Absorption Measurements on PC1
... Installing the Absorption Accessory Although the standard use of the accessory will be for the left emission channel of the instrument (filter holder channel), the accessory can be used also with acquisition through the right emission channel (monochromator channel). In the following, we will assume ...
... Installing the Absorption Accessory Although the standard use of the accessory will be for the left emission channel of the instrument (filter holder channel), the accessory can be used also with acquisition through the right emission channel (monochromator channel). In the following, we will assume ...
Free-electron lasers
... M. Suga et al. “Native structure of photosystem II at 1.95 A resolution viewed by femtosecond X-ray pulses”, Nature Letters. Motivation: Photo-synthesis converts light from the sun very effective into chemical energy that triggers the conversion of CO2 to O2. If Photo-synthesis would be fully unders ...
... M. Suga et al. “Native structure of photosystem II at 1.95 A resolution viewed by femtosecond X-ray pulses”, Nature Letters. Motivation: Photo-synthesis converts light from the sun very effective into chemical energy that triggers the conversion of CO2 to O2. If Photo-synthesis would be fully unders ...
CHAPTER 10: Molecules and Solids
... They are made up of many smaller crystals. Solids lacking any significant lattice structure are called amorphous and are referred to as “glasses.” Why do solids form as they do? When the material changes from the liquid to the solid state, the atoms can each find a place that creates the minimum ene ...
... They are made up of many smaller crystals. Solids lacking any significant lattice structure are called amorphous and are referred to as “glasses.” Why do solids form as they do? When the material changes from the liquid to the solid state, the atoms can each find a place that creates the minimum ene ...
High-quality energy
... Science Has Some Limitations 1. Particular hypotheses, theories, or laws have a high probability of being true while not being absolute 2. Bias can be minimized by scientists ...
... Science Has Some Limitations 1. Particular hypotheses, theories, or laws have a high probability of being true while not being absolute 2. Bias can be minimized by scientists ...
Title Magnetic Properties of Several Iron Compounds Studied by the
... studies were carried out. The one is the particle size dependenceof the Mossbauerspectra. The occurrenceof the superparamagnetism was confirmed in the spectrum of ultra fine particles. The other is a utilization of oriented particles. Making use of the anisotropic particle shape, orientedsamples wer ...
... studies were carried out. The one is the particle size dependenceof the Mossbauerspectra. The occurrenceof the superparamagnetism was confirmed in the spectrum of ultra fine particles. The other is a utilization of oriented particles. Making use of the anisotropic particle shape, orientedsamples wer ...
Lecture 7_Quantum Chemistry
... Non-radiative energy transfer – a quantum mechanical process of resonance between transition dipoles Effective between 10-100 Å only Emission and excitation spectrum must significantly overlap Donor transfers non-radiatively to the acceptor ...
... Non-radiative energy transfer – a quantum mechanical process of resonance between transition dipoles Effective between 10-100 Å only Emission and excitation spectrum must significantly overlap Donor transfers non-radiatively to the acceptor ...
atomic theory - unit a
... 1) n = principal quantum number, where n is energy shell. Values for n = 1,2,3,4... (n = 1 closest shell to nucleus) Generally, energy increases with increasing n. 2) Principle energy levels can be subdivided into subshells. • Electrons within a subshell have identical energy. • There are 4 known su ...
... 1) n = principal quantum number, where n is energy shell. Values for n = 1,2,3,4... (n = 1 closest shell to nucleus) Generally, energy increases with increasing n. 2) Principle energy levels can be subdivided into subshells. • Electrons within a subshell have identical energy. • There are 4 known su ...
Molecular energy levels and spectroscopy
... region of the spectrum. The gross selection rule for a vibrational transition is d/dt ≠ 0. i.e. the molecule must have a dipole moment that changes during the course of the vibration (important note: this requirement may be satisfied without the molecule having a permane ...
... region of the spectrum. The gross selection rule for a vibrational transition is d/dt ≠ 0. i.e. the molecule must have a dipole moment that changes during the course of the vibration (important note: this requirement may be satisfied without the molecule having a permane ...
supplemental problems
... f) The secondary emission ratio of a dynode is 4, i.e. each dynode emits an average of 4 electrons for each incident electron. Find the total number of electrons collected at the anode each second for this 550 nm light. g) What size current is produced by these electrons? 4.3 Consider a Hydrogen ato ...
