Continental drift - La Salle Elementary School
... o Only explanation – places where fossils found must have been closer More evidence found in rock formations in Africa match ones in South America Glacial deposits are similar in Africa, South America, India, Australia, and Antarctica were left by same ice sheets. ...
... o Only explanation – places where fossils found must have been closer More evidence found in rock formations in Africa match ones in South America Glacial deposits are similar in Africa, South America, India, Australia, and Antarctica were left by same ice sheets. ...
Document
... Much of the oceanic crust and its topographic features are related to igneous activity. Rocks of the ocean crust have not been deformed by strong compression: simple structure in contrast to the complex structure of the continents. All oceanic crusts are less than 200 million years old. Abyssal hil ...
... Much of the oceanic crust and its topographic features are related to igneous activity. Rocks of the ocean crust have not been deformed by strong compression: simple structure in contrast to the complex structure of the continents. All oceanic crusts are less than 200 million years old. Abyssal hil ...
Mid-Ocean Ridge
... So why are scientists so surprised to find life so deep in the ocean? What did they previously think organisms needed to survive? ...
... So why are scientists so surprised to find life so deep in the ocean? What did they previously think organisms needed to survive? ...
oceans
... • less dense, rocks that floated to the surface when the Earth was formed • between 35km and 70km thick. – not a continuous layer of rock • Split into plates, which are free to drift slowly across the surface of the planet. ...
... • less dense, rocks that floated to the surface when the Earth was formed • between 35km and 70km thick. – not a continuous layer of rock • Split into plates, which are free to drift slowly across the surface of the planet. ...
Lesson 2.1 Continental Drift
... Closed when India moved into Asia Panthalassic Ocean: Huge ocean surrounding Pangea Became the Pacific Atlantic Ocean: Formed when North America separated from Eurasia Indian Ocean: Formed when Gondwanaland broke apart ...
... Closed when India moved into Asia Panthalassic Ocean: Huge ocean surrounding Pangea Became the Pacific Atlantic Ocean: Formed when North America separated from Eurasia Indian Ocean: Formed when Gondwanaland broke apart ...
2013年1月12日托福写作真题回忆
... temperature under oceans and continents are sufficient to produce convection in the mantle of the earth with rising convection currents under the mid-ocean ridges and sinking currents under the continents. Theoretically, this convection would carry the continental plates along as though they were on ...
... temperature under oceans and continents are sufficient to produce convection in the mantle of the earth with rising convection currents under the mid-ocean ridges and sinking currents under the continents. Theoretically, this convection would carry the continental plates along as though they were on ...
THE OCEANS AND THE ATMOSPHERE
... • Salts added are balanced by salts removed by organisms and by precipitation and deposition on sea floor. ...
... • Salts added are balanced by salts removed by organisms and by precipitation and deposition on sea floor. ...
Chapter 2
... Trenches • Plate descends into the mantle • Sea floor slopes steeply downward • Deepest parts of the world ocean • Mariana Trench – Western Pacific – 11,022 m or (36,163 ft) deep ...
... Trenches • Plate descends into the mantle • Sea floor slopes steeply downward • Deepest parts of the world ocean • Mariana Trench – Western Pacific – 11,022 m or (36,163 ft) deep ...
Sea-Floor Spreading - Catawba County Schools
... by which the ocean floor sinks beneath a deepocean trench and back into the mantle. ...
... by which the ocean floor sinks beneath a deepocean trench and back into the mantle. ...
Seafloor Spreading
... The _____________________________ the most extensive chain of mountains on earth, but more than ________________ of this mountain range lies in the deep ocean. The midocean ridge wraps around the globe for more than 65,000 km like the seam of a baseball. 2. ____________________________ – Rocks that ...
... The _____________________________ the most extensive chain of mountains on earth, but more than ________________ of this mountain range lies in the deep ocean. The midocean ridge wraps around the globe for more than 65,000 km like the seam of a baseball. 2. ____________________________ – Rocks that ...
2007 Exam 1 - MSU Billings
... A) They formed after all the gas had been used up. B) They are so cold that all their gases have frozen into deposits below their surface. C) They formed before the solar nebula had captured any gas. D) They are so small that their gravity is too weak to retain an atmosphere. 2. Felsic rocks … A) ar ...
... A) They formed after all the gas had been used up. B) They are so cold that all their gases have frozen into deposits below their surface. C) They formed before the solar nebula had captured any gas. D) They are so small that their gravity is too weak to retain an atmosphere. 2. Felsic rocks … A) ar ...
Exploring the Ocean 2014
... Driven by the sun. The ocean is an important part of the water cycle because nearly all of Earth’s water is in the ocean. ...
... Driven by the sun. The ocean is an important part of the water cycle because nearly all of Earth’s water is in the ocean. ...
Earth Model Project
... (Example: to show which layers are cool and which are hot, and to show which layers are rock and which are metal) ...
... (Example: to show which layers are cool and which are hot, and to show which layers are rock and which are metal) ...
Geologic Trips San Francisco and the Bay Area
... Coast Ranges into many large blocks. Some of these blocks continued to be uplifted whereas other subsided. Still others went up and then changed their minds and went down. The high blocks became mountain ranges. Sedimentary rocks were deposited in the low basin areas between the high blocks. Sedimen ...
... Coast Ranges into many large blocks. Some of these blocks continued to be uplifted whereas other subsided. Still others went up and then changed their minds and went down. The high blocks became mountain ranges. Sedimentary rocks were deposited in the low basin areas between the high blocks. Sedimen ...
