Contents
... In Section 10.2, it was shown that 46.0 g of sodium were needed to exactly react with 71.0 g of chlorine gas. Supposing, instead, only 10.0 g of sodium were available, what mass of chlorine would be necessary to use up the 10.0 g of sodium? This is where the application of mole calculations becomes ...
... In Section 10.2, it was shown that 46.0 g of sodium were needed to exactly react with 71.0 g of chlorine gas. Supposing, instead, only 10.0 g of sodium were available, what mass of chlorine would be necessary to use up the 10.0 g of sodium? This is where the application of mole calculations becomes ...
I Examen I Trim Science
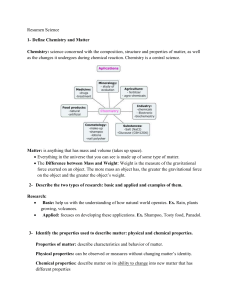
... Can’t be reverser, only by other chemical changes. Characteristics Composition Reversing Changes Identity Properties ...
... Can’t be reverser, only by other chemical changes. Characteristics Composition Reversing Changes Identity Properties ...
Why Study Chemistry
... – how hot or cold something is (a physical property) – related to the average (kinetic) energy of the substance (not the total energy) – Measured in units of • Degrees Fahrenheit (oF) • Degrees Celsius (oC) ...
... – how hot or cold something is (a physical property) – related to the average (kinetic) energy of the substance (not the total energy) – Measured in units of • Degrees Fahrenheit (oF) • Degrees Celsius (oC) ...
Chemical Reactions
... - To observe some chemical reactions and identify reactants and products of those reactions. - To classify reactions as to type and write symbols showing phases. - To practice and learn the splint test for gases. ...
... - To observe some chemical reactions and identify reactants and products of those reactions. - To classify reactions as to type and write symbols showing phases. - To practice and learn the splint test for gases. ...
chemical reaction
... which an element replaces another element that is part of a compound. The products of single-displacement reactions are a new compound and a different element. • Reactivity of Elements In a single-displacement reaction, a more reactive element can displace a less reactive element in a compound. ...
... which an element replaces another element that is part of a compound. The products of single-displacement reactions are a new compound and a different element. • Reactivity of Elements In a single-displacement reaction, a more reactive element can displace a less reactive element in a compound. ...
Physical and Chemical Changes Worksheet
... Physical and Chemical Changes Part A Can you recognize the chemical and physical changes that happen all around us? If you change the way something looks, but haven’t made a new substance, a physical change (P) has occurred. If the substance has been changes into another substance, a chemical change ...
... Physical and Chemical Changes Part A Can you recognize the chemical and physical changes that happen all around us? If you change the way something looks, but haven’t made a new substance, a physical change (P) has occurred. If the substance has been changes into another substance, a chemical change ...
matter
... change) is a change in a substance or substances that results in a totally new substance – Ex: 2H2(g) + O2(g) 2H2O(g) Notice that the reactants (the substances you start with) combine to form a new substance (the product) ...
... change) is a change in a substance or substances that results in a totally new substance – Ex: 2H2(g) + O2(g) 2H2O(g) Notice that the reactants (the substances you start with) combine to form a new substance (the product) ...
___Mg + ___O ___MgO • Mole : Mole ratio
... ‘runs’ out first in a chemical reaction. This is the chemical that determines how much of the product(s) are made. *The true amount of excess reactant is also determined by the limiting reactant. *Excess reactants: chemical substances that you have more than enough needed for the reaction. For examp ...
... ‘runs’ out first in a chemical reaction. This is the chemical that determines how much of the product(s) are made. *The true amount of excess reactant is also determined by the limiting reactant. *Excess reactants: chemical substances that you have more than enough needed for the reaction. For examp ...
7.5.9 Compare physical properties of matter to the chemical property
... Density is a property that describes the relationship between the mass of a material and its volume Substances that are denser contain MORE matter in a given volume ...
... Density is a property that describes the relationship between the mass of a material and its volume Substances that are denser contain MORE matter in a given volume ...
Unit 1. Materials: Formulating Matter A. How do chemists describe
... So far, none of the models you have drawn or interpreted are of metals. How can you visualize solid metals? The following picture shows a common use of aluminum foil. Although we use the chemical symbol "Al" to represent aluminum, what we visualize is actually a large collection of aluminum atoms. L ...
... So far, none of the models you have drawn or interpreted are of metals. How can you visualize solid metals? The following picture shows a common use of aluminum foil. Although we use the chemical symbol "Al" to represent aluminum, what we visualize is actually a large collection of aluminum atoms. L ...
Chemical Bonding Quiz
... Study Guide: Chemical Bonding Quiz Students should be able to understand and apply the following Chemical Bonding concepts: ...
... Study Guide: Chemical Bonding Quiz Students should be able to understand and apply the following Chemical Bonding concepts: ...
Unit 2 matter - Kowenscience.com
... experiments in which he carefully weighed the chemical reactants, carried out a chemical reaction (combustion), and then carefully collected and weighed the products. • He found that there is no detectable change in mass during an ordinary chemical reaction. Mass is conserved in a chemical reaction! ...
... experiments in which he carefully weighed the chemical reactants, carried out a chemical reaction (combustion), and then carefully collected and weighed the products. • He found that there is no detectable change in mass during an ordinary chemical reaction. Mass is conserved in a chemical reaction! ...
exo and endo experiments
... The Law of Conservation of Mass was officially established in the year 1789 by the French Chemist, Antoine Lavoisier. The Law of Conservation of Mass states that mass is neither lost nor gained in chemical reactions, it states that it simply changes form. For that reason, if you had a certain number ...
... The Law of Conservation of Mass was officially established in the year 1789 by the French Chemist, Antoine Lavoisier. The Law of Conservation of Mass states that mass is neither lost nor gained in chemical reactions, it states that it simply changes form. For that reason, if you had a certain number ...