UV-Vis Absorption Spectroscopy
... The output from the source at the low wavelength range is minimal. Also, the detector has best sensitivities around 550 nm which means that away up and down this value, the sensitivity significantly decrease. However, scattered radiation, and stray radiation in general, will reach the detector with ...
... The output from the source at the low wavelength range is minimal. Also, the detector has best sensitivities around 550 nm which means that away up and down this value, the sensitivity significantly decrease. However, scattered radiation, and stray radiation in general, will reach the detector with ...
Gilad Haran - Laboratoire Léon Brillouin
... heterogeneous dynamics of folding proteins. We are using a custom-developed set of methodologies, based on intra-molecular fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET), to study folding in real time. In particular, surface-tethered lipid vesicles are used for mild immobilization of protein molecule ...
... heterogeneous dynamics of folding proteins. We are using a custom-developed set of methodologies, based on intra-molecular fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET), to study folding in real time. In particular, surface-tethered lipid vesicles are used for mild immobilization of protein molecule ...
energy is used anytime a change in matter occurs
... or more elements combined chemically compounds have properties different from those of the original elements ...
... or more elements combined chemically compounds have properties different from those of the original elements ...
Isotope Shift of Hydrogen and Deuterium
... There are two main causes for the isotope shift, the volume effect and the mass effect. The volume effect dominates the mass effect for heavy atoms. The larger nucleus expands, which changes the 1/r potential field. For isotopes this expansion depends, with a constant number of protons in the nucleu ...
... There are two main causes for the isotope shift, the volume effect and the mass effect. The volume effect dominates the mass effect for heavy atoms. The larger nucleus expands, which changes the 1/r potential field. For isotopes this expansion depends, with a constant number of protons in the nucleu ...
PHYS-201 LAB-03 Bohr`s Model and Emission Spectra of Hydrogen
... It should be emphasized that eq.[6] models a singly ionized helium atom and not a neutral helium atom. Therefore, every line that you observe in the helium spectrum can not be described by eq. [7]. According to [6], the energy required to remove the second electron from the He+ is 54.4eV as experime ...
... It should be emphasized that eq.[6] models a singly ionized helium atom and not a neutral helium atom. Therefore, every line that you observe in the helium spectrum can not be described by eq. [7]. According to [6], the energy required to remove the second electron from the He+ is 54.4eV as experime ...
CHEM WKST: EQUILIBRIUM / LE CHATELIER`S PRINCIPLE
... f) The volume of the container is tripled. shifts → 7) For the endothermic reaction: 2SO3(g) ⇄ 2SO2(g) + O2(g) indicate the direction the equilibrium will shift for each of the following cases. a) Concentration of SO3 is increased. shifts → b) Concentration of O2 is increased. shifts ← c) Some SO2 i ...
... f) The volume of the container is tripled. shifts → 7) For the endothermic reaction: 2SO3(g) ⇄ 2SO2(g) + O2(g) indicate the direction the equilibrium will shift for each of the following cases. a) Concentration of SO3 is increased. shifts → b) Concentration of O2 is increased. shifts ← c) Some SO2 i ...
The Spectrophotometer
... machines. Since we are using ions in solution, not isolated atoms, the absorption observed is a broad band pattern rather than a simple line spectrum. In the sample absorption spectrum shown below, you see a broad peak over 200 nm wide in the blue to yellow portions of the visible portion of the spe ...
... machines. Since we are using ions in solution, not isolated atoms, the absorption observed is a broad band pattern rather than a simple line spectrum. In the sample absorption spectrum shown below, you see a broad peak over 200 nm wide in the blue to yellow portions of the visible portion of the spe ...
Violation of the Schiff theorem for unstable atomic - Plasma-Gate
... (5) we see that expression (23) identically coincides with the energy shift (5) which is derived from the balance of momenta. In conclusion we formulate the results of the present work. The Schiff theorem (screening of an external static homogeneous electric field on the nucleus of a neutral atom) i ...
... (5) we see that expression (23) identically coincides with the energy shift (5) which is derived from the balance of momenta. In conclusion we formulate the results of the present work. The Schiff theorem (screening of an external static homogeneous electric field on the nucleus of a neutral atom) i ...
METO 621
... • A quantum of radiative energy is called a photon, and is given the symbol hn . Hence in a chemical equation we write: O3 + hn →O2 + O • The energy of a photon in terms of its wavelength l is E=119625/l kJ mol-1 or 1239.8/ l in eV • To get enough energy to break up a molecule (dissociation) the wav ...