... f) The secondary emission ratio of a dynode is 4, i.e. each dynode emits an average of 4 electrons for each incident electron. Find the total number of electrons collected at the anode each second for this 550 nm light. g) What size current is produced by these electrons? 4.3 Consider a Hydrogen ato ...
Radiative Transitions between Electronic States
... 4.4 Light as an Oscillating Electric Field Frequency () of oscillating field must “match” a possible electronic oscillation frequency (conservation of energy) There must be an interaction or coupling between the field (oscillating dipoles) and the electron Interaction strength depends on field ...
... 4.4 Light as an Oscillating Electric Field Frequency () of oscillating field must “match” a possible electronic oscillation frequency (conservation of energy) There must be an interaction or coupling between the field (oscillating dipoles) and the electron Interaction strength depends on field ...
... electron abstractions, and cyclic voltammetry showed these reactions to be reversible and the intermediates to be stable. We describe here the electrolytic and chemical preparation of cation radicals of various porphyrins and of ethyl chlorophyllide a as well as the formation of the dication of magn ...
4/10/2006 Chapter 37 Lasers, a Model Atom and Zero Point Energy
... onto a solid theoretical foundation with the development of the Schrodinger Wave Equation. This equation can be used to calculate the energy values for electrons in hydrogen (and other atoms). This field of physics dealing with “Wave Mechanics” came to be called Quantum Mechanics. The next few chapt ...
... onto a solid theoretical foundation with the development of the Schrodinger Wave Equation. This equation can be used to calculate the energy values for electrons in hydrogen (and other atoms). This field of physics dealing with “Wave Mechanics” came to be called Quantum Mechanics. The next few chapt ...
Microsoft Word Format - University of Toronto Physics
... Lastly, we note that the target electrons are not free as has been assumed so far, but bound in atoms, molecules, often in condensed matter. However, the low-Z elements do not have tightly bound electrons. For example, the average K-shell binding energy of oxygen electrons is 0.7 keV, which is very ...
... Lastly, we note that the target electrons are not free as has been assumed so far, but bound in atoms, molecules, often in condensed matter. However, the low-Z elements do not have tightly bound electrons. For example, the average K-shell binding energy of oxygen electrons is 0.7 keV, which is very ...
Finite Nuclear Size Effect - Physics
... a uniform distribution of charge. This will produce an energy potential that will require a different approach. After producing the potential from the assumption of a uniformly distributed charge over a finite sized nucleus, the Hamiltonian is all but trivial to form. Applying first order perturbati ...
... a uniform distribution of charge. This will produce an energy potential that will require a different approach. After producing the potential from the assumption of a uniformly distributed charge over a finite sized nucleus, the Hamiltonian is all but trivial to form. Applying first order perturbati ...
Rules for Assigning Oxidation Numbers to Inorganic Compounds
... 1. Elements and compounds with only one type of atom have oxidation number ...
... 1. Elements and compounds with only one type of atom have oxidation number ...
Visible Spectroscopy
... differences between shells and energy levels in the quantum theory model of the atom. Typically it is valence electrons that are involved in these jumps. Atoms have two kinds of states; a ground state and an excited state. The ground state is the state in which the electrons in the atom are in their ...
... differences between shells and energy levels in the quantum theory model of the atom. Typically it is valence electrons that are involved in these jumps. Atoms have two kinds of states; a ground state and an excited state. The ground state is the state in which the electrons in the atom are in their ...
Lecture 33 - Stimulated Absorption
... Today we will work through the concepts of spontaneous and stimulated emission, first propounded by Einstein in 1916-1917: i. Spontaneous emission is just like radioactive decay, with less energetic byproducts: an atom in an excited state has a finite probability of decay per unit time, a decay prob ...
... Today we will work through the concepts of spontaneous and stimulated emission, first propounded by Einstein in 1916-1917: i. Spontaneous emission is just like radioactive decay, with less energetic byproducts: an atom in an excited state has a finite probability of decay per unit time, a decay prob ...
Lecture 38
... The exclusion principle limits the maximum number of electrons in each subshell to 2(2l + 1). ...
