... Heritability is estimated by observing the amount of variation among relatives who have a known fraction of genes in common (known as genetic relatedness) Heritability can be estimated only for the population under study and the environmental condition in effect at the time of the study ...
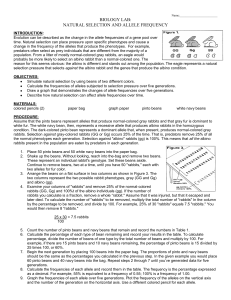
BIOLOGY LAB: NATURAL SELECTION AND ALLELE FREQUENCY
... Evolution can be described as the change in the allele frequencies of a gene pool over time. Natural selection can place pressure upon specific phenotypes and cause a change in the frequency of the alleles that produce the phenotypes. For example, predators often select as prey individuals that are ...
... Evolution can be described as the change in the allele frequencies of a gene pool over time. Natural selection can place pressure upon specific phenotypes and cause a change in the frequency of the alleles that produce the phenotypes. For example, predators often select as prey individuals that are ...
The Inheritance of Complex Traits
... Heritability is estimated by observing the amount of variation among relatives who have a known fraction of genes in common (known as genetic relatedness) Heritability can be estimated only for the population under study and the environmental condition in effect at the time of the study ...
... Heritability is estimated by observing the amount of variation among relatives who have a known fraction of genes in common (known as genetic relatedness) Heritability can be estimated only for the population under study and the environmental condition in effect at the time of the study ...
BIOLOGY LAB: NATURAL SELECTION AND ALLELE FREQUENCY
... Evolution can be described as the change in the allele frequencies of a gene pool over time. Natural selection can place pressure upon specific phenotypes and cause a change in the frequency of the alleles that produce the phenotypes. For example, predators often select as prey individuals that are ...
... Evolution can be described as the change in the allele frequencies of a gene pool over time. Natural selection can place pressure upon specific phenotypes and cause a change in the frequency of the alleles that produce the phenotypes. For example, predators often select as prey individuals that are ...
Population genetics

Population genetics is the study of the distribution and change in frequency of alleles within populations, and as such it sits firmly within the field of evolutionary biology. The main processes of evolution (natural selection, genetic drift, gene flow, mutation, and genetic recombination) form an integral part of the theory that underpins population genetics. Studies in this branch of biology examine such phenomena as adaptation, speciation, population subdivision, and population structure.Population genetics was a vital ingredient in the emergence of the modern evolutionary synthesis. Its primary founders were Sewall Wright, J. B. S. Haldane and Ronald Fisher, who also laid the foundations for the related discipline of quantitative genetics.Traditionally a highly mathematical discipline, modern population genetics encompasses theoretical, lab and field work. Computational approaches, often utilising coalescent theory, have played a central role since the 1980s.