... • A quantum of radiative energy is called a photon, and is given the symbol hn . Hence in a chemical equation we write: O3 + hn →O2 + O • The energy of a photon in terms of its wavelength l is E=119625/l kJ mol-1 or 1239.8/ l in eV • To get enough energy to break up a molecule (dissociation) the wav ...
Physical chemistry exam, quiz, homework with Solution
... 21. Which of the following is NOT a correct aspect of the Born-Oppenheimer approximation (A) The electrons in a molecule move much faster than the nuclei. (B) Excited electronic states have the same equilibrium internuclear distance as the ground electronic state. (C) The electronic and vibrational ...
... 21. Which of the following is NOT a correct aspect of the Born-Oppenheimer approximation (A) The electrons in a molecule move much faster than the nuclei. (B) Excited electronic states have the same equilibrium internuclear distance as the ground electronic state. (C) The electronic and vibrational ...
Structure of the Atom - Dr. Vernon-
... No two electrons in an atom can have the same set of four quantum numbers. Taken together, the four quantum numbers describe the state of a particular electron. For example, an electron may have these quantum numbers: 1,0,0,-1/2 (corresponding to n,l,lm, and ls). Think of these as a social security ...
... No two electrons in an atom can have the same set of four quantum numbers. Taken together, the four quantum numbers describe the state of a particular electron. For example, an electron may have these quantum numbers: 1,0,0,-1/2 (corresponding to n,l,lm, and ls). Think of these as a social security ...
Slide 1 - Science and Mathematics Academy
... interactions with biomolecules. This involves investigating the properties of AuNPs, the factors that affect the binding of AuNPs with biomolecules, and the characterization methods that can be used to determine where and why binding may occur. AuNPs are the most stable of the metal NPs. They range ...
... interactions with biomolecules. This involves investigating the properties of AuNPs, the factors that affect the binding of AuNPs with biomolecules, and the characterization methods that can be used to determine where and why binding may occur. AuNPs are the most stable of the metal NPs. They range ...
Knight_ch41
... 1. the Schrödinger principle. 2. the Pauli exclusion principle. 3. Stern’s law. 4. the Heisenberg uncertainty principle. 5. Fermi’s rule. ...
... 1. the Schrödinger principle. 2. the Pauli exclusion principle. 3. Stern’s law. 4. the Heisenberg uncertainty principle. 5. Fermi’s rule. ...
2 NaCl + MgO → Na2O + MgCl2 CuSO4 Mg(NO3)2
... numbers assigned to the _____________ in a chemical ____________ that give the _______________ charge of the ________________. ...
... numbers assigned to the _____________ in a chemical ____________ that give the _______________ charge of the ________________. ...
Part 1
... differences between shells and energy levels in the quantum theory model of the atom. Typically it is valence electrons that are involved in these jumps. Atoms have two kinds of states; a ground state and an excited state. The ground state is the state in which the electrons in the atom are in their ...
... differences between shells and energy levels in the quantum theory model of the atom. Typically it is valence electrons that are involved in these jumps. Atoms have two kinds of states; a ground state and an excited state. The ground state is the state in which the electrons in the atom are in their ...
worksheet 7b answers - Iowa State University
... Iowa State University 1) Effective Nuclear Charge: the net positive charge experienced by an electron in a many-electron atom. What is the equation? Zeff = Z – S Z = atoms number (# of protons or electrons) S = Shielding/Screening electrons Same n: 0.35 n-1: 0.85 n-2,3+: 1 ...
... Iowa State University 1) Effective Nuclear Charge: the net positive charge experienced by an electron in a many-electron atom. What is the equation? Zeff = Z – S Z = atoms number (# of protons or electrons) S = Shielding/Screening electrons Same n: 0.35 n-1: 0.85 n-2,3+: 1 ...
"Particles or waves"()
... that are so fragile that they break up if they have too much energy. An example is the nucleus of deuterium, or heavy hydrogen, consisting of just a proton and a neutron bound together very weakly. Each nucleus has its own unique pattern of possible excited energies. These ‘fingerprints’ are importa ...
... that are so fragile that they break up if they have too much energy. An example is the nucleus of deuterium, or heavy hydrogen, consisting of just a proton and a neutron bound together very weakly. Each nucleus has its own unique pattern of possible excited energies. These ‘fingerprints’ are importa ...
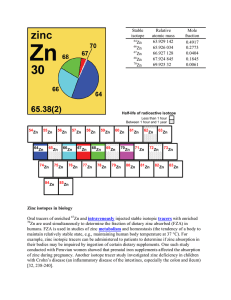
Zinc isotopes in biology Oral tracers of enriched Zn and
... atomic number (Z) – The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. atomic weight (relative mean atomic mass) – the sum of the products of the relative atomic mass and the mole fraction of each stable and long-lived radioactive isotope of that element in the sample. The symbol of the atomic weight ...