... The exclusion principle limits the maximum number of electrons in each subshell to 2(2l + 1). ...
Phys 282 EXP 8
... OBJECT: To study the time dependence of radioactive decay. To find half-life time for different materials. APPARATUS: Geiger-Mueller counter with computer interface, radioactive sources. ...
... OBJECT: To study the time dependence of radioactive decay. To find half-life time for different materials. APPARATUS: Geiger-Mueller counter with computer interface, radioactive sources. ...
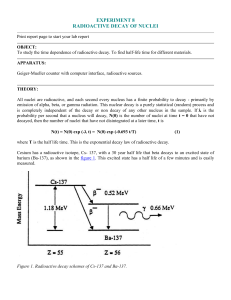
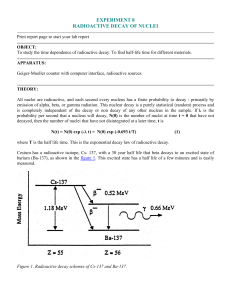
experiment 8 radioactive decay of nuclei
... To study the time dependence of radioactive decay. To find half-life time for different materials. APPARATUS: Geiger-Mueller counter with computer interface, radioactive sources. THEORY: All nuclei are radioactive, and each second every nucleus has a finite probability to decay - primarily by emissi ...
... To study the time dependence of radioactive decay. To find half-life time for different materials. APPARATUS: Geiger-Mueller counter with computer interface, radioactive sources. THEORY: All nuclei are radioactive, and each second every nucleus has a finite probability to decay - primarily by emissi ...
Spectroscopic methods for biology and medicine
... perform most catalytic and regulatory functions in the cells and might be called the molecular machinery of life. Proteins can be very big (thousands of kDa) and their structure is usually discussed in terms of: primary structure (amino acid sequence), secondary structure (regular local folding patt ...
... perform most catalytic and regulatory functions in the cells and might be called the molecular machinery of life. Proteins can be very big (thousands of kDa) and their structure is usually discussed in terms of: primary structure (amino acid sequence), secondary structure (regular local folding patt ...
Medical Laboratory Instrumentation 2010
... almost any type of sample. • AAS are that no information is obtained on the chemical form of the analyte (no “speciation”) and that often only one element can be determined at a time. • This last disadvantage makes AAS of very limited use for qualitative analysis. • AAS is used almost exclusively fo ...
... almost any type of sample. • AAS are that no information is obtained on the chemical form of the analyte (no “speciation”) and that often only one element can be determined at a time. • This last disadvantage makes AAS of very limited use for qualitative analysis. • AAS is used almost exclusively fo ...
Chapter 2
... Science Has Some Limitations 1. Particular hypotheses, theories, or laws have a high probability of being true while not being absolute 2. Bias can be minimized by scientists ...
... Science Has Some Limitations 1. Particular hypotheses, theories, or laws have a high probability of being true while not being absolute 2. Bias can be minimized by scientists ...
chemistry1Tutorial12Week7
... It is a standard analytical tool employed in the chemistry laboratory. Radiation falls on a sample contained in a standard cell, used for measurement. It is a rectangular cell, with transparent walls, and has a length l ; contains a solution with concentration of C moles per litre of the species. Co ...
... It is a standard analytical tool employed in the chemistry laboratory. Radiation falls on a sample contained in a standard cell, used for measurement. It is a rectangular cell, with transparent walls, and has a length l ; contains a solution with concentration of C moles per litre of the species. Co ...
Mössbauer spectroscopy

Mössbauer spectroscopy is a spectroscopic technique based on the Mössbauer effect. This effect, discovered by Rudolf Mössbauer in 1957, consists in the recoil-free, resonant absorption and emission of gamma rays in solids.Like NMR spectroscopy, Mössbauer spectroscopy probes tiny changes in the energy levels of an atomic nucleus in response to its environment. Typically, three types of nuclear interactions may be observed: an isomeric shift, also known as a chemical shift; quadrupole splitting; and magnetic or hyperfine splitting, also known as the Zeeman effect. Due to the high energy and extremely narrow line widths of gamma rays, Mössbauer spectroscopy is a very sensitive technique in terms of energy (and hence frequency) resolution, capable of detecting change in just a few parts per 1011.