Group Quiz Review Game
... 1a. This is an area of volcanic activity created by a weakened area of the earth’s crust. 2a. It contains the oldest rocks known. 3a. It is located where magma rises to the surface of the oceanic crust. 4a. It creates composite volcanoes from the melting of low-density crust. 5a. It is the longest m ...
... 1a. This is an area of volcanic activity created by a weakened area of the earth’s crust. 2a. It contains the oldest rocks known. 3a. It is located where magma rises to the surface of the oceanic crust. 4a. It creates composite volcanoes from the melting of low-density crust. 5a. It is the longest m ...
Earth`s Structure and Tectonics Overview 2014
... 9. As more molten material rises and hardens, it forces the sea floor to move apart. This process is called _______________ ____________________ ______________________. 10. Sea floor spreading (at divergent boundary points A, B, D) results in the creation of new crust. However, the Earth’s total sur ...
... 9. As more molten material rises and hardens, it forces the sea floor to move apart. This process is called _______________ ____________________ ______________________. 10. Sea floor spreading (at divergent boundary points A, B, D) results in the creation of new crust. However, the Earth’s total sur ...
2015-16 - School of Earth Sciences
... Answer all parts of this question. This section counts for 40% of the total mark for this examination and each part is weighted equally. Use diagrams and equations to illustrate your answer wherever possible. 1. Why and how does mantle convection occur in the Earth? Explain the physical processes an ...
... Answer all parts of this question. This section counts for 40% of the total mark for this examination and each part is weighted equally. Use diagrams and equations to illustrate your answer wherever possible. 1. Why and how does mantle convection occur in the Earth? Explain the physical processes an ...
Introduction (MS doc)
... occurred beneath the continental slope and shelf off the west coast in the more distant past. These “great” quakes originate on the 1000 km long thrust fault that separates the Juan de Fuca and North America plates, in what is known as the Cascadia subduction zone. A magnitude 9 earthquake releases ...
... occurred beneath the continental slope and shelf off the west coast in the more distant past. These “great” quakes originate on the 1000 km long thrust fault that separates the Juan de Fuca and North America plates, in what is known as the Cascadia subduction zone. A magnitude 9 earthquake releases ...
01 - 6th Grade Science with Mrs. Harlow
... Exploring the Oceans and Movement of Ocean Water 1. Name all the world’s ocean and include their size. Pacific – largest Atlantic – 2nd largest Indian – 3rd largest Southern - Extends from coast of Antartica to 60 degrees south latitude 2. What is evaporation? When a liquid changes into a vapor or g ...
... Exploring the Oceans and Movement of Ocean Water 1. Name all the world’s ocean and include their size. Pacific – largest Atlantic – 2nd largest Indian – 3rd largest Southern - Extends from coast of Antartica to 60 degrees south latitude 2. What is evaporation? When a liquid changes into a vapor or g ...
Convergent Plate Margins, Subduction Zones, and
... Convergent Plate Margin, Subduction Zone, and Arc-Trench System Convergent Plate Margin: 2-D (surficial) plate boundary that is geometrically required for Plate Tectonic theory. Subduction Zone: 3-D region defined by asymmetric sinking of lithosphere into the mantle. Defined by earthquakes at depths ...
... Convergent Plate Margin, Subduction Zone, and Arc-Trench System Convergent Plate Margin: 2-D (surficial) plate boundary that is geometrically required for Plate Tectonic theory. Subduction Zone: 3-D region defined by asymmetric sinking of lithosphere into the mantle. Defined by earthquakes at depths ...
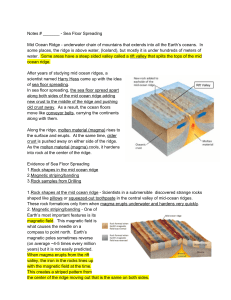
Notes # ______ Sea Floor Spreading Mid Ocean Ridge underwater
... in the central valley of midocean ridges. These rock formations only form when magma erupts underwater and hardens very quickly ...
... in the central valley of midocean ridges. These rock formations only form when magma erupts underwater and hardens very quickly ...
Unit 3: Plate Tectonics: Test Review
... 29. What type of boundary does it occur along? Why? Divergent, because it is spreading. 30. Is new crust created, destroyed or neither? Created 31. What happens when continental crust meets continental crust? Mountains ...
... 29. What type of boundary does it occur along? Why? Divergent, because it is spreading. 30. Is new crust created, destroyed or neither? Created 31. What happens when continental crust meets continental crust? Mountains ...
part 1 - Research at UVU
... Lab 1A: Review of Landforms, Faults, and Plate Tectonics Part A of this lab is designed to help review macro landforms and other features that are indicative of plate boundary activity as well as major landforms that we will encounter in Utah. Plate Boundary Landforms and Features. Q1: Use the attac ...
... Lab 1A: Review of Landforms, Faults, and Plate Tectonics Part A of this lab is designed to help review macro landforms and other features that are indicative of plate boundary activity as well as major landforms that we will encounter in Utah. Plate Boundary Landforms and Features. Q1: Use the attac ...
Marine Geology
... – thin outer layer • less dense, rocks that floated to the surface when the Earth was formed • between 35km and 70km thick. – not a continuous layer of rock • Split into plates, which are free to drift slowly across the surface of the planet. ...
... – thin outer layer • less dense, rocks that floated to the surface when the Earth was formed • between 35km and 70km thick. – not a continuous layer of rock • Split into plates, which are free to drift slowly across the surface of the planet. ...