... atomic number (Z) – The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. atomic weight (relative mean atomic mass) – the sum of the products of the relative atomic mass and the mole fraction of each stable and long-lived radioactive isotope of that element in the sample. The symbol of the atomic weight ...
Chapter 9 - "Atomic Structure"
... • Defines energy sublevels within the main energy levels • s, p, d, or f designating the type of orbital and also the orbital shape. • The Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle states that you cannot measure the momentum and exact position of an electron at the same time. – What you can measure is the pr ...
... • Defines energy sublevels within the main energy levels • s, p, d, or f designating the type of orbital and also the orbital shape. • The Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle states that you cannot measure the momentum and exact position of an electron at the same time. – What you can measure is the pr ...
NMR: Technical Background
... (the vector representations of the net magnetic properties of hydrogen atoms) will point in random directions. 1 When exposed to an externally applied magnetic field, however, these magnetic moments tend to align themselves either parallel to or antiparallel to the magnetic field. 2 Because the ener ...
... (the vector representations of the net magnetic properties of hydrogen atoms) will point in random directions. 1 When exposed to an externally applied magnetic field, however, these magnetic moments tend to align themselves either parallel to or antiparallel to the magnetic field. 2 Because the ener ...
Photo Acoustic Effect And it`s usage for spectroscopy
... depend on transmission or reflection of the light beam – can work with opaque materials, higher immunity to scattering effects May work in various wavelengths Signal depends on various characteristics of medium in addition to absorption (heat capacity, acoustic velocity) that may be used to impr ...
... depend on transmission or reflection of the light beam – can work with opaque materials, higher immunity to scattering effects May work in various wavelengths Signal depends on various characteristics of medium in addition to absorption (heat capacity, acoustic velocity) that may be used to impr ...
Inverse problems of vibrational spectroscopy Gulnara Kuramshina
... The first part of this course gives a basic introduction to the physical and mathematical backgrounds of the data processing in vibrational (Infrared and Raman) spectroscopy. The second part deals with the application of new stable numerical methods based on the theory of regularization to the inver ...
... The first part of this course gives a basic introduction to the physical and mathematical backgrounds of the data processing in vibrational (Infrared and Raman) spectroscopy. The second part deals with the application of new stable numerical methods based on the theory of regularization to the inver ...
+1/2 and
... electron cloud. Hydrogenic atoms (or ions) have only one electron on their outside (valence) shell. This is a good approximation for these type atoms. All other atoms are far from this model, their description is very complicate. ...
... electron cloud. Hydrogenic atoms (or ions) have only one electron on their outside (valence) shell. This is a good approximation for these type atoms. All other atoms are far from this model, their description is very complicate. ...
Latest Lattice Results for Baryon Spectroscopy
... Challenges - II • States at rest are characterized by their behavior under rotations - SO(3) • Lattice does not possess full symmetry of the continuum allowed energies characterised by cubic symmetry, or the octahedral point group Oh ...
... Challenges - II • States at rest are characterized by their behavior under rotations - SO(3) • Lattice does not possess full symmetry of the continuum allowed energies characterised by cubic symmetry, or the octahedral point group Oh ...
Snímek 1
... 4) Shell model explains spin of nuclei. Even-even nucleus protons and neutrons are paired. Spin and orbital angular momenta for pair are zeroed. Either proton or neutron is left over in odd nuclei. Half-integral spin of this nucleon is summed with integral angular momentum of rest of nucleus hal ...
... 4) Shell model explains spin of nuclei. Even-even nucleus protons and neutrons are paired. Spin and orbital angular momenta for pair are zeroed. Either proton or neutron is left over in odd nuclei. Half-integral spin of this nucleon is summed with integral angular momentum of rest of nucleus hal ...
Mössbauer spectroscopy

Mössbauer spectroscopy is a spectroscopic technique based on the Mössbauer effect. This effect, discovered by Rudolf Mössbauer in 1957, consists in the recoil-free, resonant absorption and emission of gamma rays in solids.Like NMR spectroscopy, Mössbauer spectroscopy probes tiny changes in the energy levels of an atomic nucleus in response to its environment. Typically, three types of nuclear interactions may be observed: an isomeric shift, also known as a chemical shift; quadrupole splitting; and magnetic or hyperfine splitting, also known as the Zeeman effect. Due to the high energy and extremely narrow line widths of gamma rays, Mössbauer spectroscopy is a very sensitive technique in terms of energy (and hence frequency) resolution, capable of detecting change in just a few parts per 1011.